
Home Composting vs Commercial Composting Illustration
Home composting allows individuals to recycle kitchen scraps and garden waste, promoting sustainability and reducing landfill use. Commercial composting operates on a larger scale, processing diverse organic materials more efficiently and producing nutrient-rich compost faster. Both methods contribute to waste reduction but differ in scale, speed, and the types of materials they can effectively handle.
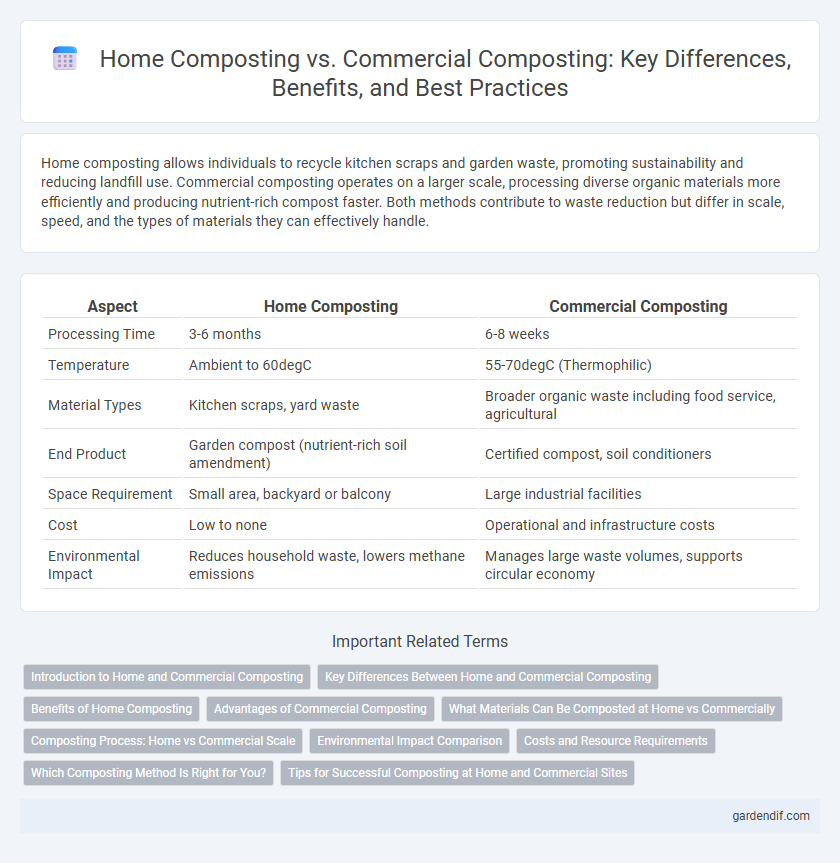
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Home Composting | Commercial Composting |
|---|---|---|
| Processing Time | 3-6 months | 6-8 weeks |
| Temperature | Ambient to 60degC | 55-70degC (Thermophilic) |
| Material Types | Kitchen scraps, yard waste | Broader organic waste including food service, agricultural |
| End Product | Garden compost (nutrient-rich soil amendment) | Certified compost, soil conditioners |
| Space Requirement | Small area, backyard or balcony | Large industrial facilities |
| Cost | Low to none | Operational and infrastructure costs |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces household waste, lowers methane emissions | Manages large waste volumes, supports circular economy |
Introduction to Home and Commercial Composting
Home composting involves the decomposition of organic waste using simple methods suitable for small-scale household environments, typically producing compost within a few months. Commercial composting utilizes advanced industrial processes that handle larger volumes of organic materials, including food scraps and yard waste, under controlled conditions to accelerate decomposition and eliminate pathogens. Both methods transform organic waste into nutrient-rich soil amendments but differ significantly in scale, processing time, and operational complexity.
Key Differences Between Home and Commercial Composting
Home composting involves decomposing organic waste in small batches using kitchen scraps, garden clippings, and biodegradable materials, typically yielding compost within 3 to 6 months. Commercial composting operates on an industrial scale, utilizing advanced temperature control (usually between 130degF and 160degF), aeration systems, and specialized equipment to break down a wider range of materials, including meat and dairy, in as little as 2 to 8 weeks. Key differences include scale, processing speed, temperature regulation, and variety of acceptable waste inputs, with commercial composting supporting higher efficiency and pathogen elimination.
Benefits of Home Composting
Home composting reduces household waste by recycling organic materials directly, decreasing landfill contributions and greenhouse gas emissions. It produces nutrient-rich compost that enhances soil health and supports sustainable gardening practices without the need for transportation or industrial processing. This method fosters environmental awareness and encourages eco-friendly habits at a personal level.
Advantages of Commercial Composting
Commercial composting processes organic waste at high temperatures, efficiently breaking down materials like meat, dairy, and synthetic fibers that home composting cannot handle safely. This method produces nutrient-rich compost on a large scale, supporting agricultural productivity and waste reduction goals more effectively than individual home systems. Centralized facilities also monitor and control environmental factors, ensuring consistent quality and reducing greenhouse gas emissions compared to decentralized home compost bins.
What Materials Can Be Composted at Home vs Commercially
Home composting typically accommodates organic kitchen scraps such as fruit and vegetable peels, coffee grounds, eggshells, and yard waste like grass clippings and leaves. Commercial composting facilities process a wider range of materials, including meat, dairy, bones, and treated wood, due to their higher temperature composting processes that eliminate pathogens. Understanding the types of materials suitable for each method optimizes decomposition efficiency and reduces contamination risks.
Composting Process: Home vs Commercial Scale
Home composting relies on aerobic decomposition of kitchen scraps and yard waste in small, controlled environments, typically taking several months to produce nutrient-rich humus. Commercial composting uses larger-scale, regulated processes with optimized temperature, moisture, and aeration, accelerating breakdown through thermophilic microbes within weeks. The enhanced conditions in commercial facilities ensure pathogen destruction and uniform compost quality, unlike home systems where temperature control is limited.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Home composting reduces organic waste locally, lowering methane emissions from landfills and minimizing transportation-related carbon footprints. Commercial composting facilities manage larger volumes with controlled conditions that accelerate decomposition and effectively process diverse materials, reducing greenhouse gas output on a broader scale. Comparing both, home composting offers lower immediate environmental impact through localized waste diversion, while commercial composting maximizes efficiency and scalability for substantial carbon footprint reduction.
Costs and Resource Requirements
Home composting requires minimal financial investment, typically involving basic tools like bins and garden waste, making it a cost-effective option for households. Commercial composting demands significant infrastructure, including specialized machinery and controlled environments, resulting in higher operational costs but enabling processing of larger volumes of organic waste efficiently. Resource requirements for home composting are limited to space and time commitment, whereas commercial facilities need substantial energy, labor, and technology to ensure faster decomposition and regulatory compliance.
Which Composting Method Is Right for You?
Home composting offers individuals control over organic waste recycling, producing nutrient-rich compost suitable for gardens, while commercial composting handles larger volumes and processes materials like meat and dairy that home systems cannot safely decompose. Factors such as available space, time commitment, type of waste generated, and desired compost quality influence the choice between home and commercial composting. Selecting the right method hinges on balancing convenience, waste type, and environmental impact to maximize organic waste diversion and soil enrichment.
Tips for Successful Composting at Home and Commercial Sites
Home composting thrives with regular turning, maintaining a balanced mix of green and brown materials, and moisture control to accelerate decomposition. Commercial composting benefits from larger-scale aeration systems, temperature monitoring, and systematic feedstock sorting to optimize breakdown and reduce contaminants. Both methods require consistent monitoring to ensure efficient organic waste recycling and nutrient-rich compost production.
Home Composting vs Commercial Composting Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com