
Passive Solar Heating vs Electric Heaters Illustration
Passive solar heating in greenhouses harnesses natural sunlight to maintain warmth, significantly reducing energy costs and environmental impact. Electric heaters provide quick and controllable heat, ensuring optimal temperatures during cloudy or cold conditions but often result in higher electricity bills. Combining passive solar techniques with electric heaters creates an efficient and reliable climate control system for year-round plant growth.
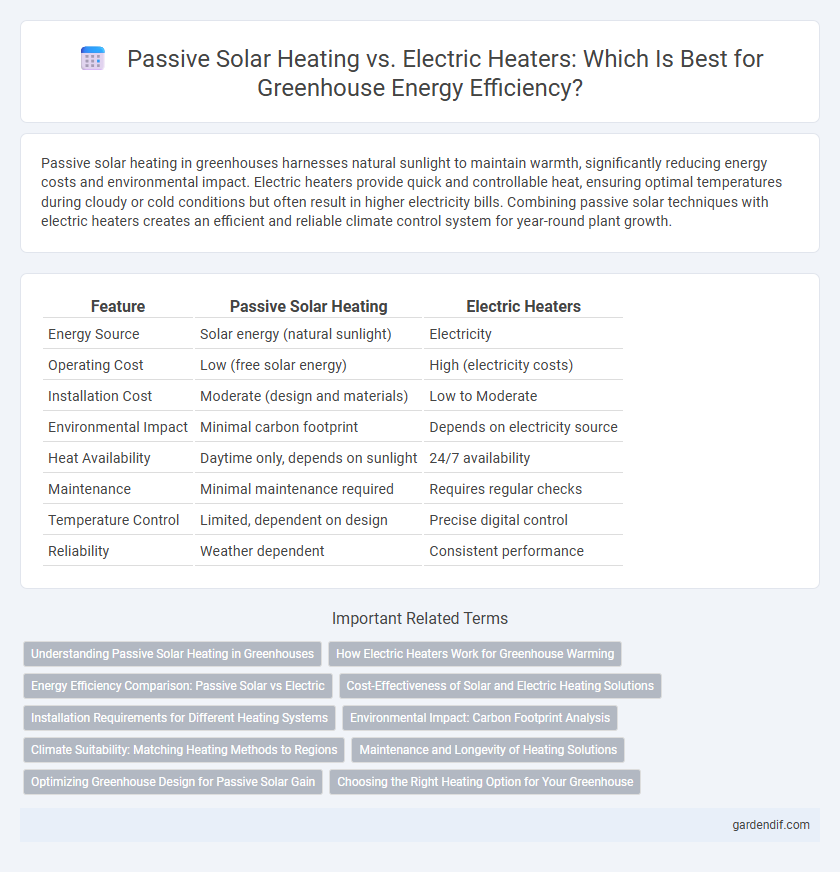
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Passive Solar Heating | Electric Heaters |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Source | Solar energy (natural sunlight) | Electricity |
| Operating Cost | Low (free solar energy) | High (electricity costs) |
| Installation Cost | Moderate (design and materials) | Low to Moderate |
| Environmental Impact | Minimal carbon footprint | Depends on electricity source |
| Heat Availability | Daytime only, depends on sunlight | 24/7 availability |
| Maintenance | Minimal maintenance required | Requires regular checks |
| Temperature Control | Limited, dependent on design | Precise digital control |
| Reliability | Weather dependent | Consistent performance |
Understanding Passive Solar Heating in Greenhouses
Passive solar heating in greenhouses harnesses sunlight through transparent materials like glass, allowing solar radiation to warm the interior without additional energy sources. The thermal mass, such as concrete or water barrels, absorbs and gradually releases heat, maintaining stable temperatures during cooler periods. This method reduces reliance on electric heaters, lowering energy costs and minimizing environmental impact while promoting sustainable plant growth.
How Electric Heaters Work for Greenhouse Warming
Electric heaters in greenhouses convert electrical energy into heat through resistive heating elements, providing consistent and controllable warmth regardless of external weather conditions. These heaters distribute heat evenly, maintaining optimal temperatures for plant growth and extending the growing season, especially during cold periods. Unlike passive solar heating, electric heaters offer immediate temperature adjustments, allowing for precise climate control to support diverse plant species.
Energy Efficiency Comparison: Passive Solar vs Electric
Passive solar heating in greenhouses harnesses natural sunlight to maintain warmth, reducing energy consumption and lowering utility costs compared to electric heaters. Electric heaters rely on electricity, often generated from non-renewable sources, resulting in higher operational expenses and carbon emissions. Utilizing passive solar design enhances energy efficiency by minimizing reliance on electric heating, promoting sustainable greenhouse climate control.
Cost-Effectiveness of Solar and Electric Heating Solutions
Passive solar heating in greenhouses harnesses natural sunlight, significantly reducing operational energy costs by minimizing reliance on electricity. Electric heaters incur higher ongoing expenses due to electricity consumption but provide precise temperature control essential for sensitive crops during low sunlight periods. Over time, passive solar systems offer greater cost-effectiveness through low maintenance and zero fuel costs, while electric heating requires consistent energy expenditure and potential infrastructure upgrades.
Installation Requirements for Different Heating Systems
Installing passive solar heating in a greenhouse requires strategic orientation, high thermal mass materials like concrete or stone, and large south-facing windows to maximize sunlight absorption. Electric heaters demand straightforward electrical wiring, thermostats, and placement considerations to ensure even heat distribution without excess energy consumption. Both systems need insulation and ventilation adjustments, but electric heaters typically offer easier installation and precise temperature control for varying climates.
Environmental Impact: Carbon Footprint Analysis
Passive solar heating in greenhouses significantly reduces carbon emissions by utilizing natural sunlight, resulting in a minimal carbon footprint compared to electric heaters. Electric heaters rely on electricity, often generated from fossil fuels, which increases greenhouse gas emissions and overall environmental impact. Implementing passive solar heating systems can lower operational costs and contribute to sustainable greenhouse management by minimizing reliance on non-renewable energy sources.
Climate Suitability: Matching Heating Methods to Regions
Passive solar heating excels in sunny, temperate climates by harnessing natural sunlight to maintain warmth with minimal energy costs, making it ideal for regions with consistent daylight and mild winters. Electric heaters offer reliable, controllable heat regardless of external weather conditions, suitable for colder or less sunny areas where passive methods may fall short. Selecting the appropriate heating system depends heavily on regional solar exposure and temperature patterns to optimize energy efficiency and plant growth in greenhouses.
Maintenance and Longevity of Heating Solutions
Passive solar heating systems in greenhouses require minimal maintenance, relying on natural sunlight and thermal mass, which significantly reduces operational costs and extends their lifespan beyond 20 years with proper design. Electric heaters demand regular maintenance such as cleaning, component checks, and occasional repairs to ensure efficient performance, with an average lifespan of 10 to 15 years depending on usage and quality. The durability and low upkeep of passive solar solutions make them an eco-friendly and cost-effective alternative to electric heaters for long-term greenhouse climate control.
Optimizing Greenhouse Design for Passive Solar Gain
Maximizing passive solar gain in greenhouse design reduces reliance on electric heaters by leveraging strategically placed south-facing glass, high thermal mass materials, and proper insulation to retain heat. Integrating thermal curtains and venting systems further enhances temperature regulation, minimizing energy consumption. Optimized orientation and glazing selection ensure maximum sunlight absorption, fostering a sustainable and cost-effective growing environment.
Choosing the Right Heating Option for Your Greenhouse
Passive solar heating utilizes natural sunlight to warm the greenhouse, reducing energy costs and promoting sustainable temperature regulation. Electric heaters provide precise and consistent heat control, essential during extended cloudy periods or extreme cold conditions. Selecting the right heating option depends on factors such as climate, greenhouse size, insulation quality, and budget constraints to ensure optimal plant growth and energy efficiency.
Passive Solar Heating vs Electric Heaters Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com