
Selective Picking vs Strip Picking Illustration
Selective picking targets only ripe fruits, ensuring optimal quality and reducing waste, while strip picking involves harvesting all fruits from a plant regardless of ripeness. This method enhances efficiency but may sacrifice fruit quality and market value. Choosing between selective and strip picking depends on crop type, labor availability, and quality requirements.
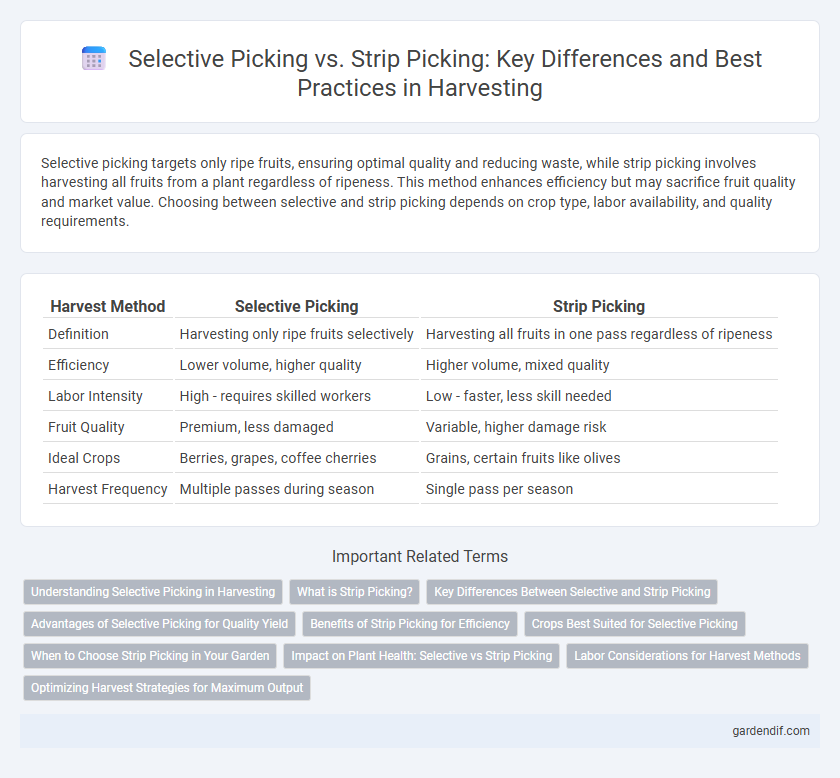
Table of Comparison
| Harvest Method | Selective Picking | Strip Picking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Harvesting only ripe fruits selectively | Harvesting all fruits in one pass regardless of ripeness |
| Efficiency | Lower volume, higher quality | Higher volume, mixed quality |
| Labor Intensity | High - requires skilled workers | Low - faster, less skill needed |
| Fruit Quality | Premium, less damaged | Variable, higher damage risk |
| Ideal Crops | Berries, grapes, coffee cherries | Grains, certain fruits like olives |
| Harvest Frequency | Multiple passes during season | Single pass per season |
Understanding Selective Picking in Harvesting
Selective picking in harvesting targets only ripe or high-quality fruits, ensuring optimal crop quality and reducing waste. This method requires skilled labor and careful timing to identify and harvest mature produce while leaving unripe items on the plant for future harvests. Compared to strip picking, selective picking enhances market value by maintaining fruit integrity and extending harvest periods.
What is Strip Picking?
Strip picking is a harvest method where entire rows or large sections of crops are harvested in a single pass, without differentiating between ripe and unripe produce. This technique increases efficiency by reducing labor time but may result in lower overall product quality due to the inclusion of immature or overripe items. Farms growing uniform crops like grains or certain fruits often use strip picking to maximize speed and reduce costs.
Key Differences Between Selective and Strip Picking
Selective picking involves harvesting only ripe fruits or crops at varying times to ensure optimal quality and reduce waste, while strip picking removes all crops from a section at once regardless of ripeness. Selective picking requires more labor and time but results in higher market value due to superior product quality, whereas strip picking is faster, cost-effective, and suitable for mechanized harvests. The choice between methods depends on crop type, market demands, and resource availability.
Advantages of Selective Picking for Quality Yield
Selective picking enhances quality yield by allowing farmers to harvest only ripe, fully mature fruits, minimizing damage and ensuring superior flavor and texture. This method reduces waste by preventing premature harvesting and promotes plant health through targeted fruit removal, leading to more consistent high-quality produce over multiple harvests. Selective picking also supports sustainable farming practices by optimizing resource use and improving overall crop longevity.
Benefits of Strip Picking for Efficiency
Strip picking significantly enhances harvest efficiency by allowing faster crop collection across entire fields, reducing labor time compared to selective picking. This method maximizes yield by harvesting all ripe and unripe produce simultaneously, minimizing the need for multiple passes. Equipment automation integrated with strip picking further streamlines operations, cutting costs and increasing overall productivity.
Crops Best Suited for Selective Picking
Selective picking is ideal for high-value crops such as grapes, coffee, and certain fruits like strawberries and blueberries, where individual fruit ripeness significantly impacts quality and market value. This method allows for the careful harvest of only ripe produce, reducing waste and enhancing overall crop quality compared to strip picking, which removes entire plants or sections regardless of maturity. Selective picking is especially advantageous for perishable crops requiring multiple harvests over a growing season, optimizing yield and maintaining consistent freshness.
When to Choose Strip Picking in Your Garden
Strip picking is ideal for gardeners with large, uniform crops like strawberries or tomatoes requiring quick harvests, maximizing efficiency while minimizing labor. Choosing strip picking suits situations where fruit maturity occurs simultaneously, enabling rapid collection without detailed sorting. This method improves workflow and reduces time spent in fields, especially when market demand favors volume over selective quality.
Impact on Plant Health: Selective vs Strip Picking
Selective picking enhances plant health by harvesting only ripe fruits, reducing stress and minimizing damage to stems and foliage, which supports continued growth and productivity. In contrast, strip picking removes all fruits regardless of ripeness, often causing mechanical injury and increasing vulnerability to pests and diseases. Maintaining plant vitality is more effective with selective picking, promoting sustainable harvest cycles and long-term yield.
Labor Considerations for Harvest Methods
Selective picking requires skilled labor to identify and harvest only ripe produce, increasing labor costs and time investment, but optimizing crop quality. Strip picking demands less skilled labor, allowing faster harvests and reduced labor expenses, though it may compromise crop quality due to unripe or damaged fruit collection. Labor availability, cost, and quality control are critical factors when choosing between selective and strip harvesting methods.
Optimizing Harvest Strategies for Maximum Output
Selective picking targets only ripe fruits, enhancing quality and reducing waste, while strip picking removes entire crop sections regardless of maturity, speeding up harvest but often sacrificing yield quality. Optimizing harvest strategies involves balancing labor costs and crop characteristics by integrating selective picking for premium produce markets and strip picking for bulk processing demands. Employing precision agriculture technologies and real-time crop monitoring further maximizes output by enabling timely and efficient harvesting decisions.
Selective Picking vs Strip Picking Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com