
Single picking vs multiple picking Illustration
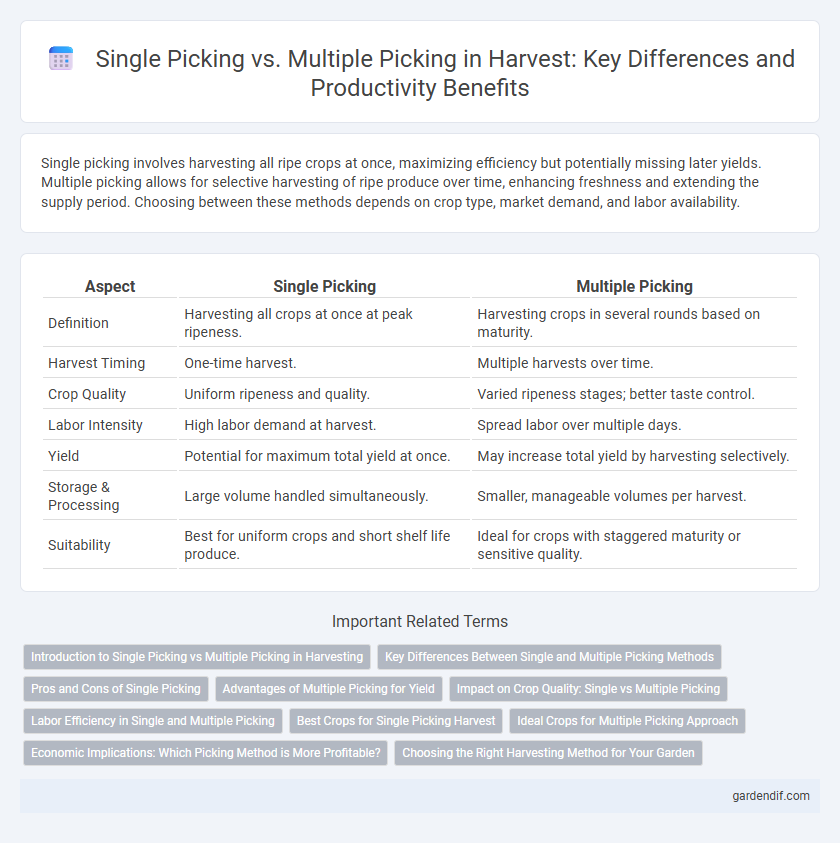
Single picking involves harvesting all ripe crops at once, maximizing efficiency but potentially missing later yields. Multiple picking allows for selective harvesting of ripe produce over time, enhancing freshness and extending the supply period. Choosing between these methods depends on crop type, market demand, and labor availability.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Single Picking | Multiple Picking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Harvesting all crops at once at peak ripeness. | Harvesting crops in several rounds based on maturity. |
| Harvest Timing | One-time harvest. | Multiple harvests over time. |
| Crop Quality | Uniform ripeness and quality. | Varied ripeness stages; better taste control. |
| Labor Intensity | High labor demand at harvest. | Spread labor over multiple days. |
| Yield | Potential for maximum total yield at once. | May increase total yield by harvesting selectively. |
| Storage & Processing | Large volume handled simultaneously. | Smaller, manageable volumes per harvest. |
| Suitability | Best for uniform crops and short shelf life produce. | Ideal for crops with staggered maturity or sensitive quality. |
Introduction to Single Picking vs Multiple Picking in Harvesting
Single picking in harvesting involves collecting all ripe crops in one pass, optimizing operational efficiency for uniform maturation crops such as wheat or barley. Multiple picking refers to repeated harvesting sessions, essential for crops with staggered ripening like berries or tomatoes, ensuring peak quality and minimal waste. Choosing between single and multiple picking methods depends on crop type, growth patterns, and desired harvest quality, impacting labor, equipment use, and yield outcomes.
Key Differences Between Single and Multiple Picking Methods
Single picking involves harvesting all ripe fruits or crops in one pass, optimizing efficiency and reducing labor costs by minimizing repeated field visits. Multiple picking requires several passes to selectively harvest only fully mature produce each time, ensuring higher quality by avoiding overripe or unripe crops. Key differences focus on labor intensity, crop quality control, and timing flexibility, with single picking favoring speed and multiple picking enhancing produce quality and reducing post-harvest losses.
Pros and Cons of Single Picking
Single picking in harvest allows for selective fruit or crop removal at peak ripeness, ensuring higher quality produce and reducing waste. It requires more labor and time compared to multiple picking methods, potentially increasing operational costs. However, single picking minimizes damage to plants and extends the harvesting season, benefiting long-term crop sustainability.
Advantages of Multiple Picking for Yield
Multiple picking significantly enhances overall yield by allowing multiple harvests from the same crop, maximizing resource use and reducing waste. This method improves fruit or vegetable quality since only ripe produce is harvested during each session, leading to better marketability. Continuous monitoring during each picking also helps identify and address crop issues early, ensuring healthier plants and sustained productivity.
Impact on Crop Quality: Single vs Multiple Picking
Single picking during harvest ensures optimal crop quality by allowing fruits and vegetables to reach full maturity before being harvested, preserving flavor and nutritional content. Multiple picking can lead to inconsistent ripeness and increased handling, which may cause bruising and reduce overall quality. Selecting the appropriate picking strategy directly affects crop freshness, shelf life, and market value.
Labor Efficiency in Single and Multiple Picking
Single picking minimizes labor hours by concentrating harvest activities in one session, reducing repeated field entries and optimizing worker deployment. Multiple picking demands more labor input, as workers revisit the same plots several times, increasing travel time and operational costs per unit harvested. Efficient labor allocation in single picking enhances cost-effectiveness, whereas multiple picking may improve crop quality but at the expense of greater workforce expenses.
Best Crops for Single Picking Harvest
Single picking harvest is ideal for crops like tomatoes, strawberries, and snap peas, where fruits mature simultaneously and harvesting in one go ensures peak flavor and quality. This method reduces labor costs and minimizes crop damage by avoiding repeated handling. Crops with uniform ripening patterns benefit most from single picking, maximizing yield efficiency and market value.
Ideal Crops for Multiple Picking Approach
Multiple picking is ideal for crops like strawberries, tomatoes, and leafy greens, where continuous yield can be harvested over extended periods. This method maximizes crop quality and market availability by allowing selective harvesting of mature produce while immature parts continue growing. Multiple picking reduces waste and enhances overall farm profitability by aligning harvest frequency with crop growth cycles.
Economic Implications: Which Picking Method is More Profitable?
Single picking often reduces labor costs and minimizes fruit damage, leading to higher market prices due to better quality produce, making it more profitable for premium crops. Multiple picking increases yield by harvesting fruit at varying ripeness levels but raises labor expenses and sorting complexities, which can erode profit margins. Economic profitability depends on crop type, market demand, and labor availability, with single picking favored for high-value fruits and multiple picking suited to bulk commodities.
Choosing the Right Harvesting Method for Your Garden
Single picking targets ripe fruits or vegetables in one harvest, ideal for plants with uniform maturity like tomatoes or peppers. Multiple picking involves harvesting in intervals, suiting crops such as beans or zucchinis that produce continuously, maximizing yield throughout the growing season. Selecting the right harvesting method depends on crop type, growth patterns, and desired harvest frequency to optimize garden productivity and quality.
Single picking vs multiple picking Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com