
Seed priming vs Seed pelleting Illustration
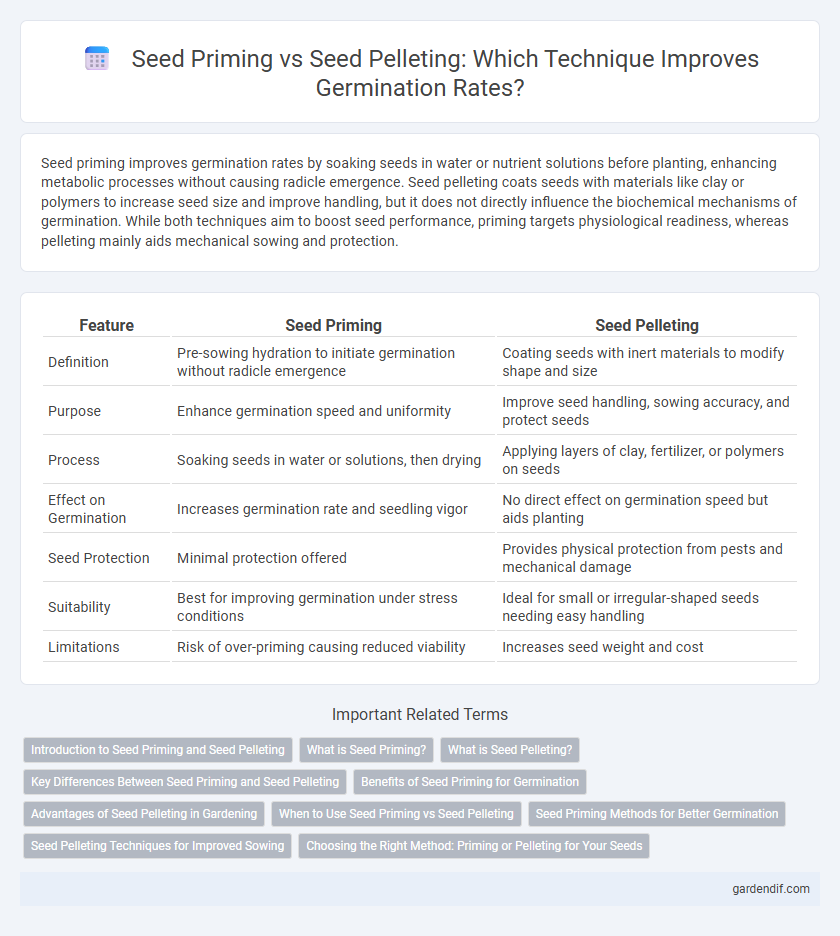
Seed priming improves germination rates by soaking seeds in water or nutrient solutions before planting, enhancing metabolic processes without causing radicle emergence. Seed pelleting coats seeds with materials like clay or polymers to increase seed size and improve handling, but it does not directly influence the biochemical mechanisms of germination. While both techniques aim to boost seed performance, priming targets physiological readiness, whereas pelleting mainly aids mechanical sowing and protection.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Seed Priming | Seed Pelleting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-sowing hydration to initiate germination without radicle emergence | Coating seeds with inert materials to modify shape and size |
| Purpose | Enhance germination speed and uniformity | Improve seed handling, sowing accuracy, and protect seeds |
| Process | Soaking seeds in water or solutions, then drying | Applying layers of clay, fertilizer, or polymers on seeds |
| Effect on Germination | Increases germination rate and seedling vigor | No direct effect on germination speed but aids planting |
| Seed Protection | Minimal protection offered | Provides physical protection from pests and mechanical damage |
| Suitability | Best for improving germination under stress conditions | Ideal for small or irregular-shaped seeds needing easy handling |
| Limitations | Risk of over-priming causing reduced viability | Increases seed weight and cost |
Introduction to Seed Priming and Seed Pelleting
Seed priming enhances germination by partially hydrating seeds to activate metabolic processes without triggering radicle emergence, improving uniformity and speed of seedling growth. Seed pelleting involves coating seeds with inert materials to alter seed size and shape, facilitating mechanized sowing and protecting seeds from pests and environmental stress. Both techniques optimize seed performance but target different challenges in the germination and planting phases.
What is Seed Priming?
Seed priming is a controlled hydration process that initiates the early stages of germination without allowing radicle emergence, enhancing seed vigor and uniformity. This technique improves the metabolic activities crucial for faster and synchronized seedling development under various environmental conditions. Unlike seed pelleting, which modifies seed shape and size for ease of planting, priming directly boosts germination speed and stress tolerance.
What is Seed Pelleting?
Seed pelleting involves coating seeds with a mixture of inert materials, enhancing seed size and shape for uniform planting and improved handling. This technique can include nutrients, pesticides, or growth regulators to promote germination and seedling vigor. Seed pelleting is particularly beneficial for small or irregularly shaped seeds, ensuring precise sowing and better crop establishment.
Key Differences Between Seed Priming and Seed Pelleting
Seed priming involves controlled hydration of seeds to initiate metabolic processes without radicle emergence, enhancing germination speed and uniformity. Seed pelleting encases seeds in inert materials to improve handling, protect from pests, and optimize sowing precision, often altering seed size and shape. The primary difference between the two lies in seed priming activating physiological processes internally, while pelleting focuses on external physical modifications for mechanical advantages.
Benefits of Seed Priming for Germination
Seed priming enhances germination by initiating metabolic processes before sowing, leading to faster and more uniform seedling emergence. This technique improves seed vigor, stress tolerance, and overall germination rate compared to untreated seeds. Unlike seed pelleting, which primarily aids in seed handling and placement, seed priming directly boosts physiological readiness for germination.
Advantages of Seed Pelleting in Gardening
Seed pelleting enhances germination by improving seed handling and precise sowing, reducing seed loss during planting. It provides uniform seed size and weight, facilitating mechanical planting and ensuring even seed distribution in the garden. The protective coating in pelleted seeds also aids in moisture retention and can incorporate nutrients or pesticides, boosting early seedling vigor and growth.
When to Use Seed Priming vs Seed Pelleting
Seed priming is most effective for improving germination speed and uniformity in crops prone to uneven emergence or stress conditions such as drought or low temperatures, enabling seeds to begin metabolic processes before sowing. Seed pelleting is ideal when precise seed placement and protection are required, especially in mechanical planting systems or for very small seeds that benefit from increased size and weight. Selecting between seed priming and seed pelleting depends on the specific crop requirements, environmental conditions, and planting technology to optimize seedling establishment.
Seed Priming Methods for Better Germination
Seed priming methods such as hydropriming, osmopriming, and biopriming enhance germination by improving seed water uptake and metabolic activation before sowing. These techniques reduce germination time, increase seedling vigor, and improve uniformity by initiating physiological processes without radicle emergence. Compared to seed pelleting, which mainly facilitates seed handling and sowing, seed priming directly optimizes the seed's germination potential and stress tolerance.
Seed Pelleting Techniques for Improved Sowing
Seed pelleting techniques involve coating seeds with materials like clay, binders, and nutrients to improve seed handling and uniformity during sowing, enhancing germination rates and seedling establishment. These coatings protect seeds from pests and diseases while optimizing moisture retention and soil contact, resulting in better germination under adverse environmental conditions. Advanced pelleting technologies integrate growth promoters and protective agents, ensuring precise seed placement and improved crop performance compared to traditional seed priming methods.
Choosing the Right Method: Priming or Pelleting for Your Seeds
Seed priming enhances germination speed and uniformity by partially hydrating seeds, optimizing metabolic processes before sowing, which is ideal for crops requiring faster emergence. Seed pelleting modifies seed size and shape for easier handling and precise planting, benefiting small or irregularly shaped seeds by improving seed-to-soil contact and compatibility with mechanical planters. Selecting the right method depends on seed type, desired planting efficiency, and specific agricultural goals, with priming favored for physiological improvements and pelleting chosen for physical seed enhancement.
Seed priming vs Seed pelleting Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com