
Staggered Harvest vs Simultaneous Harvest Illustration
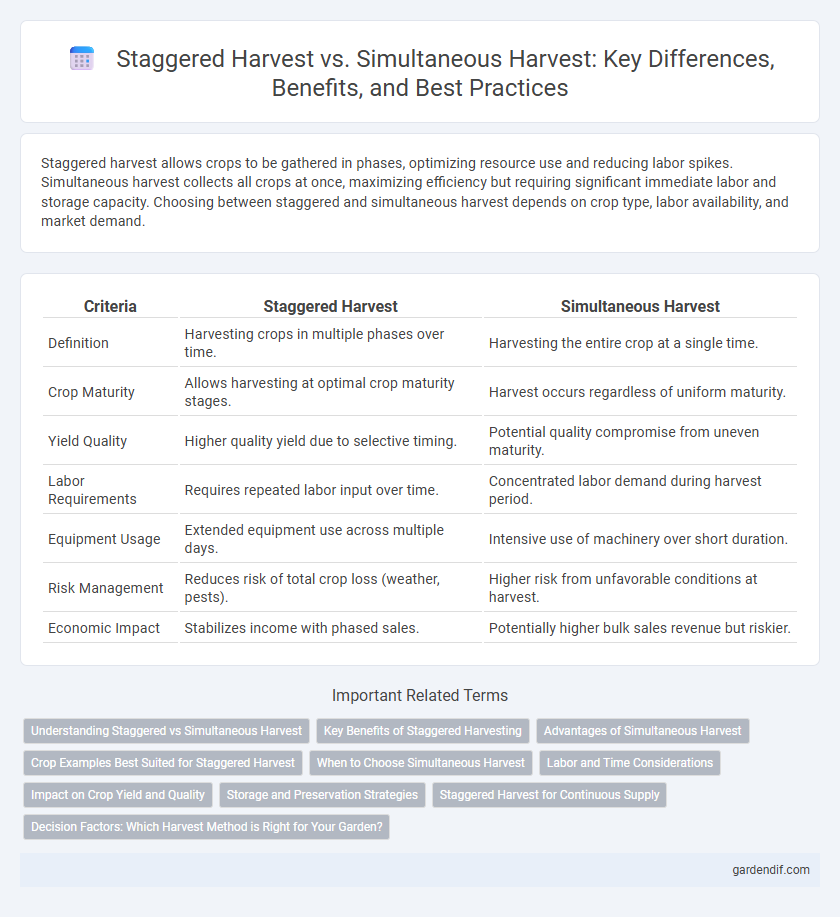
Staggered harvest allows crops to be gathered in phases, optimizing resource use and reducing labor spikes. Simultaneous harvest collects all crops at once, maximizing efficiency but requiring significant immediate labor and storage capacity. Choosing between staggered and simultaneous harvest depends on crop type, labor availability, and market demand.
Table of Comparison
| Criteria | Staggered Harvest | Simultaneous Harvest |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Harvesting crops in multiple phases over time. | Harvesting the entire crop at a single time. |
| Crop Maturity | Allows harvesting at optimal crop maturity stages. | Harvest occurs regardless of uniform maturity. |
| Yield Quality | Higher quality yield due to selective timing. | Potential quality compromise from uneven maturity. |
| Labor Requirements | Requires repeated labor input over time. | Concentrated labor demand during harvest period. |
| Equipment Usage | Extended equipment use across multiple days. | Intensive use of machinery over short duration. |
| Risk Management | Reduces risk of total crop loss (weather, pests). | Higher risk from unfavorable conditions at harvest. |
| Economic Impact | Stabilizes income with phased sales. | Potentially higher bulk sales revenue but riskier. |
Understanding Staggered vs Simultaneous Harvest
Staggered harvest involves collecting crops at different intervals based on their individual maturity, optimizing yield and quality by targeting peak ripeness for each batch. Simultaneous harvest gathers all crops at once, prioritizing efficiency but risking variability in crop quality due to differing maturation stages. Understanding the timing and crop-specific factors is crucial for selecting between staggered or simultaneous harvesting methods to maximize agricultural productivity.
Key Benefits of Staggered Harvesting
Staggered harvesting enhances crop quality by allowing fruits or vegetables to mature at optimal ripeness, reducing losses from overripening or underdevelopment. This method improves labor efficiency by spreading workload over time, mitigating peak demand on resources and equipment. It also supports market flexibility, enabling producers to supply fresh produce consistently and capitalize on favorable pricing throughout the harvest season.
Advantages of Simultaneous Harvest
Simultaneous harvest optimizes labor efficiency by allowing all crops to be gathered at once, reducing overall labor costs and time. It minimizes equipment wear and operational expenses, leading to a more cost-effective harvesting process. This method also supports better coordination in storage and transportation, enhancing the supply chain's reliability and crop quality preservation.
Crop Examples Best Suited for Staggered Harvest
Staggered harvest is particularly effective for crops like tomatoes, peppers, and leafy greens, which have extended maturation periods allowing multiple pickings. Crops such as potatoes and corn, which mature uniformly, are less suited to staggered harvest, benefiting more from simultaneous harvesting. Implementing staggered harvest in suitable crops optimizes yield quality and reduces labor peaks during the harvest season.
When to Choose Simultaneous Harvest
Simultaneous harvest is ideal when crop maturity is uniform across the field, allowing for efficient use of machinery and labor while minimizing field passes. This method reduces the risk of crop loss due to adverse weather conditions by completing harvest quickly in a concentrated timeframe. Farms experiencing tight scheduling constraints or aiming to optimize storage and processing logistics often benefit most from simultaneous harvest strategies.
Labor and Time Considerations
Staggered harvest reduces labor intensity by spreading work over multiple days, allowing smaller teams to manage crops efficiently and minimizing peak labor costs. Simultaneous harvest demands a large labor force for a short period, increasing coordination complexity but enabling faster processing and market delivery. Time management in staggered harvests supports extended market availability, while simultaneous harvests optimize machinery use and reduce crop spoilage risk.
Impact on Crop Yield and Quality
Staggered harvest allows crops to mature fully at different times, often leading to improved yield quality and reduced losses due to over-ripening or pest damage. Simultaneous harvest maximizes operational efficiency but may result in uneven crop maturity, potentially compromising overall yield and quality. Research shows staggered harvesting can enhance nutrient content and market value by aligning with peak crop readiness.
Storage and Preservation Strategies
Staggered harvest allows for extended storage by spreading crop intake over time, reducing the pressure on storage facilities and enabling better preservation through controlled environments. Simultaneous harvest requires immediate, large-scale storage solutions, increasing the risk of spoilage if storage capacity or preservation technology is inadequate. Optimizing temperature, humidity, and ventilation is critical in both methods to maintain crop quality and extend shelf life.
Staggered Harvest for Continuous Supply
Staggered harvest involves carefully timing the planting and harvesting of crops in phases to ensure a continuous supply of fresh produce throughout the season. This method optimizes market availability, reduces labor peak loads, and improves soil health by allowing periodic field rest. Farmers using staggered harvest benefit from steady income flow and minimized risk of crop loss due to adverse weather events compared to simultaneous harvest where all crops mature at once.
Decision Factors: Which Harvest Method is Right for Your Garden?
Choosing between staggered harvest and simultaneous harvest depends on factors such as crop type, garden size, and yield goals. Staggered harvest suits gardens aiming for continuous fresh produce and extended crop availability, while simultaneous harvest is ideal for maximizing efficiency and processing large quantities at once. Consider plant maturation rates, labor availability, and storage capacity to determine the most suitable method for your garden's needs.
Staggered Harvest vs Simultaneous Harvest Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com