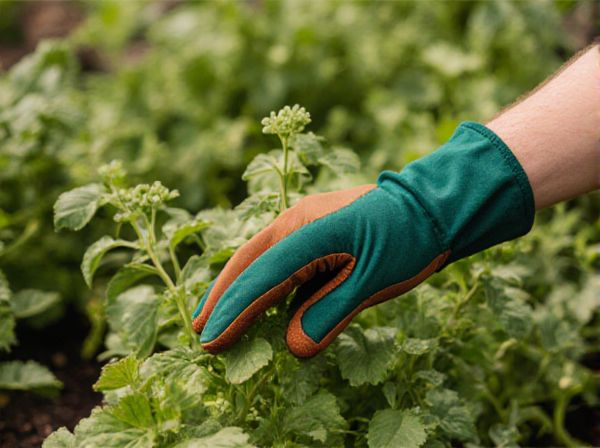

Snap Harvest vs Cut Harvest Illustration
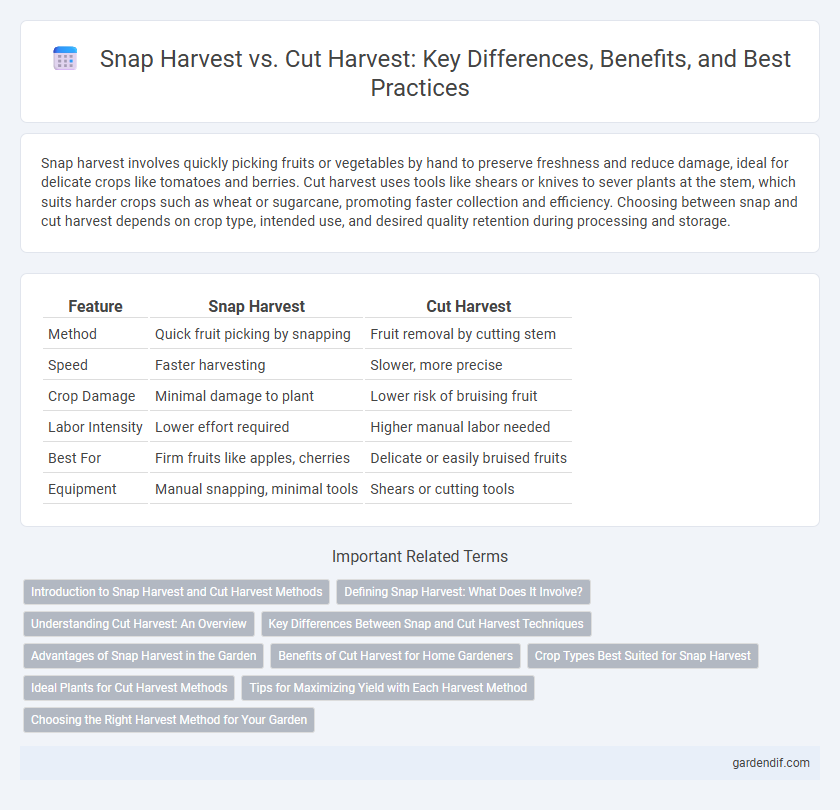
Snap harvest involves quickly picking fruits or vegetables by hand to preserve freshness and reduce damage, ideal for delicate crops like tomatoes and berries. Cut harvest uses tools like shears or knives to sever plants at the stem, which suits harder crops such as wheat or sugarcane, promoting faster collection and efficiency. Choosing between snap and cut harvest depends on crop type, intended use, and desired quality retention during processing and storage.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Snap Harvest | Cut Harvest |
|---|---|---|
| Method | Quick fruit picking by snapping | Fruit removal by cutting stem |
| Speed | Faster harvesting | Slower, more precise |
| Crop Damage | Minimal damage to plant | Lower risk of bruising fruit |
| Labor Intensity | Lower effort required | Higher manual labor needed |
| Best For | Firm fruits like apples, cherries | Delicate or easily bruised fruits |
| Equipment | Manual snapping, minimal tools | Shears or cutting tools |
Introduction to Snap Harvest and Cut Harvest Methods
Snap harvest involves quickly detaching mature fruits or vegetables from plants at peak ripeness, minimizing damage and ensuring optimal quality. Cut harvest requires using tools to cut crops, such as stems or roots, promoting efficient collection of certain produce like grains or leafy greens. Both methods are crucial in agricultural practices, selected based on crop type and desired post-harvest handling.
Defining Snap Harvest: What Does It Involve?
Snap Harvest involves rapidly harvesting crops by cutting plants near their base and collecting them immediately to preserve freshness and nutritional quality. This method minimizes exposure to environmental stressors, reducing spoilage and maximizing yield efficiency. Compared to traditional cut harvest, snap harvest emphasizes speed and precision to maintain optimal produce condition from field to market.
Understanding Cut Harvest: An Overview
Cut harvest involves manually or mechanically severing crops at the base, allowing the plants to be gathered and processed efficiently. Unlike snap harvest, which targets specific portions of the plant, cut harvest removes the entire stalk, making it ideal for crops like wheat, barley, and corn. This method maximizes yield by ensuring all mature produce is collected, facilitating easier transportation and storage.
Key Differences Between Snap and Cut Harvest Techniques
Snap harvest involves breaking the crop stem by hand just above the node, preserving the plant's ability to regrow and often used for crops like kale or certain leafy vegetables. Cut harvest, on the other hand, entails using tools like knives or sickles to sever the entire plant at or near the base, allowing complete removal but preventing further regrowth. Snap harvest minimizes damage and promotes sustainability by enabling multiple harvest cycles, whereas cut harvest is typically faster and suitable for crops requiring full removal.
Advantages of Snap Harvest in the Garden
Snap harvest allows for selective picking of ripe produce, reducing waste and ensuring peak freshness in the garden. It promotes continuous growth by leaving unripe fruits intact, leading to longer harvest periods and sustained yield. This method minimizes plant damage compared to cut harvest, preserving plant health and enhancing overall productivity.
Benefits of Cut Harvest for Home Gardeners
Cut harvest allows home gardeners to selectively trim plants, promoting continuous growth and extending the productive season. Unlike snap harvest, which involves removing entire fruits or vegetables, cut harvesting minimizes plant damage and encourages healthier yields. This method is especially beneficial for herbs and leafy greens, providing fresh produce over a longer period.
Crop Types Best Suited for Snap Harvest
Snap harvest is highly effective for crops like snap beans, peas, and certain varieties of corn where pods or kernels need to be collected intact to preserve quality. This method minimizes damage to delicate produce, making it ideal for fresh-market vegetables requiring immediate processing or packaging. Snap harvest ensures higher market value by reducing bruising and maintaining optimal freshness for perishable crops.
Ideal Plants for Cut Harvest Methods
Cut harvest methods are ideal for plants with sturdy stems and a high tolerance for regrowth, such as tomatoes, peppers, and leafy greens like kale and spinach. These crops benefit from repeated harvesting without damaging the main plant structure, allowing for multiple yield cycles. Snap harvest is less suitable for these plants due to the risk of stem damage and reduced regrowth capacity.
Tips for Maximizing Yield with Each Harvest Method
Maximize yield in Snap Harvest by harvesting crops early at optimal size to enhance quality and reduce waste, focusing on consistent, frequent picking cycles. Cut Harvest benefits from strategic timing, cutting mature plants at peak biomass to promote regrowth and support multiple harvests per season. Employ tailored irrigation and nutrient management alongside each method to ensure sustained plant health and maximize overall crop output.
Choosing the Right Harvest Method for Your Garden
Snap harvest preserves the freshness and nutrients of fruits and vegetables by picking them at their peak ripeness, ensuring optimal flavor and texture. Cut harvest involves severing crops from their stems, which can speed up collection for larger gardens but may reduce shelf life and nutrient retention. Selecting the ideal harvest method depends on the type of crop, garden size, and desired quality, with snap harvesting favored for delicate produce and cut harvesting suited to bulk yields.
Snap Harvest vs Cut Harvest Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com