
Early Harvest vs Late Harvest Illustration
Early harvest grapes are picked before reaching full ripeness, resulting in higher acidity and lower sugar levels that produce crisp, fresh wines. Late harvest grapes remain on the vine longer, allowing sugars to concentrate and develop sweeter, more complex flavors ideal for dessert wines. The choice between early and late harvest influences the wine's balance, sweetness, and overall character.
Table of Comparison
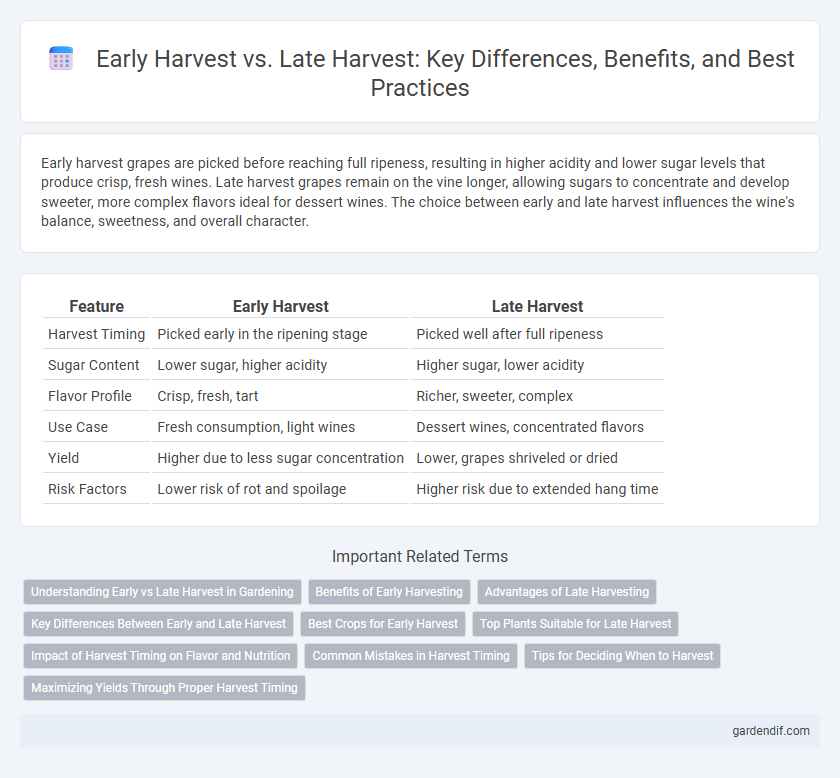
| Feature | Early Harvest | Late Harvest |
|---|---|---|
| Harvest Timing | Picked early in the ripening stage | Picked well after full ripeness |
| Sugar Content | Lower sugar, higher acidity | Higher sugar, lower acidity |
| Flavor Profile | Crisp, fresh, tart | Richer, sweeter, complex |
| Use Case | Fresh consumption, light wines | Dessert wines, concentrated flavors |
| Yield | Higher due to less sugar concentration | Lower, grapes shriveled or dried |
| Risk Factors | Lower risk of rot and spoilage | Higher risk due to extended hang time |
Understanding Early vs Late Harvest in Gardening
Early harvest in gardening refers to picking fruits or vegetables as soon as they reach initial maturity, resulting in smaller yields but often more tender, flavorful produce. Late harvest allows crops to fully mature on the plant, increasing sugar content and size, which is especially advantageous for sweeter fruits and wine grapes. Gardeners must balance timing based on crop type and desired taste profile, optimizing for freshness or enhanced sweetness.
Benefits of Early Harvesting
Early harvesting preserves the optimal nutrient content and freshness of fruits and vegetables, leading to higher market value and reduced spoilage. It enhances crop resilience by minimizing exposure to pests and adverse weather conditions, ensuring consistent yield quality. Early harvest also accelerates turnover rates, allowing farmers to plant subsequent crops sooner and maximize productivity.
Advantages of Late Harvesting
Late harvesting allows grapes to develop higher sugar content and richer flavor profiles, which enhance the complexity and sweetness of wines such as dessert and fortified varieties. Extended hang-time on the vine promotes phenolic maturity, improving tannin structure and color intensity crucial for premium red wines. This method also reduces acidity, creating a balanced and smooth finish favored by winemakers aiming for depth and richness.
Key Differences Between Early and Late Harvest
Early harvest grapes are picked before full ripeness, resulting in higher acidity and lower sugar content, which produces crisp, fresh wines often used for sparkling varieties. Late harvest grapes are harvested after full ripeness or post-botrytis infection, yielding sweeter, more concentrated wines with richer flavors and higher sugar levels. The timing of harvest also affects the wine's alcohol content, acidity balance, and potential aging capacity, with early harvest wines generally lighter and late harvest wines richer and more dessert-style.
Best Crops for Early Harvest
Early harvest crops include leafy greens like spinach and lettuce, root vegetables such as radishes and carrots, and certain fruits like strawberries, all known for their rapid growth and early maturity. These crops thrive in cooler temperatures and shorter growing seasons, making them ideal for spring planting and quick turnover. Selecting early harvest varieties maximizes yield efficiency and extends the growing calendar for farmers.
Top Plants Suitable for Late Harvest
Late harvest favors varieties like Cabernet Sauvignon, Zinfandel, and Riesling, which benefit from extended ripening to develop richer flavors and higher sugar content. These plants tolerate cooler temperatures and resist rot, making them ideal for late-season picking and producing intensely sweet, complex wines. Late harvest grapes offer concentrated acidity and aromatic profiles that enhance dessert wine quality.
Impact of Harvest Timing on Flavor and Nutrition
Early harvest grapes typically yield wines with higher acidity, vibrant flavors, and increased antioxidant levels due to shorter ripening periods, enhancing overall nutritional benefits. Late harvest grapes develop richer, sweeter profiles with lower acidity and amplified sugar content, often used in dessert wines, but may have reduced vitamin concentrations. The timing of harvest profoundly influences the balance of flavor compounds and nutrient density, crucial for both taste and health attributes in fruit-based products.
Common Mistakes in Harvest Timing
Common mistakes in harvest timing include harvesting early when grapes have insufficient sugar levels, resulting in underdeveloped flavors and high acidity. Late harvest often leads to overripe fruit prone to rot and excessive sugar concentration, causing imbalance in wine profiles. Understanding optimal harvest periods based on grape variety, climatic conditions, and desired wine style is crucial to avoid these errors.
Tips for Deciding When to Harvest
Choosing the optimal time for harvest depends on the crop's maturity indicators, such as color, size, and firmness, which signal peak nutrient content and flavor. Early harvest captures higher acidity and freshness, ideal for crops like grapes aimed at vibrant, crisp wines, while late harvest yields higher sugar levels suited for sweeter products and preserved goods. Monitoring weather patterns and understanding specific crop requirements ensure harvest timing maximizes yield quality and storage longevity.
Maximizing Yields Through Proper Harvest Timing
Early harvest preserves higher acidity and vibrant flavors, enhancing wine freshness but may result in lower sugar levels and yields. Late harvest increases sugar concentration for richer, sweeter profiles, yet risks overripe fruit and potential yield loss due to shriveling or rot. Proper harvest timing balances these factors by monitoring grape maturity, sugar levels (Brix), and weather conditions to maximize both yield and quality.
Early Harvest vs Late Harvest Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com