
Soil-Based Growing vs Soilless Growing Illustration
Soil-based growing relies on natural soil as the medium for plant roots, offering nutrients and microbial life essential for healthy growth, but it may pose challenges such as soil-borne diseases and slower drainage. Soilless growing, including methods like hydroponics and aeroponics, uses nutrient-rich water solutions or inert media, enabling precise control over nutrient delivery and often resulting in faster growth and higher yields. Choosing between soil-based and soilless growing depends on factors like crop type, available space, water efficiency, and the desired level of automation in the greenhouse environment.
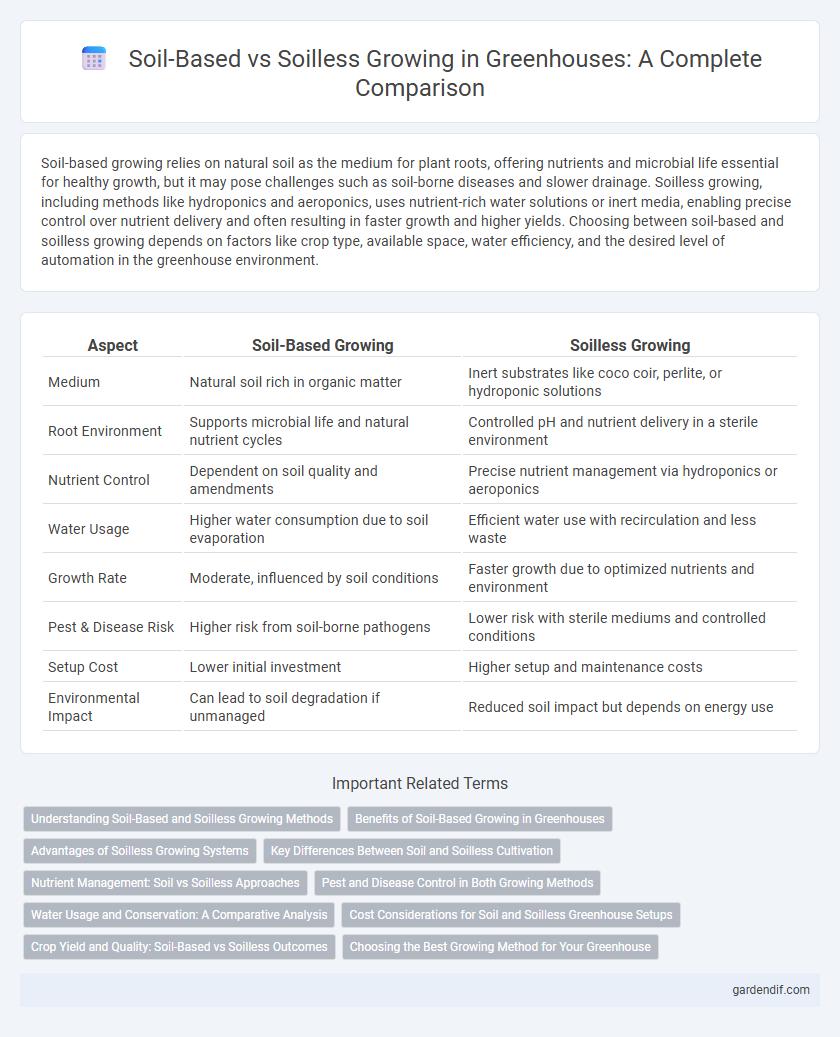
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Soil-Based Growing | Soilless Growing |
|---|---|---|
| Medium | Natural soil rich in organic matter | Inert substrates like coco coir, perlite, or hydroponic solutions |
| Root Environment | Supports microbial life and natural nutrient cycles | Controlled pH and nutrient delivery in a sterile environment |
| Nutrient Control | Dependent on soil quality and amendments | Precise nutrient management via hydroponics or aeroponics |
| Water Usage | Higher water consumption due to soil evaporation | Efficient water use with recirculation and less waste |
| Growth Rate | Moderate, influenced by soil conditions | Faster growth due to optimized nutrients and environment |
| Pest & Disease Risk | Higher risk from soil-borne pathogens | Lower risk with sterile mediums and controlled conditions |
| Setup Cost | Lower initial investment | Higher setup and maintenance costs |
| Environmental Impact | Can lead to soil degradation if unmanaged | Reduced soil impact but depends on energy use |
Understanding Soil-Based and Soilless Growing Methods
Soil-based growing involves cultivating plants directly in natural soil, which provides essential nutrients, beneficial microorganisms, and water retention necessary for plant growth. Soilless growing methods, such as hydroponics and aeroponics, utilize nutrient-rich water solutions or misting systems, allowing precise control over nutrient delivery and reducing risks of soil-borne diseases. Understanding the differences enables growers to select the optimal system based on crop type, space availability, and desired resource efficiency in greenhouse environments.
Benefits of Soil-Based Growing in Greenhouses
Soil-based growing in greenhouses enhances nutrient retention and organic matter, promoting healthier plant root systems and improving water-holding capacity for sustained growth. This method supports beneficial microorganisms that contribute to disease resistance and nutrient cycling, leading to higher crop yields. Soil also provides a natural buffer against rapid pH changes, ensuring stable growing conditions essential for optimal plant development.
Advantages of Soilless Growing Systems
Soilless growing systems, such as hydroponics and aeroponics, offer precise nutrient control, resulting in faster plant growth and higher yields compared to traditional soil-based methods. These systems reduce the risk of soil-borne diseases and pests, minimizing the need for pesticides and enhancing crop quality. Efficient water use and space-saving designs make soilless systems ideal for urban greenhouses and sustainable agriculture.
Key Differences Between Soil and Soilless Cultivation
Soil-based growing relies on natural earth that contains essential nutrients, organic matter, and microorganisms vital for plant development, whereas soilless cultivation uses inert mediums like coco coir, perlite, or hydroponic solutions to deliver precise nutrient control. The primary difference lies in nutrient management: soil acts as a natural reservoir requiring balanced fertilization, while soilless systems allow direct delivery of tailored nutrient solutions, often resulting in faster growth and higher yields. Water usage efficiency and disease control also differ, with soilless systems typically reducing water consumption and minimizing soil-borne pathogens, making them ideal for controlled greenhouse environments.
Nutrient Management: Soil vs Soilless Approaches
Soil-based growing relies on organic matter and natural microbial activity to supply nutrients, requiring regular soil testing and amendments to maintain optimal fertility. In contrast, soilless growing employs precise nutrient solutions tailored to plant needs, allowing for direct control over nutrient availability and reducing the risk of deficiencies or toxicities. This controlled nutrient management in soilless systems enhances growth efficiency, water use, and crop yields in greenhouse environments.
Pest and Disease Control in Both Growing Methods
Soil-based growing often faces challenges with soil-borne pests and diseases such as nematodes, fungi, and bacteria, requiring regular soil treatments and crop rotation to mitigate infestations. Soilless growing methods like hydroponics and aeroponics reduce soil-related pathogen risks by eliminating soil, but they demand vigilant water management and sanitation protocols to prevent waterborne diseases and algae growth. Integrated pest management strategies tailored for each system enhance crop health by combining biological controls, environmental monitoring, and targeted interventions.
Water Usage and Conservation: A Comparative Analysis
Soil-based growing in greenhouses typically requires more water due to soil's natural absorption and evaporation rates, whereas soilless systems like hydroponics deliver water directly to plant roots, enhancing efficiency and reducing waste. Soilless growing methods enable precise control over nutrient and water application, resulting in water savings of up to 90% compared to traditional soil cultivation. Conservation efforts benefit from soilless systems' closed-loop irrigation, which recycles water and minimizes runoff, promoting sustainable greenhouse practices.
Cost Considerations for Soil and Soilless Greenhouse Setups
Soil-based greenhouse setups typically require lower initial investment in infrastructure but incur ongoing costs for soil management, pest control, and nutrient amendments. Soilless growing systems, such as hydroponics or aeroponics, demand higher upfront expenses for equipment, nutrient solutions, and environmental controls but offer faster crop cycles and reduced labor related to soil maintenance. Cost efficiency depends on factors like crop type, greenhouse scale, and long-term sustainability goals, with soilless systems often proving more profitable for high-value crops despite their initial capital intensity.
Crop Yield and Quality: Soil-Based vs Soilless Outcomes
Soilless growing methods like hydroponics and aeroponics often produce higher crop yields and enhanced quality due to precise nutrient and water control compared to traditional soil-based cultivation. Soil-based growing can yield nutrient-rich, flavorful crops but is more susceptible to pests and soil-borne diseases, potentially reducing overall productivity. Optimizing environmental conditions and nutrient delivery in soilless systems typically results in faster growth rates and consistent quality, benefiting commercial greenhouse operations.
Choosing the Best Growing Method for Your Greenhouse
Soil-based growing in greenhouses offers natural nutrient cycles and improved microbial activity, enhancing plant health and flavor profiles. Soilless growing methods like hydroponics and aeroponics provide precise nutrient control, faster growth rates, and reduced pest risks, optimizing space and resource efficiency. Selecting the best method depends on crop type, environmental conditions, resource availability, and desired yield quality within your greenhouse operation.
Soil-Based Growing vs Soilless Growing Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com