
Wet Season Harvest vs Dry Season Harvest Illustration
Wet season harvests often yield crops with higher moisture content, requiring careful post-harvest drying to prevent spoilage, while dry season harvests typically produce drier, more durable crops ideal for immediate storage. Soil conditions during the wet season can enhance nutrient absorption, boosting crop growth, whereas dry season harvests benefit from reduced fungal diseases but may require irrigation to maintain yield. Choosing the optimal season depends on crop type, water availability, and storage capabilities to maximize quality and minimize loss.
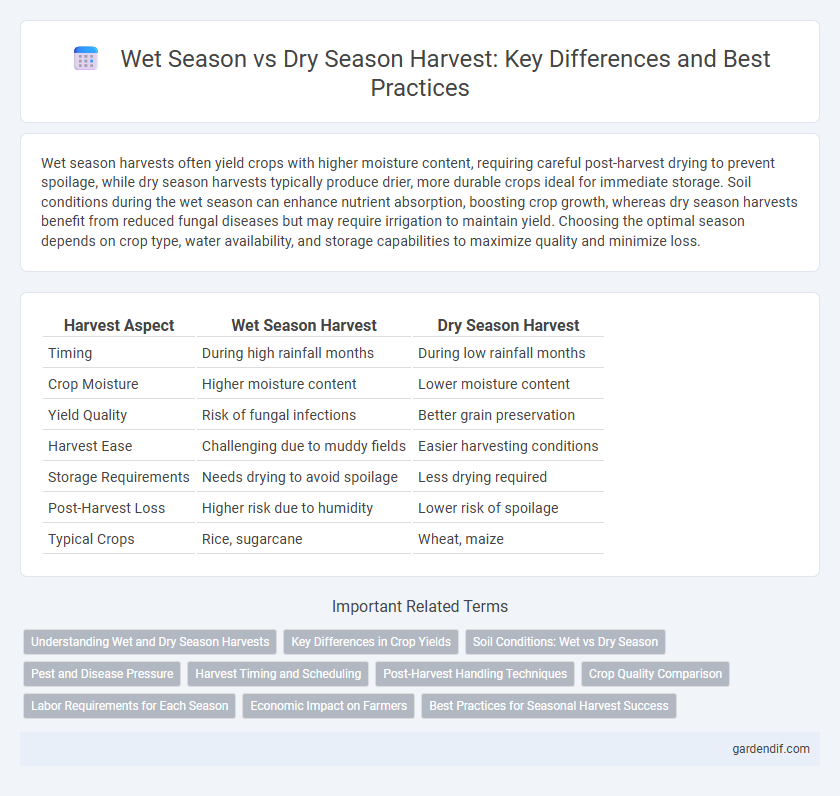
Table of Comparison
| Harvest Aspect | Wet Season Harvest | Dry Season Harvest |
|---|---|---|
| Timing | During high rainfall months | During low rainfall months |
| Crop Moisture | Higher moisture content | Lower moisture content |
| Yield Quality | Risk of fungal infections | Better grain preservation |
| Harvest Ease | Challenging due to muddy fields | Easier harvesting conditions |
| Storage Requirements | Needs drying to avoid spoilage | Less drying required |
| Post-Harvest Loss | Higher risk due to humidity | Lower risk of spoilage |
| Typical Crops | Rice, sugarcane | Wheat, maize |
Understanding Wet and Dry Season Harvests
Wet season harvests yield crops with higher moisture content, requiring immediate post-harvest drying techniques to prevent spoilage and maintain quality. Dry season harvests benefit from lower humidity, resulting in easier grain drying and reduced fungal contamination risks, enhancing storage longevity. Understanding these seasonal differences is crucial for optimizing harvesting schedules, crop quality, and storage strategies in agriculture.
Key Differences in Crop Yields
Wet season harvests typically result in higher crop yields due to abundant rainfall supporting robust plant growth and nutrient uptake. Dry season harvests often produce lower yields as crops experience water stress, requiring irrigation and drought-resistant practices to sustain production. Soil moisture levels and pest prevalence also vary, influencing overall productivity between the two seasons.
Soil Conditions: Wet vs Dry Season
Wet season harvest occurs when soil moisture is abundant, leading to softer, more waterlogged soil that can complicate machinery use and increase the risk of crop damage. Dry season harvest benefits from firmer, drier soil conditions, enabling easier access for harvesting equipment and reducing soil compaction and erosion. Optimal soil management during both seasons is crucial to maintain soil structure and maximize crop yield quality.
Pest and Disease Pressure
Wet season harvest often faces higher pest and disease pressure due to increased humidity and favorable conditions for fungal growth and insect proliferation. In contrast, dry season harvest generally experiences reduced pest activity and lower disease incidence because drier conditions inhibit pathogen development. Effective pest management strategies during wet seasons are crucial to minimize crop losses and maintain optimal yield quality.
Harvest Timing and Scheduling
Wet season harvests typically require precise timing to avoid crop damage from excessive moisture and ensure optimal yield quality, often necessitating accelerated scheduling around unpredictable rainfall patterns. Dry season harvests allow for more flexible timing due to lower humidity and reduced disease pressure, enabling better planning and implementation of mechanized harvesting techniques. Efficient scheduling during both seasons is crucial to maximize productivity and minimize post-harvest losses, with wet season demands emphasizing rapid response and dry season favoring strategic coordination.
Post-Harvest Handling Techniques
Post-harvest handling techniques vary significantly between wet season and dry season harvests due to differences in moisture levels and environmental conditions. Wet season harvests require enhanced drying methods, such as mechanical dryers or solar drying, to prevent fungal growth and spoilage, while dry season harvests focus more on moisture retention to avoid shrinkage and weight loss. Proper storage practices, including ventilation and humidity control, are essential in both seasons to maintain crop quality and reduce post-harvest losses.
Crop Quality Comparison
Wet season harvests often yield crops with higher moisture content, resulting in softer textures and increased susceptibility to fungal diseases, while dry season harvests typically produce firmer, more nutrient-dense crops with longer shelf life. The dry season's lower humidity favors the accumulation of sugars and essential oils, enhancing flavor profiles and overall crop quality. However, wet season conditions may benefit certain crops by promoting faster growth and higher yields despite the potential compromise in quality.
Labor Requirements for Each Season
Wet season harvest demands intensive labor due to persistent rainfall causing muddy fields and slower crop maturation, requiring more manual handling and careful timing. Dry season harvest benefits from firmer soil and more predictable weather, allowing for easier mechanization and reduced labor costs. Seasonal labor allocation affects overall productivity and determines optimal workforce management in agricultural planning.
Economic Impact on Farmers
Wet season harvests generally yield higher crop volumes due to abundant rainfall, which can boost farmers' short-term income but may incur increased post-harvest losses from humidity and pests, affecting overall profitability. Dry season harvests often result in lower yields but offer better crop quality and reduced storage risks, leading to potentially higher market prices and improved economic sustainability for farmers. Seasonal variability influences input costs and labor demand, with wet season requiring more investment in pest control and drying, whereas dry season minimizes these expenses, impacting farmers' net earnings differently.
Best Practices for Seasonal Harvest Success
Wet season harvest requires careful management of moisture levels to prevent crop spoilage, emphasizing timely harvesting during dry spells to maintain grain quality. Dry season harvest benefits from reduced humidity and lower pest pressure, allowing for extended field drying and optimized yield preservation. Implementing seasonal-specific practices such as moisture monitoring for wet season and pest control for dry season maximizes harvest success and crop profitability.
Wet Season Harvest vs Dry Season Harvest Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com