
Pile composting vs Bin composting Illustration
Pile composting allows organic materials to decompose in large, open heaps, promoting aeration and faster breakdown through natural microbial activity. Bin composting contains waste within enclosed structures, minimizing pests and odors while maintaining moisture and temperature control for more efficient decomposition. Both methods convert organic waste into nutrient-rich compost but differ in space requirements, management ease, and suitability for urban or rural settings.
Table of Comparison
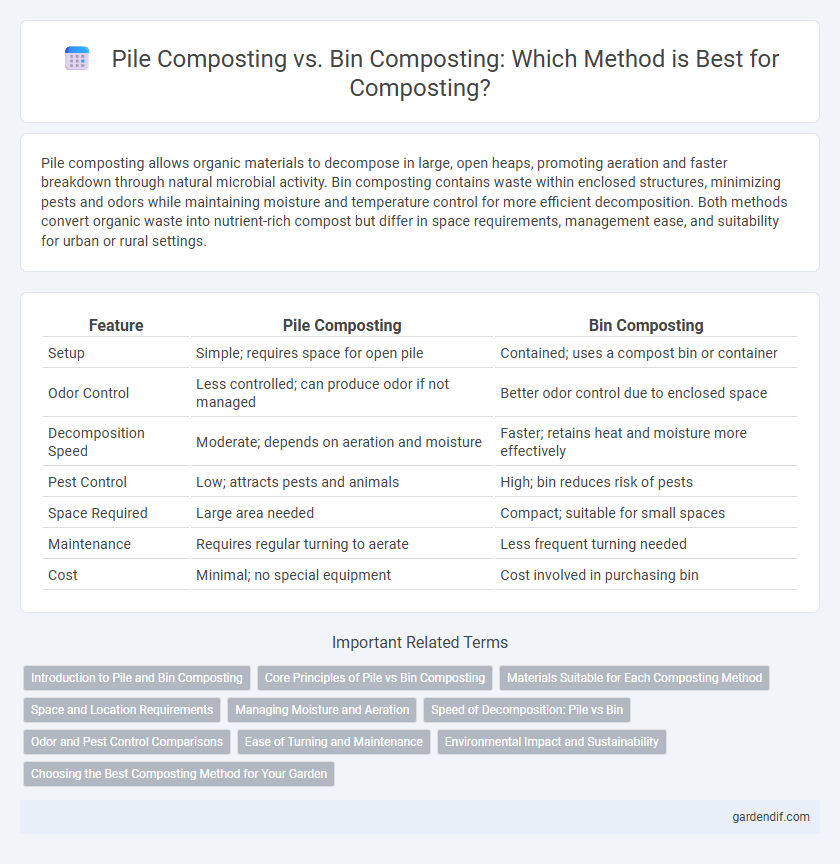
| Feature | Pile Composting | Bin Composting |
|---|---|---|
| Setup | Simple; requires space for open pile | Contained; uses a compost bin or container |
| Odor Control | Less controlled; can produce odor if not managed | Better odor control due to enclosed space |
| Decomposition Speed | Moderate; depends on aeration and moisture | Faster; retains heat and moisture more effectively |
| Pest Control | Low; attracts pests and animals | High; bin reduces risk of pests |
| Space Required | Large area needed | Compact; suitable for small spaces |
| Maintenance | Requires regular turning to aerate | Less frequent turning needed |
| Cost | Minimal; no special equipment | Cost involved in purchasing bin |
Introduction to Pile and Bin Composting
Pile composting involves creating large, open heaps of organic waste that decompose naturally through aerobic microbial activity, requiring occasional turning for aeration and moisture control. Bin composting uses enclosed containers designed to retain heat and moisture, accelerating the breakdown process while minimizing pests and odors. Both methods transform kitchen scraps, garden waste, and other biodegradable materials into nutrient-rich compost beneficial for soil health.
Core Principles of Pile vs Bin Composting
Pile composting relies on layering organic materials in large, open heaps to promote natural aeration and microbial activity, facilitating efficient decomposition through heat retention. Bin composting confines the materials within a container, enhancing moisture and temperature control while minimizing pests and odors. Both methods prioritize balanced carbon-to-nitrogen ratios, regular turning or aeration, and adequate moisture to sustain optimal microbial processes for nutrient-rich compost.
Materials Suitable for Each Composting Method
Pile composting efficiently accommodates large volumes of yard waste such as leaves, grass clippings, and branches, ideal for suburban and rural settings with ample space. Bin composting suits kitchen scraps, coffee grounds, and small garden waste, providing controlled aeration and moisture retention in confined urban environments. Both methods benefit from balancing greens (nitrogen-rich materials) and browns (carbon-rich materials) to optimize decomposition rates and nutrient-rich humus production.
Space and Location Requirements
Pile composting demands a spacious outdoor area with good air circulation to support efficient decomposition, making it ideal for larger gardens or farms. Bin composting requires less space and can be placed in confined areas such as patios or small backyards, offering more control over moisture and pests. Both methods need well-drained locations, but bins provide a neater, more contained environment suitable for urban or limited-space settings.
Managing Moisture and Aeration
Pile composting allows for natural aeration through regular turning, which helps maintain optimal oxygen levels and moisture balance essential for microbial activity. Bin composting provides a controlled environment that can better retain moisture but may require manual aeration through stirring to prevent anaerobic conditions. Effective moisture management in both methods involves monitoring for dampness comparable to a wrung-out sponge, ensuring decomposition proceeds efficiently without odors.
Speed of Decomposition: Pile vs Bin
Pile composting accelerates decomposition by allowing greater airflow and heat retention, which supports faster microbial activity. Bin composting tends to slow the process since confined spaces can restrict oxygen flow and moisture control. Optimal pile size and turning frequency directly impact the rapid breakdown of organic material compared to the often passive bin method.
Odor and Pest Control Comparisons
Pile composting often experiences more odor issues and pest attraction due to less controlled airflow and exposure. Bin composting provides better odor management and pest control by containing materials and limiting air and moisture fluctuations. Enclosed bins reduce access for rodents and insects, maintaining a cleaner composting environment.
Ease of Turning and Maintenance
Pile composting allows for easier turning and aeration due to its open structure, facilitating faster decomposition and simpler maintenance. Bin composting contains the material within a confined space, which can make turning more strenuous but helps in retaining heat and moisture effectively. Maintaining pile composts requires more space and regular monitoring to prevent nutrient loss, while bin systems are more compact and controlled, ideal for small areas and consistent upkeep.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Pile composting enhances aeration and heat retention, resulting in faster organic matter breakdown and reduced methane emissions compared to anaerobic landfill decomposition. Bin composting offers controlled conditions that minimize odor and pest attraction, promoting consistent nutrient recycling and preventing nutrient runoff into waterways. Both methods support soil health improvement and waste reduction, but pile composting's open system can increase carbon loss, while bin composting optimizes moisture retention, enhancing sustainability in urban environments.
Choosing the Best Composting Method for Your Garden
Pile composting offers greater volume capacity and faster decomposition for large garden waste, making it ideal for spacious outdoor areas. Bin composting provides a compact, pest-resistant solution with better moisture control, suitable for small gardens or urban settings. Selecting the best composting method depends on garden size, waste type, space availability, and ease of maintenance preferences.
Pile composting vs Bin composting Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com