
Continuous Composting vs Batch Composting Illustration
Continuous composting allows for the ongoing addition of organic materials, enabling a steady production of finished compost ideal for large-scale operations. Batch composting processes organic waste in separate, closed cycles, ensuring thorough decomposition before harvesting the compost, which is suited for small-scale or experimental setups. Both methods optimize nutrient recycling, but continuous composting offers greater efficiency in time and labor management.
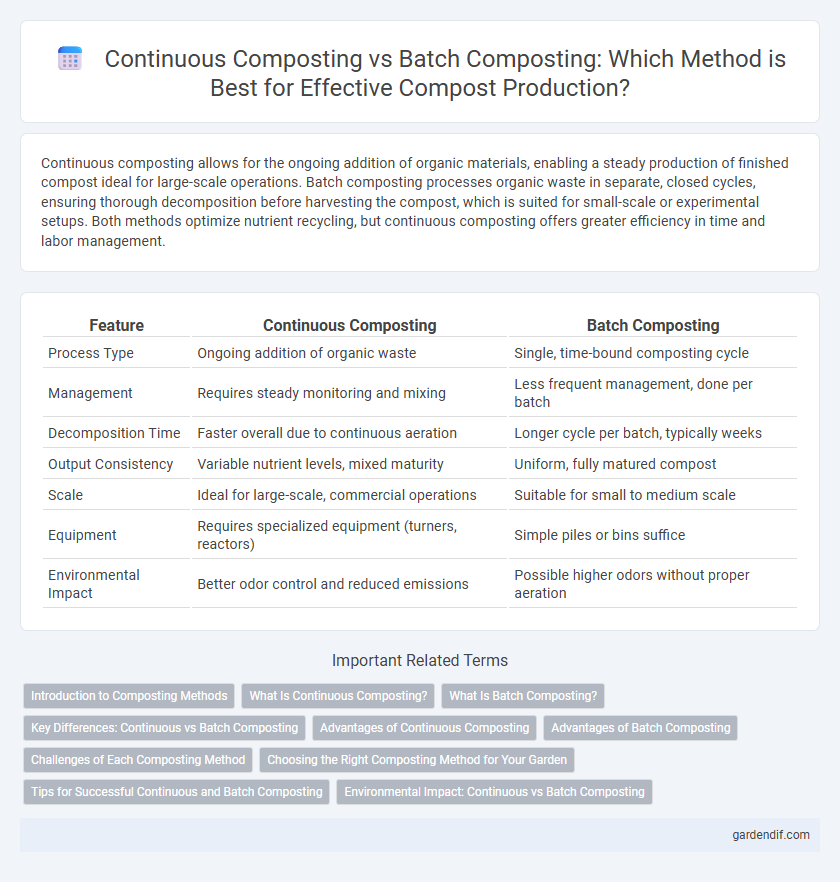
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Continuous Composting | Batch Composting |
|---|---|---|
| Process Type | Ongoing addition of organic waste | Single, time-bound composting cycle |
| Management | Requires steady monitoring and mixing | Less frequent management, done per batch |
| Decomposition Time | Faster overall due to continuous aeration | Longer cycle per batch, typically weeks |
| Output Consistency | Variable nutrient levels, mixed maturity | Uniform, fully matured compost |
| Scale | Ideal for large-scale, commercial operations | Suitable for small to medium scale |
| Equipment | Requires specialized equipment (turners, reactors) | Simple piles or bins suffice |
| Environmental Impact | Better odor control and reduced emissions | Possible higher odors without proper aeration |
Introduction to Composting Methods
Continuous composting enables ongoing addition of organic waste, promoting steady microbial activity and faster decomposition, ideal for large-scale or commercial operations. Batch composting processes a set volume of organic material at once, ensuring uniform conditions and thorough breakdown before the next batch begins, suited for smaller-scale or backyard composting. Both methods optimize nutrient recycling and waste reduction through controlled aerobic decomposition.
What Is Continuous Composting?
Continuous composting is a method where organic waste is added regularly to the compost pile, allowing ongoing decomposition without interruption. This process maintains optimal conditions for microbial activity, such as temperature and moisture, promoting faster and more efficient breakdown of materials. Continuous composting is ideal for managing large-scale waste streams due to its ability to handle steady input volume and reduce processing time.
What Is Batch Composting?
Batch composting involves loading a set amount of organic materials into a compost bin or pile, allowing the materials to decompose together over a defined period without adding new inputs. This method requires turning the compost periodically to aerate the pile and maintain optimal moisture and temperature levels, promoting efficient microbial activity. Batch composting is ideal for small-scale composters or gardeners seeking a straightforward, controlled decomposition process that yields nutrient-rich compost in a few months.
Key Differences: Continuous vs Batch Composting
Continuous composting allows for the ongoing addition of organic waste, promoting steady microbial activity and faster decomposition, while batch composting processes a fixed amount of material in a single cycle until fully decomposed. Continuous systems support constant temperature and moisture control, enhancing nutrient stability, whereas batch systems often experience fluctuating conditions impacting microbial efficiency. The choice between continuous and batch composting hinges on scale, input consistency, and desired processing speed, with continuous favored for large-scale operations and batch suited to small, manageable loads.
Advantages of Continuous Composting
Continuous composting offers a streamlined process with consistent feedstock input, enabling faster organic matter decomposition and steady production of nutrient-rich compost. This method reduces labor intensity by eliminating the need for periodic emptying and refilling, resulting in improved operational efficiency. Enhanced temperature control and microbial activity in continuous systems promote higher quality compost suitable for agricultural and horticultural applications.
Advantages of Batch Composting
Batch composting offers precise control over the composting process, enabling optimal temperature and moisture regulation for efficient organic matter breakdown. This method typically results in higher-quality, pathogen-free compost due to its ability to maintain thermophilic conditions for extended periods. Furthermore, batch composting facilitates easier monitoring and troubleshooting, reducing the risk of incomplete decomposition and odor issues.
Challenges of Each Composting Method
Continuous composting faces challenges like managing consistent aeration and moisture levels to prevent anaerobic conditions and odor issues, while batch composting struggles with longer processing times and space inefficiency due to the need for periodic turning and waiting for each batch to mature. Continuous systems require careful monitoring to maintain microbial activity balance, whereas batch methods risk incomplete decomposition if temperature fluctuations occur or if batches are not adequately mixed. Both methods demand tailored management strategies to optimize nutrient cycling and minimize environmental impacts such as leachate production or greenhouse gas emissions.
Choosing the Right Composting Method for Your Garden
Continuous composting provides a steady supply of nutrient-rich compost by adding organic waste daily, making it ideal for gardeners seeking ongoing soil enrichment. Batch composting involves processing a single, large pile of organic materials all at once, delivering compost in larger, less frequent quantities suited for seasonal or intensive garden use. Selecting between these methods depends on garden size, waste volume, and the desired timing of compost availability.
Tips for Successful Continuous and Batch Composting
Maintain optimal moisture levels and aeration by regularly turning the pile in batch composting to enhance microbial activity and speed up decomposition. For continuous composting, consistently add balanced green and brown materials while monitoring temperature to prevent odor issues and ensure steady breakdown of organic matter. Utilizing proper bin design with drainage and ventilation improves efficiency in both methods, supporting healthy microorganism populations and high-quality compost output.
Environmental Impact: Continuous vs Batch Composting
Continuous composting reduces greenhouse gas emissions by maintaining aerobic conditions and accelerating organic waste breakdown, minimizing methane production compared to batch composting. Batch composting often involves anaerobic pockets during initial phases, increasing methane and nitrous oxide emissions linked to climate change. Efficient aeration and moisture control in continuous systems enhance carbon-to-nitrogen ratio stability, promoting lower environmental impact through optimized microbial activity.
Continuous Composting vs Batch Composting Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com