
Hydroponics vs Soil-based Growing Illustration
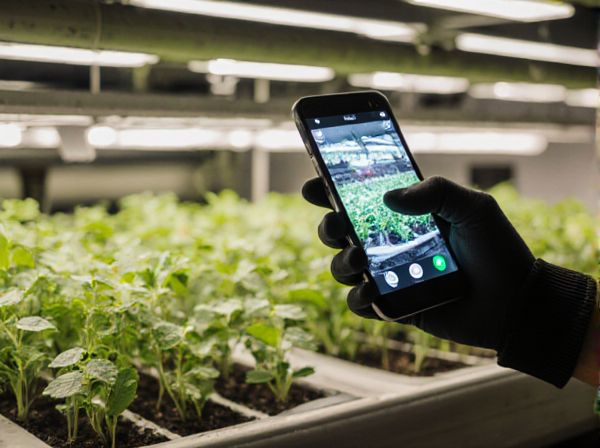
Hydroponics offers precise nutrient control and faster plant growth compared to soil-based growing, reducing water usage and space requirements. Soil-based growing supports natural microbial activity that enhances plant flavor and resilience but can be slower and less resource-efficient. Selecting between hydroponics and soil depends on factors like crop type, environmental control, and sustainability goals.
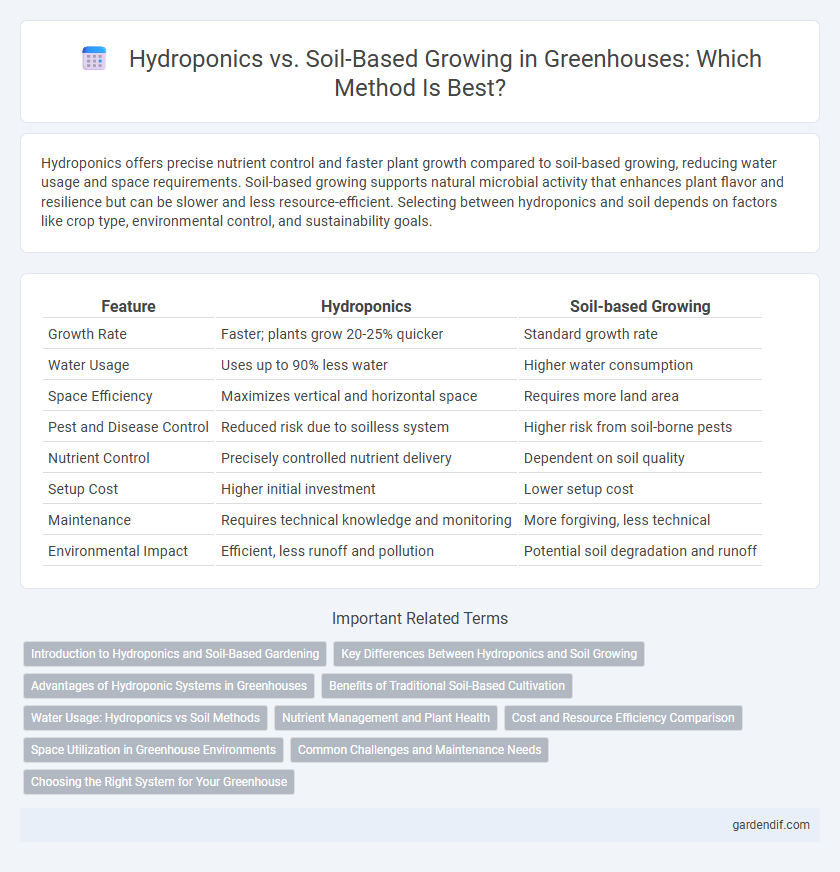
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Hydroponics | Soil-based Growing |
|---|---|---|
| Growth Rate | Faster; plants grow 20-25% quicker | Standard growth rate |
| Water Usage | Uses up to 90% less water | Higher water consumption |
| Space Efficiency | Maximizes vertical and horizontal space | Requires more land area |
| Pest and Disease Control | Reduced risk due to soilless system | Higher risk from soil-borne pests |
| Nutrient Control | Precisely controlled nutrient delivery | Dependent on soil quality |
| Setup Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower setup cost |
| Maintenance | Requires technical knowledge and monitoring | More forgiving, less technical |
| Environmental Impact | Efficient, less runoff and pollution | Potential soil degradation and runoff |
Introduction to Hydroponics and Soil-Based Gardening
Hydroponics is a soilless cultivation method using nutrient-rich water solutions to deliver essential minerals directly to plant roots, enabling faster growth and higher yields compared to traditional soil-based gardening. Soil-based growing relies on natural earth filled with organic matter, microorganisms, and minerals that support plant health through biological processes and nutrient cycling. Hydroponic systems require precise control of pH, nutrients, and water, while soil gardening depends on soil composition, texture, and fertility for plant development.
Key Differences Between Hydroponics and Soil Growing
Hydroponics uses nutrient-rich water solutions to grow plants without soil, enabling precise control over nutrient delivery and reducing water usage by up to 90% compared to soil-based growing. Soil-based growing relies on natural soil, which provides organic matter and microorganisms that support plant health but can introduce variability and pests. Hydroponic systems often result in faster growth rates and higher yields due to optimized conditions and reduced disease risk, while soil growing supports traditional farming practices and natural ecosystems.
Advantages of Hydroponic Systems in Greenhouses
Hydroponic systems in greenhouses offer significant advantages such as increased growth rates and higher yields due to precise nutrient control and optimized water use. These systems reduce soil-borne diseases and pests, minimizing the need for chemical pesticides and promoting healthier plant development. Enhanced space efficiency and year-round cultivation capabilities make hydroponics a sustainable choice for maximizing production in controlled greenhouse environments.
Benefits of Traditional Soil-Based Cultivation
Traditional soil-based cultivation offers natural nutrient cycling, improving plant health through diverse microbial activity found in rich, organic soils. Soil's water retention capabilities enable efficient moisture management, reducing irrigation needs and preventing root stress. This method supports sustainable ecosystems by maintaining soil biodiversity and enhancing carbon sequestration compared to hydroponic systems.
Water Usage: Hydroponics vs Soil Methods
Hydroponics systems use up to 90% less water than traditional soil-based growing by recirculating nutrient solutions directly to plant roots, minimizing evaporation and runoff. Soil-based methods typically require frequent watering due to water loss from soil absorption, evaporation, and drainage, resulting in higher overall water consumption. Efficient water management in hydroponic greenhouses significantly reduces demand on freshwater resources compared to conventional soil cultivation.
Nutrient Management and Plant Health
Hydroponics offers precise nutrient management by delivering a balanced solution directly to plant roots, ensuring optimal nutrient uptake and minimizing waste compared to soil-based growing. Soil-based systems rely on soil composition and microbial activity to supply nutrients, which can lead to variability in nutrient availability and potential deficiencies. Hydroponic systems reduce the risk of soil-borne diseases, promoting healthier plant growth and higher yields through controlled environmental conditions.
Cost and Resource Efficiency Comparison
Hydroponics systems typically incur higher initial setup costs than soil-based growing but offer significantly greater resource efficiency by using up to 90% less water and enabling precise nutrient delivery to plants. Soil-based growing involves lower upfront expenses but often results in higher water consumption and nutrient runoff, increasing long-term operational costs and environmental impact. Hydroponics maximizes yield per square foot, reducing the need for large land areas and optimizing resource use for sustainable greenhouse production.
Space Utilization in Greenhouse Environments
Hydroponics maximizes space utilization in greenhouse environments by allowing vertical stacking and denser plant arrangements, significantly increasing crop yield per square foot compared to soil-based growing. Soil-based methods require more horizontal space due to root expansion and soil maintenance needs, limiting planting density. Efficient space management in hydroponic systems leads to enhanced resource use and optimized greenhouse productivity.
Common Challenges and Maintenance Needs
Hydroponics systems require precise nutrient management and constant monitoring of water pH and oxygen levels to prevent plant stress and disease, while soil-based growing faces challenges such as soil-borne pests, nutrient imbalances, and the need for regular soil conditioning. Both methods demand consistent pest control and environmental regulation within the greenhouse, but hydroponics often involves higher initial setup complexity and energy input for maintaining water circulation and lighting. Maintenance in hydroponics focuses on system cleanliness and nutrient solution replacement, whereas soil-based cultivation relies on soil fertility management and periodic crop rotation to sustain productivity.
Choosing the Right System for Your Greenhouse
Hydroponics offers precise control over nutrient delivery and faster plant growth, making it ideal for maximizing yield in limited greenhouse spaces. Soil-based growing enhances plant flavor and supports beneficial microorganisms crucial for long-term soil health. Selecting the right system depends on factors such as crop type, available resources, and desired harvest cycles to optimize productivity and sustainability in your greenhouse.
Hydroponics vs Soil-based Growing Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com