
Foliar feeding vs Soil application Illustration
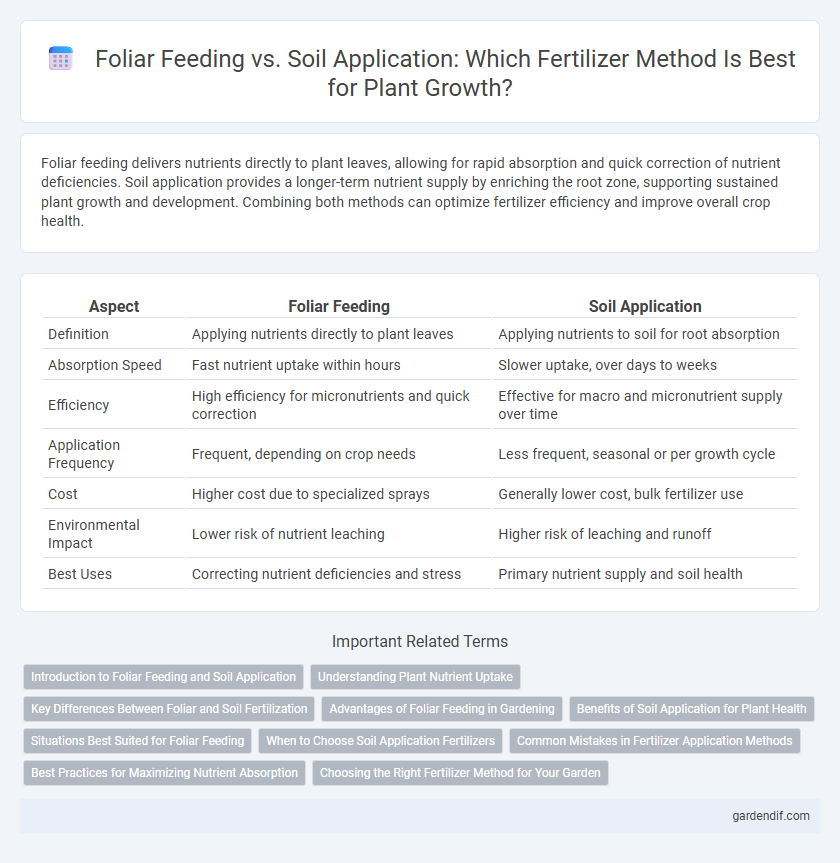
Foliar feeding delivers nutrients directly to plant leaves, allowing for rapid absorption and quick correction of nutrient deficiencies. Soil application provides a longer-term nutrient supply by enriching the root zone, supporting sustained plant growth and development. Combining both methods can optimize fertilizer efficiency and improve overall crop health.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Foliar Feeding | Soil Application |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Applying nutrients directly to plant leaves | Applying nutrients to soil for root absorption |
| Absorption Speed | Fast nutrient uptake within hours | Slower uptake, over days to weeks |
| Efficiency | High efficiency for micronutrients and quick correction | Effective for macro and micronutrient supply over time |
| Application Frequency | Frequent, depending on crop needs | Less frequent, seasonal or per growth cycle |
| Cost | Higher cost due to specialized sprays | Generally lower cost, bulk fertilizer use |
| Environmental Impact | Lower risk of nutrient leaching | Higher risk of leaching and runoff |
| Best Uses | Correcting nutrient deficiencies and stress | Primary nutrient supply and soil health |
Introduction to Foliar Feeding and Soil Application
Foliar feeding involves the direct application of nutrient-rich solutions to plant leaves, allowing for rapid nutrient absorption and immediate correction of deficiencies. Soil application delivers fertilizers through soil integration, promoting root uptake and improving long-term soil fertility and structure. Each method targets specific growth stages and environmental conditions to optimize nutrient availability and plant health.
Understanding Plant Nutrient Uptake
Foliar feeding delivers nutrients directly to plant leaves, enabling rapid absorption and immediate correction of nutrient deficiencies, especially for micronutrients like zinc and iron. Soil application provides a sustained nutrient supply through root uptake, promoting long-term plant health by improving soil fertility and microbial activity. Understanding plant nutrient uptake mechanisms highlights that foliar feeding is most effective for quick nutrient supplementation, while soil application supports overall growth and nutrient balance.
Key Differences Between Foliar and Soil Fertilization
Foliar feeding delivers nutrients directly to plant leaves, allowing for faster absorption and immediate correction of nutrient deficiencies, while soil application relies on root uptake, providing a longer-term nutrient supply. Foliar fertilization is most effective for micronutrients and during critical growth stages, whereas soil fertilization supports overall plant development and improves soil fertility. Environmental factors like soil pH and moisture strongly influence soil application efficiency, whereas foliar feeding is affected by leaf surface conditions and spray timing.
Advantages of Foliar Feeding in Gardening
Foliar feeding in gardening allows for rapid nutrient absorption directly through plant leaves, resulting in faster correction of nutrient deficiencies compared to soil application. This method enhances nutrient uptake efficiency, especially in conditions where soil nutrient availability is limited by factors such as pH imbalance or poor soil structure. Foliar feeding also reduces fertilizer runoff and environmental impact by targeting specific nutrient delivery to plants, promoting healthier growth and higher yields.
Benefits of Soil Application for Plant Health
Soil application delivers nutrients directly to the root zone, promoting deep and sustained nutrient absorption essential for robust plant growth. It enhances soil structure and microbial activity, improving nutrient availability and root development over time. This method reduces nutrient runoff and leaching, ensuring efficient fertilizer use and long-term soil fertility.
Situations Best Suited for Foliar Feeding
Foliar feeding is best suited for addressing micronutrient deficiencies quickly during critical growth stages, especially when soil conditions limit nutrient availability or uptake. It is effective in situations requiring rapid correction of nutrient imbalances, such as during drought, root damage, or alkaline soils that immobilize nutrients. Foliar application targets leaves directly, enhancing nutrient absorption efficiency for elements like iron, zinc, and manganese where soil application proves less effective.
When to Choose Soil Application Fertilizers
Soil application fertilizers are ideal when plants require long-term nutrient availability and improved root development. This method is preferred for crops grown in nutrient-deficient soils or when targeting deep-rooted plants that absorb nutrients primarily from the soil. Choosing soil application supports sustained growth and is effective for essential nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium.
Common Mistakes in Fertilizer Application Methods
Applying fertilizer through foliar feeding often leads to common mistakes such as over-concentration, causing leaf burn and nutrient imbalances, while soil application errors typically include uneven distribution and improper timing, reducing nutrient uptake efficiency. Farmers frequently neglect soil pH testing, which affects nutrient availability, and fail to adjust foliar spray concentrations to crop species and growth stages. Understanding the differences in nutrient absorption rates and environmental conditions can optimize fertilizer effectiveness and minimize wastage.
Best Practices for Maximizing Nutrient Absorption
Foliar feeding optimizes nutrient absorption by delivering essential elements directly to the leaves, facilitating rapid uptake and targeted correction of deficiencies. Soil application enhances root zone fertility, promoting sustained nutrient availability and improved microbial activity critical for plant health. Combining both methods with appropriate timing, correct nutrient formulation, and environmental monitoring maximizes overall nutrient efficiency and crop yield.
Choosing the Right Fertilizer Method for Your Garden
Foliar feeding delivers nutrients directly to plant leaves, ensuring rapid absorption and correcting deficiencies quickly, while soil application provides a slow, steady nutrient release that supports long-term root development and overall soil health. Selecting the right fertilization method depends on your garden's specific needs, including plant type, growth stage, and nutrient availability in the soil. Combining foliar feeding with soil application can optimize nutrient uptake, improve plant vigor, and enhance crop yield.
Foliar feeding vs Soil application Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com