
EC (Electrical Conductivity) vs pH Illustration
Monitoring Electrical Conductivity (EC) in hydroponics ensures optimal nutrient concentration for healthy plant growth, while maintaining pH levels controls nutrient availability and uptake efficiency. Balancing EC and pH is crucial to prevent nutrient lockout and promote robust root development. Precise adjustment of both parameters enhances crop yield and quality in hydroponic systems.
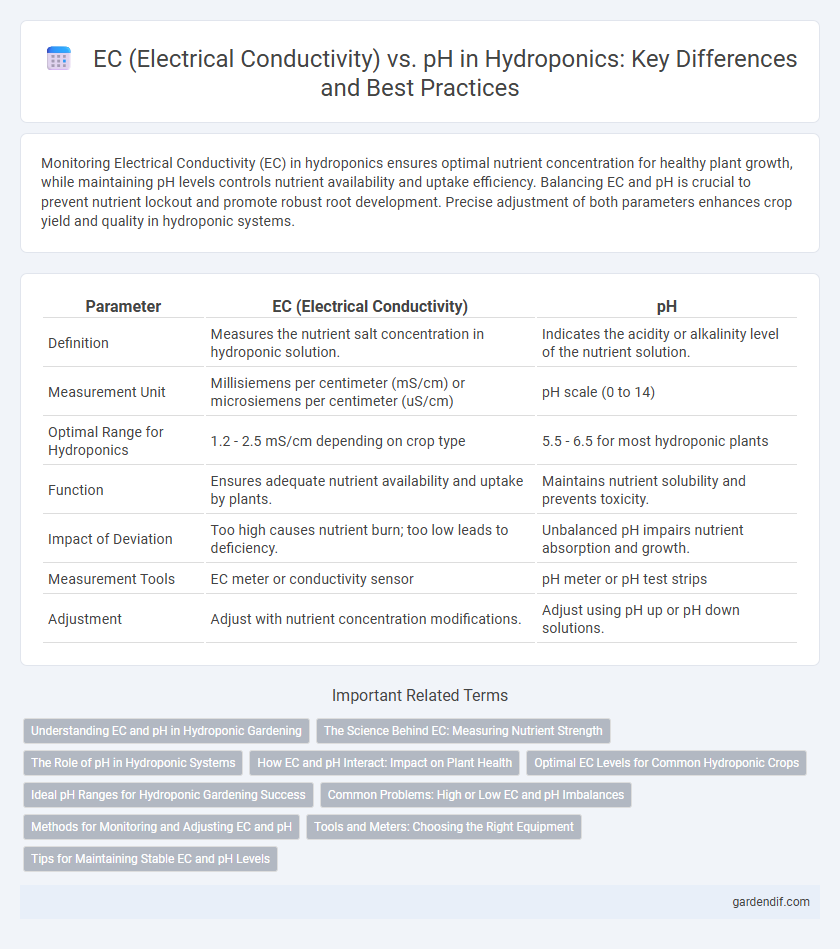
Table of Comparison
| Parameter | EC (Electrical Conductivity) | pH |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Measures the nutrient salt concentration in hydroponic solution. | Indicates the acidity or alkalinity level of the nutrient solution. |
| Measurement Unit | Millisiemens per centimeter (mS/cm) or microsiemens per centimeter (uS/cm) | pH scale (0 to 14) |
| Optimal Range for Hydroponics | 1.2 - 2.5 mS/cm depending on crop type | 5.5 - 6.5 for most hydroponic plants |
| Function | Ensures adequate nutrient availability and uptake by plants. | Maintains nutrient solubility and prevents toxicity. |
| Impact of Deviation | Too high causes nutrient burn; too low leads to deficiency. | Unbalanced pH impairs nutrient absorption and growth. |
| Measurement Tools | EC meter or conductivity sensor | pH meter or pH test strips |
| Adjustment | Adjust with nutrient concentration modifications. | Adjust using pH up or pH down solutions. |
Understanding EC and pH in Hydroponic Gardening
Electrical Conductivity (EC) measures the nutrient concentration in hydroponic solutions, ensuring plants receive the optimal amount of dissolved salts for growth, while pH indicates the acidity or alkalinity affecting nutrient availability and absorption. Maintaining an EC range between 1.2 to 2.0 mS/cm and a pH level of 5.5 to 6.5 is crucial for maximizing nutrient uptake and preventing deficiencies or toxicities in hydroponic systems. Monitoring both EC and pH regularly enables precise control of the nutrient environment, promoting healthy root development and robust plant growth.
The Science Behind EC: Measuring Nutrient Strength
Electrical Conductivity (EC) measures the total concentration of dissolved salts and nutrients in hydroponic solutions, directly indicating nutrient strength. Optimal EC levels ensure that plants receive the right balance of essential minerals, while pH controls nutrient availability and uptake efficiency. Maintaining precise EC alongside a balanced pH range (typically 5.5 to 6.5) maximizes nutrient absorption and promotes healthy hydroponic crop growth.
The Role of pH in Hydroponic Systems
pH in hydroponic systems regulates nutrient availability and absorption efficiency by controlling the solubility of minerals essential for plant growth. Maintaining an optimal pH range, typically between 5.5 and 6.5, ensures balanced nutrient uptake, preventing deficiencies or toxicities influenced by electrical conductivity (EC) levels. Monitoring and adjusting pH alongside EC measurements optimize nutrient solution performance, promoting healthy root development and maximizing crop yield.
How EC and pH Interact: Impact on Plant Health
EC (Electrical Conductivity) measures nutrient concentration in hydroponic solutions, directly influencing plant nutrient uptake efficiency. pH affects nutrient availability by determining the solubility of essential minerals, with optimal pH ranges between 5.5 and 6.5 allowing the best nutrient absorption. Imbalances in EC and pH can cause nutrient lockout or toxicity, leading to stunted growth and reduced crop yields in hydroponic systems.
Optimal EC Levels for Common Hydroponic Crops
Optimal EC levels in hydroponic systems vary significantly among common crops, with leafy greens like lettuce thriving between 1.2 to 2.0 mS/cm, whereas fruiting plants such as tomatoes require higher ECs around 2.0 to 3.5 mS/cm. Maintaining EC within these ranges ensures balanced nutrient uptake, preventing osmotic stress and promoting vigorous growth. Monitoring pH concurrently between 5.5 and 6.5 is critical, as pH influences nutrient availability and EC readings, guiding precise nutrient management.
Ideal pH Ranges for Hydroponic Gardening Success
Ideal pH ranges for hydroponic gardening typically fall between 5.5 and 6.5, optimizing nutrient availability and uptake in plants. Electrical Conductivity (EC) measures nutrient concentration and should be adjusted in tandem with pH to avoid nutrient lockout and ensure balanced growth. Maintaining stable pH within the ideal range while monitoring EC levels enhances overall plant health and yield in hydroponic systems.
Common Problems: High or Low EC and pH Imbalances
High or low EC levels in hydroponic systems can cause nutrient uptake issues, leading to poor plant growth and yield. pH imbalances disrupt nutrient availability, with values outside the optimal 5.5-6.5 range causing deficiencies or toxicities. Monitoring both EC and pH regularly helps prevent common problems such as nutrient lockout and root damage, ensuring healthy plant development.
Methods for Monitoring and Adjusting EC and pH
Effective hydroponic cultivation requires precise monitoring of Electrical Conductivity (EC) and pH levels to ensure optimal nutrient availability and plant health. Utilizing digital EC and pH meters with automatic temperature compensation enables accurate real-time measurements, while regular calibration with standard solutions maintains sensor accuracy. Adjusting EC involves modifying nutrient concentration using concentrated solutions or dilution with water, and pH can be regulated by adding acidifiers like phosphoric acid or alkalizers such as potassium hydroxide to maintain the ideal range for plant uptake.
Tools and Meters: Choosing the Right Equipment
Selecting precise tools for measuring Electrical Conductivity (EC) and pH levels in hydroponic systems is vital for optimal nutrient management and plant growth. High-quality EC and pH meters, equipped with automatic temperature compensation and calibration features, ensure accurate readings essential for maintaining balanced nutrient solutions. Investing in durable, easy-to-calibrate probes with digital displays facilitates real-time monitoring, helping growers adjust nutrient concentration and pH promptly to avoid plant stress and maximize yield.
Tips for Maintaining Stable EC and pH Levels
Maintaining stable EC and pH levels in hydroponic systems requires regular monitoring with calibrated meters to ensure nutrient availability and optimal plant growth. Adjust EC by diluting or concentrating nutrient solutions, and control pH by using pH up or down solutions to keep it within the ideal range of 5.5 to 6.5. Consistent water temperature and regular reservoir refreshment prevent fluctuations, supporting nutrient absorption and preventing root stress.
EC (Electrical Conductivity) vs pH Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com