
Cold frame germination vs Indoor sprouting Illustration
Cold frame germination allows seeds to benefit from natural sunlight and fluctuating outdoor temperatures, promoting hardy seedling development. Indoor sprouting offers controlled temperature and humidity, reducing risks of pests and diseases while enabling year-round germination. Both methods support early plant growth but differ in environmental exposure and resource requirements.
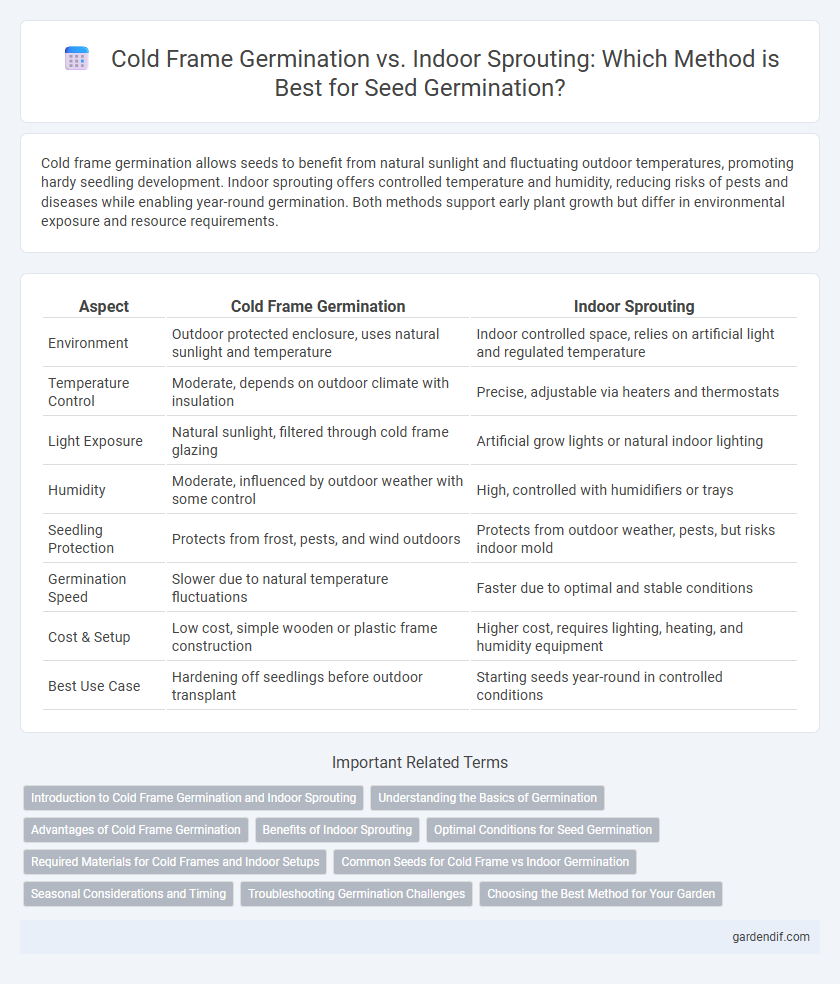
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Cold Frame Germination | Indoor Sprouting |
|---|---|---|
| Environment | Outdoor protected enclosure, uses natural sunlight and temperature | Indoor controlled space, relies on artificial light and regulated temperature |
| Temperature Control | Moderate, depends on outdoor climate with insulation | Precise, adjustable via heaters and thermostats |
| Light Exposure | Natural sunlight, filtered through cold frame glazing | Artificial grow lights or natural indoor lighting |
| Humidity | Moderate, influenced by outdoor weather with some control | High, controlled with humidifiers or trays |
| Seedling Protection | Protects from frost, pests, and wind outdoors | Protects from outdoor weather, pests, but risks indoor mold |
| Germination Speed | Slower due to natural temperature fluctuations | Faster due to optimal and stable conditions |
| Cost & Setup | Low cost, simple wooden or plastic frame construction | Higher cost, requires lighting, heating, and humidity equipment |
| Best Use Case | Hardening off seedlings before outdoor transplant | Starting seeds year-round in controlled conditions |
Introduction to Cold Frame Germination and Indoor Sprouting
Cold frame germination offers a natural, controlled environment using solar energy to warm soil and protect seeds from harsh weather, promoting earlier and more robust plant growth. Indoor sprouting provides a stable, temperature-controlled setting ideal for consistent germination regardless of outdoor conditions, allowing precise management of light and moisture. Both methods enhance seedling success by optimizing growth factors, but cold frames integrate outdoor environmental benefits, while indoor sprouting maximizes control and convenience.
Understanding the Basics of Germination
Cold frame germination leverages natural sunlight and ambient outdoor temperatures, creating a controlled environment that extends the growing season while protecting seeds from harsh weather. Indoor sprouting relies on consistent temperature control, humidity, and artificial lighting to provide optimal conditions year-round, ensuring faster and more predictable germination rates. Both methods focus on maintaining moisture, temperature, and oxygen balance crucial for seed activation and root emergence during the germination process.
Advantages of Cold Frame Germination
Cold frame germination offers superior temperature regulation by utilizing natural solar heat, promoting consistent seed germination conditions that reduce energy costs compared to indoor sprouting. It enables exposure to natural light cycles, enhancing seedling vigor and development while providing protection from harsh weather and pests. This method also supports sustainable gardening practices by minimizing reliance on artificial heat and lighting systems.
Benefits of Indoor Sprouting
Indoor sprouting offers consistent temperature control and higher humidity, creating an ideal environment for seed germination that accelerates growth compared to cold frame methods. This technique minimizes exposure to pests and harsh weather, reducing seedling stress and improving germination rates. Enhanced light management indoors further optimizes photosynthesis, resulting in healthier and more vigorous sprouts.
Optimal Conditions for Seed Germination
Cold frame germination provides seeds with natural temperature fluctuations and consistent moisture, mimicking outdoor conditions ideal for hardy plant varieties. Indoor sprouting allows precise control over temperature, humidity, and light, ensuring faster and more uniform germination for delicate seeds. Both methods optimize seed germination by maintaining appropriate soil warmth between 65-75degF and consistent moisture levels essential for seed embryo development.
Required Materials for Cold Frames and Indoor Setups
Cold frame germination requires materials such as a sturdy wooden or plastic frame, transparent glazing like glass or polycarbonate panels for sunlight exposure, insulating blankets for temperature regulation, and well-draining soil. Indoor sprouting setups need seed trays or pots, grow lights to provide consistent light, heating mats to maintain optimal soil temperature, and a humidity dome or plastic cover to retain moisture. Both methods emphasize controlled environments but differ in material requirements based on natural versus artificial temperature and light management.
Common Seeds for Cold Frame vs Indoor Germination
Cold frame germination is ideal for hardy seeds such as lettuce, spinach, and kale, which tolerate cooler temperatures and benefit from natural outdoor conditions. Indoor sprouting favors warmth-loving seeds like tomatoes, peppers, and herbs that require consistent heat and humidity for optimal germination rates. Seed selection depends on temperature tolerance and growth stage: cold frames suit cool-season crops, while indoor environments support heat-dependent varieties.
Seasonal Considerations and Timing
Cold frame germination leverages natural seasonal temperature fluctuations, ideal for early spring or late fall planting when outdoor conditions are cooler but protected from frost. Indoor sprouting offers year-round control over temperature and humidity, enabling precise timing independent of external seasons. Choosing cold frame germination suits hardier crops needing gradual acclimatization, while indoor sprouting supports sensitive seeds requiring stable warmth for optimal germination rates.
Troubleshooting Germination Challenges
Cold frame germination exposes seeds to natural temperature fluctuations and varying humidity, which can sometimes lead to inconsistent moisture levels and slower germination rates, requiring careful monitoring to prevent mold or seed rot. Indoor sprouting provides a controlled environment with stable temperatures and humidity, reducing the risk of fungal infections and enhancing seedling vigor, but may demand diligent ventilation management to avoid damping-off disease. Identifying specific issues such as poor seed quality, inadequate moisture, or temperature stress is crucial for improving germination success in both cold frame and indoor sprouting methods.
Choosing the Best Method for Your Garden
Cold frame germination harnesses natural sunlight and outdoor temperature fluctuations to stimulate seed sprouting, offering a controlled yet cost-effective environment ideal for hardier plants. Indoor sprouting provides precise climate control, consistent warmth, and protection from pests, making it suitable for delicate or tropical seeds requiring stable conditions. Selecting the best method depends on your garden's climate, plant species, space availability, and the desired level of environmental control.
Cold frame germination vs Indoor sprouting Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com