
Hydroponic containers vs soil-based containers Illustration
Hydroponic containers optimize plant growth by delivering nutrient-rich water directly to roots, resulting in faster growth and higher yields compared to soil-based containers. Unlike soil containers, hydroponic systems require less space and eliminate soil-borne diseases, promoting cleaner and more controlled growing environments. Efficient water use and reduced pest issues make hydroponic containers ideal for urban gardens and indoor farming.
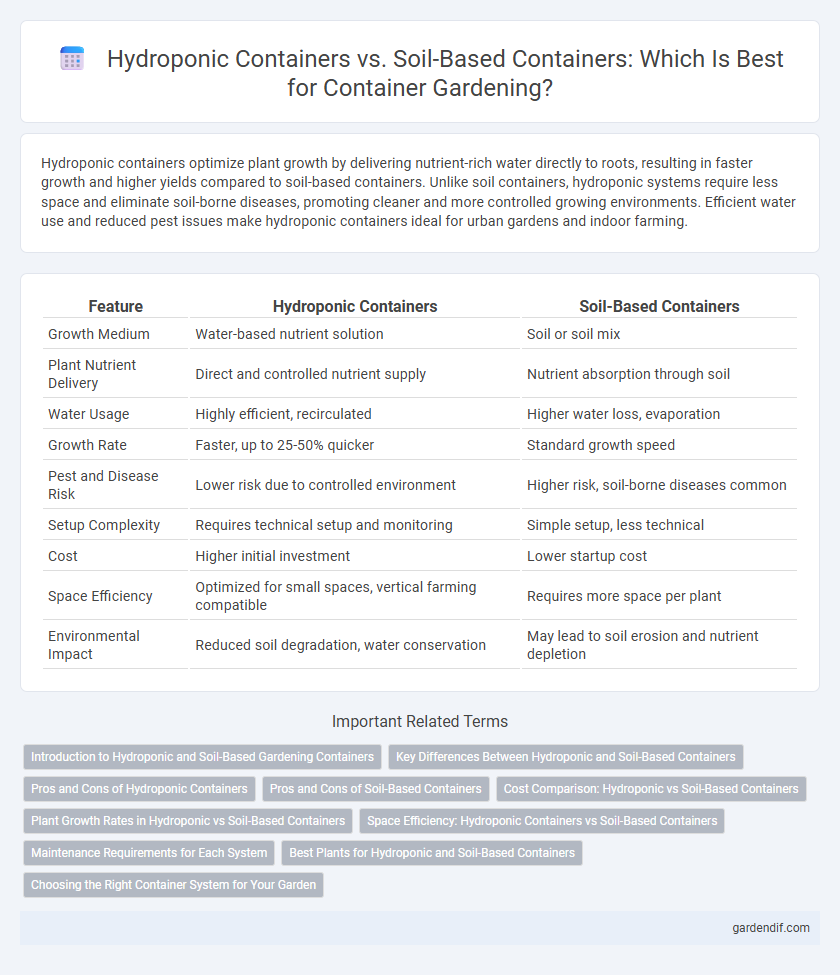
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Hydroponic Containers | Soil-Based Containers |
|---|---|---|
| Growth Medium | Water-based nutrient solution | Soil or soil mix |
| Plant Nutrient Delivery | Direct and controlled nutrient supply | Nutrient absorption through soil |
| Water Usage | Highly efficient, recirculated | Higher water loss, evaporation |
| Growth Rate | Faster, up to 25-50% quicker | Standard growth speed |
| Pest and Disease Risk | Lower risk due to controlled environment | Higher risk, soil-borne diseases common |
| Setup Complexity | Requires technical setup and monitoring | Simple setup, less technical |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower startup cost |
| Space Efficiency | Optimized for small spaces, vertical farming compatible | Requires more space per plant |
| Environmental Impact | Reduced soil degradation, water conservation | May lead to soil erosion and nutrient depletion |
Introduction to Hydroponic and Soil-Based Gardening Containers
Hydroponic containers use nutrient-rich water solutions to grow plants without soil, enabling precise control of moisture, nutrients, and oxygen for accelerated growth and higher yields. Soil-based gardening containers rely on traditional soil media, providing natural microorganisms and organic matter essential for plant health but requiring regular monitoring of soil quality and moisture levels. Both container types offer versatile options for urban gardening, with hydroponics excelling in water efficiency and soil-based containers maintaining ecosystem balance.
Key Differences Between Hydroponic and Soil-Based Containers
Hydroponic containers feature inert growing mediums like clay pellets or rock wool, allowing precise nutrient delivery through water solutions, while soil-based containers rely on natural soil to provide nutrients and support plant roots. Hydroponic setups offer faster plant growth and higher yields due to optimized oxygen levels and consistent moisture, contrasting with soil containers that can vary in nutrient availability and drainage. Maintenance in hydroponic containers involves monitoring pH and nutrient concentration, unlike soil containers that require regular soil conditioning and pest management.
Pros and Cons of Hydroponic Containers
Hydroponic containers enable precise control over nutrient delivery and water usage, promoting faster plant growth and higher yields compared to soil-based containers. They reduce soil-borne diseases and pests, minimizing the need for pesticides but require careful monitoring of nutrient solutions and pH levels to prevent plant stress. High initial setup costs and dependency on consistent power supply represent challenges for hydroponic systems despite their efficiency in space-limited environments.
Pros and Cons of Soil-Based Containers
Soil-based containers offer natural nutrient retention and microbial activity, promoting plant health and growth without the need for frequent nutrient adjustments. They provide better water retention but can lead to issues like soil compaction, poor drainage, and susceptibility to pests and diseases. Compared to hydroponic systems, soil containers require less technical knowledge but may limit root oxygen availability and slow nutrient uptake efficiency.
Cost Comparison: Hydroponic vs Soil-Based Containers
Hydroponic containers generally involve higher initial setup costs due to the need for pumps, growing media, and nutrient solutions, while soil-based containers require minimal upfront investment primarily for soil and basic pots. Operational costs for hydroponic systems can be offset by faster growth rates and higher yields, leading to better long-term economic efficiency despite ongoing expenses for electricity and nutrients. Soil-based containers have lower maintenance costs but may result in slower plant growth and increased water usage, impacting overall cost-effectiveness for commercial growers.
Plant Growth Rates in Hydroponic vs Soil-Based Containers
Hydroponic containers enable faster plant growth rates compared to soil-based containers due to optimized nutrient delivery and oxygen availability directly to the roots. Controlled environments in hydroponic systems minimize plant stress and support consistent intake of essential minerals, resulting in up to 50% quicker maturation for many crops. Soil-based containers often exhibit slower growth due to variable nutrient absorption and potential soil-borne pathogens affecting root health.
Space Efficiency: Hydroponic Containers vs Soil-Based Containers
Hydroponic containers maximize space efficiency by allowing vertical stacking and closer plant spacing due to their soil-free system, resulting in higher crop density per square foot compared to soil-based containers. Soil-based containers require more room for root expansion and often need wider spacing to prevent nutrient competition and disease spread. Therefore, hydroponic systems optimize limited urban or indoor spaces, making them ideal for high-yield, compact agriculture setups.
Maintenance Requirements for Each System
Hydroponic containers demand consistent monitoring of nutrient levels, pH balance, and water quality to maintain optimal plant growth, requiring regular system checks and occasional cleaning to prevent algae and root diseases. Soil-based containers need frequent watering schedules, soil aeration, and periodic fertilization, with attention to pest control and drainage to sustain healthy root development. Both systems require tailored maintenance protocols, but hydroponics relies more on precise environmental control while soil containers depend on natural soil management practices.
Best Plants for Hydroponic and Soil-Based Containers
Hydroponic containers excel in growing leafy greens such as lettuce, spinach, and herbs like basil due to their controlled nutrient delivery and rapid growth rates. Soil-based containers are ideal for root vegetables like carrots, potatoes, and tomatoes, which benefit from the natural soil structure and microbial activity. Both systems support peppers and strawberries, but hydroponics offers enhanced growth speed and yield through precise nutrient management.
Choosing the Right Container System for Your Garden
Hydroponic containers offer precise control over nutrient delivery and water usage, promoting faster plant growth and higher yields compared to soil-based containers. Soil-based containers provide natural microbial activity and organic matter, enhancing root health and soil fertility with less setup complexity. Selecting the right container system depends on your garden's space, crop type, maintenance preferences, and desired growth speed.
Hydroponic containers vs soil-based containers Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com