
Soil amendment vs topdressing Illustration
Soil amendment involves incorporating organic materials or nutrients directly into the soil to improve its structure, fertility, and overall health, enhancing root growth and nutrient absorption. Topdressing refers to the application of a thin layer of compost, manure, or fertilizer on the surface of the soil or turf, providing immediate nutrient availability and protecting the soil from erosion. Choosing between soil amendment and topdressing depends on the specific needs of edible plants, where amendments benefit long-term soil quality and topdressing supplies quick nutrient boosts.
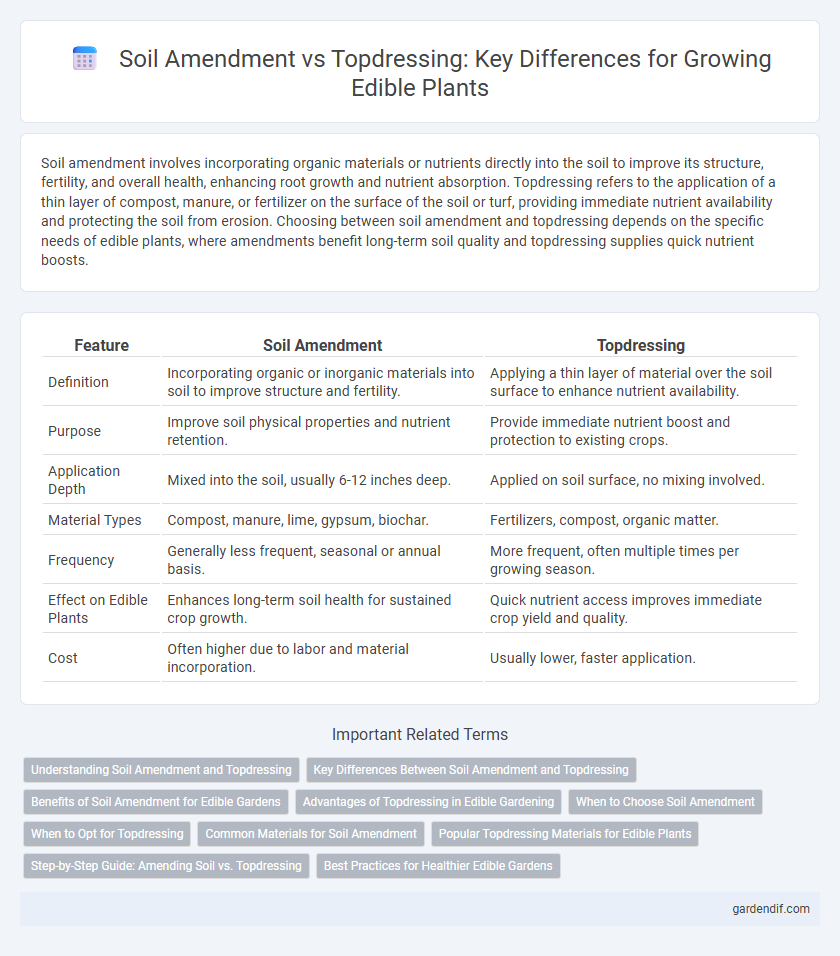
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Soil Amendment | Topdressing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Incorporating organic or inorganic materials into soil to improve structure and fertility. | Applying a thin layer of material over the soil surface to enhance nutrient availability. |
| Purpose | Improve soil physical properties and nutrient retention. | Provide immediate nutrient boost and protection to existing crops. |
| Application Depth | Mixed into the soil, usually 6-12 inches deep. | Applied on soil surface, no mixing involved. |
| Material Types | Compost, manure, lime, gypsum, biochar. | Fertilizers, compost, organic matter. |
| Frequency | Generally less frequent, seasonal or annual basis. | More frequent, often multiple times per growing season. |
| Effect on Edible Plants | Enhances long-term soil health for sustained crop growth. | Quick nutrient access improves immediate crop yield and quality. |
| Cost | Often higher due to labor and material incorporation. | Usually lower, faster application. |
Understanding Soil Amendment and Topdressing
Soil amendment improves soil structure, drainage, and nutrient content by incorporating organic matter or minerals into the soil profile, enhancing long-term plant health and productivity. Topdressing involves applying a thin layer of compost, sand, or fertilizer directly onto the soil surface or turf to provide immediate nutrient availability and improve surface conditions. Both practices optimize soil fertility but differ in application methods, timing, and their impact on soil dynamics in edible crop cultivation.
Key Differences Between Soil Amendment and Topdressing
Soil amendment involves incorporating organic or inorganic materials into the soil to improve its physical properties, nutrient content, and overall fertility, enhancing water retention and aeration. Topdressing refers to the application of a thin layer of material, such as compost or fertilizer, spread over the soil surface or grass to provide nutrients and protect the soil without disturbing the underlying layers. The key differences lie in the method of application and purpose: soil amendment alters soil structure and long-term fertility, while topdressing primarily supplies surface nutrients and soil protection.
Benefits of Soil Amendment for Edible Gardens
Soil amendment enhances edible garden productivity by improving soil structure, increasing nutrient retention, and promoting beneficial microbial activity essential for healthy plant growth. Unlike topdressing, which primarily adds surface nutrients, soil amendment integrates organic matter deeply into the soil, leading to better root development and moisture retention. This results in higher yields and improved flavor profiles for vegetables and fruits grown in amended soils.
Advantages of Topdressing in Edible Gardening
Topdressing in edible gardening enhances soil fertility by providing a slow-release source of nutrients directly to plant roots, promoting healthier growth and higher yields. It improves soil structure and moisture retention without disturbing existing plants or soil layers, preserving beneficial microorganisms essential for nutrient cycling. Applying topdressing regularly supports sustainable gardening practices by reducing erosion and nutrient runoff, leading to more productive and resilient edible landscapes.
When to Choose Soil Amendment
Soil amendment is ideal when improving soil structure, enhancing nutrient content, or correcting pH levels before planting edible crops. This method promotes deeper root growth and better moisture retention, crucial for optimal fruit and vegetable production. Use soil amendments during initial soil preparation or early in the growing season to maximize plant health and yield.
When to Opt for Topdressing
Topdressing is ideal for promoting rapid nutrient uptake during the growing season, especially when plants show signs of nutrient deficiency or stress. It allows for targeted nutrient application without disturbing the root zone, enhancing soil surface conditions and improving moisture retention. This method is preferred during active growth phases to boost plant health and yield efficiently.
Common Materials for Soil Amendment
Common materials for soil amendment include compost, manure, peat moss, and biochar, which improve soil structure, fertility, and moisture retention. These amendments increase organic matter content, enhance microbial activity, and balance soil pH, promoting healthier edible plants. Unlike topdressing, which involves surface application of nutrients, soil amendments are incorporated into the soil to provide long-term benefits.
Popular Topdressing Materials for Edible Plants
Popular topdressing materials for edible plants include organic options like compost, aged manure, and shredded leaves, which improve soil fertility and structure while providing essential nutrients. Mineral topdressings such as rock phosphate, greensand, and gypsum supply vital minerals that enhance plant growth and fruit production. These materials gradually release nutrients, supporting healthy root development and boosting crop yields in vegetable gardens and orchards.
Step-by-Step Guide: Amending Soil vs. Topdressing
Amending soil involves incorporating organic matter or amendments directly into the soil by digging or tilling to improve its structure, fertility, and drainage, typically performed before planting. Topdressing entails spreading a thin layer of compost or soil amendment over the surface of established plants or lawns, enriching the soil gradually without disturbing root systems. For edible gardens, amending soil annually ensures long-term soil health while topdressing supplements nutrients during the growing season for sustained crop vitality.
Best Practices for Healthier Edible Gardens
Soil amendment improves edible garden health by enhancing soil structure, nutrient content, and water retention, promoting strong root development and plant growth. Topdressing with organic materials like compost or mulch provides a nutrient-rich layer that conserves moisture and suppresses weeds without disturbing plant roots. Combining regular soil amendment applications with strategic topdressing optimizes soil fertility and fosters sustainable, productive edible gardens.
Soil amendment vs topdressing Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com