
Container soil mix vs garden soil Illustration
Container soil mix is specifically formulated to provide excellent drainage, aeration, and nutrient retention essential for container plants, unlike garden soil which can be heavy and compacted. Using garden soil in containers often leads to poor root growth and waterlogging because it lacks the lightweight texture and balanced composition of container mixes. For optimal plant health and growth, container soil mix ensures a well-balanced environment tailored to the confined space of pots and containers.
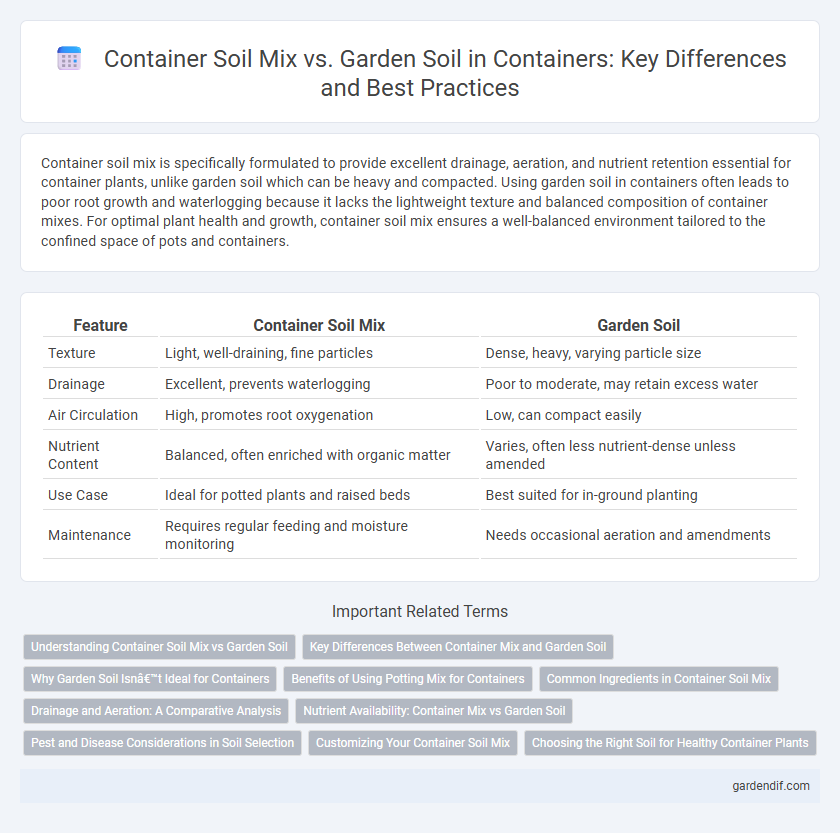
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Container Soil Mix | Garden Soil |
|---|---|---|
| Texture | Light, well-draining, fine particles | Dense, heavy, varying particle size |
| Drainage | Excellent, prevents waterlogging | Poor to moderate, may retain excess water |
| Air Circulation | High, promotes root oxygenation | Low, can compact easily |
| Nutrient Content | Balanced, often enriched with organic matter | Varies, often less nutrient-dense unless amended |
| Use Case | Ideal for potted plants and raised beds | Best suited for in-ground planting |
| Maintenance | Requires regular feeding and moisture monitoring | Needs occasional aeration and amendments |
Understanding Container Soil Mix vs Garden Soil
Container soil mix is specifically formulated to provide optimal drainage, aeration, and nutrient retention for potted plants, unlike garden soil which can be dense and poorly draining. It typically contains components like peat moss, perlite, and compost, ensuring a lightweight structure conducive to healthy root growth. Using garden soil in containers often leads to waterlogging and root rot due to its heavier texture and compaction.
Key Differences Between Container Mix and Garden Soil
Container soil mix is specifically engineered for potted plants, featuring lightweight materials like peat moss, perlite, and vermiculite to ensure excellent drainage and aeration. Garden soil tends to be denser with natural soil content, making it prone to compaction and poor drainage when used in containers. The key differences lie in texture, nutrient retention, and water-holding capacity, with container mix optimized to support root health and prevent waterlogging in confined spaces.
Why Garden Soil Isn’t Ideal for Containers
Garden soil is often too dense and heavy for containers, leading to poor drainage and root aeration issues. It can compact quickly, restricting root growth and causing waterlogging that promotes root rot. Container soil mixes are specifically formulated with lightweight materials like peat moss, perlite, and vermiculite to optimize moisture retention and air circulation, essential for healthy container plant growth.
Benefits of Using Potting Mix for Containers
Potting mix is specifically formulated to provide excellent drainage, aeration, and nutrient retention ideal for container plants, unlike garden soil that can compact and restrict root growth. It often contains components like peat moss, perlite, and vermiculite, which create a lightweight texture ensuring roots receive sufficient oxygen and moisture. Using potting mix enhances plant health and growth in containers by preventing waterlogging and supporting strong root development.
Common Ingredients in Container Soil Mix
Container soil mix commonly contains ingredients such as peat moss, perlite, vermiculite, and composted bark, which promote aeration, drainage, and nutrient retention specifically for potted plants. Garden soil typically has a denser structure with more clay and native organic matter, which can hinder proper drainage and root development in containers. Optimized container mixes balance moisture retention and air flow, creating an ideal environment for healthy plant growth in confined spaces.
Drainage and Aeration: A Comparative Analysis
Container soil mix offers superior drainage and aeration compared to garden soil, as it is specifically formulated with components like perlite, vermiculite, and peat moss that enhance water retention while preventing waterlogging. Garden soil tends to compact in containers, restricting root oxygen flow and causing poor drainage, which can lead to root rot and plant stress. Optimized aeration in container soil mix promotes healthier root development and improves overall plant growth in confined spaces.
Nutrient Availability: Container Mix vs Garden Soil
Container soil mixes are formulated to provide optimal nutrient availability with components like peat moss, vermiculite, and perlite, which enhance aeration and water retention, ensuring consistent nutrient uptake by plant roots. Garden soil often lacks the balanced texture and drainage properties needed for container plants, leading to nutrient imbalances and potential root rot. Nutrient availability in container mixes is more controlled and tailored for confined root zones, promoting healthier growth compared to standard garden soil.
Pest and Disease Considerations in Soil Selection
Container soil mix is specifically formulated to minimize pest and disease risks by using sterilized, well-draining components that deter common soil-borne pathogens and pests. Garden soil often harbors weeds, fungi, and harmful microorganisms that can lead to root rot, mold, and insect infestations in container plants. Selecting a high-quality container soil mix reduces the chances of pest invasion and disease outbreaks, ensuring healthier plant growth in confined spaces.
Customizing Your Container Soil Mix
Customizing your container soil mix allows for precise control over aeration, drainage, and nutrient content, optimizing plant health and growth. Unlike garden soil, which can be dense and poorly draining, container mixes typically combine components like peat moss, perlite, and compost to maintain an ideal balance of moisture retention and airflow. Tailoring the mix to specific plant needs enhances root development and prevents common issues such as waterlogging or nutrient deficiencies.
Choosing the Right Soil for Healthy Container Plants
Container soil mix is specifically designed with lightweight materials such as peat moss, perlite, and vermiculite to ensure excellent drainage and aeration crucial for healthy container plants. Garden soil is denser and can compact easily in pots, leading to poor root development and water retention issues. Selecting a high-quality container soil mix promotes optimal nutrient availability, prevents root rot, and supports vigorous plant growth in confined spaces.
Container soil mix vs garden soil Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com