
Backyard composting vs vermicomposting Illustration
Backyard composting efficiently breaks down kitchen scraps and yard waste through natural aerobic decomposition, producing nutrient-rich soil amendments for gardens. Vermicomposting uses worms to accelerate organic matter breakdown, resulting in highly concentrated, microbe-rich worm castings that enhance soil health. Both methods reduce landfill waste but vermicomposting requires less space and is faster for processing food scraps indoors.
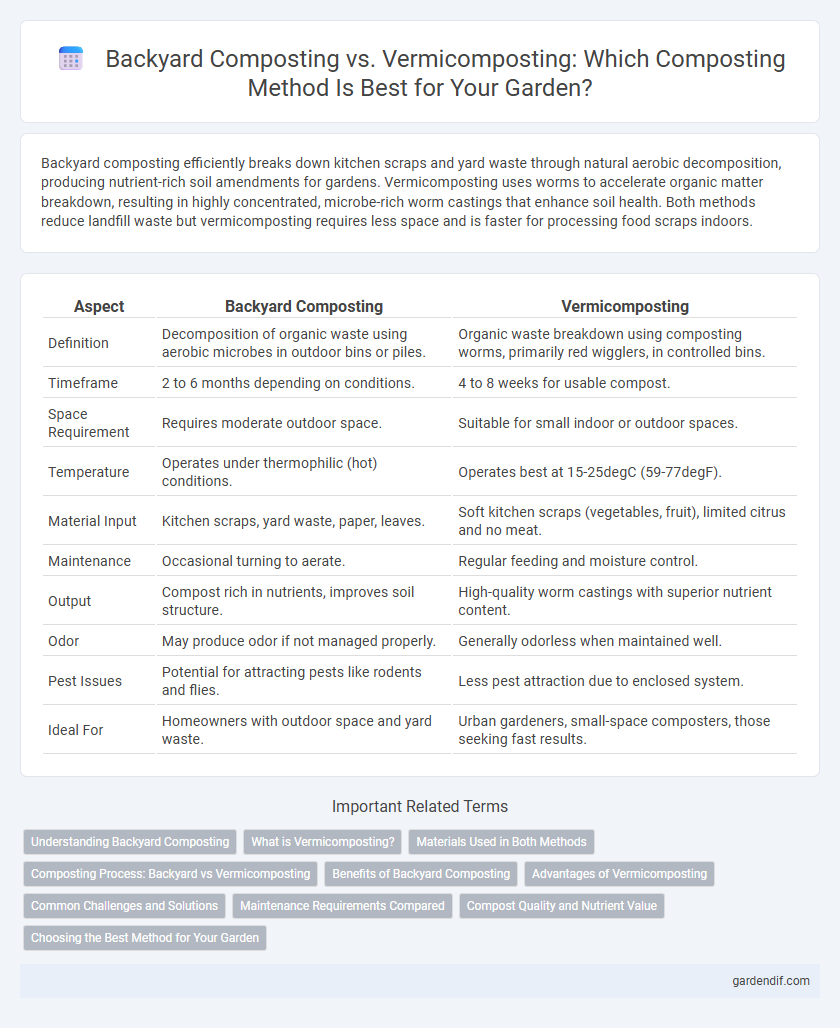
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Backyard Composting | Vermicomposting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Decomposition of organic waste using aerobic microbes in outdoor bins or piles. | Organic waste breakdown using composting worms, primarily red wigglers, in controlled bins. |
| Timeframe | 2 to 6 months depending on conditions. | 4 to 8 weeks for usable compost. |
| Space Requirement | Requires moderate outdoor space. | Suitable for small indoor or outdoor spaces. |
| Temperature | Operates under thermophilic (hot) conditions. | Operates best at 15-25degC (59-77degF). |
| Material Input | Kitchen scraps, yard waste, paper, leaves. | Soft kitchen scraps (vegetables, fruit), limited citrus and no meat. |
| Maintenance | Occasional turning to aerate. | Regular feeding and moisture control. |
| Output | Compost rich in nutrients, improves soil structure. | High-quality worm castings with superior nutrient content. |
| Odor | May produce odor if not managed properly. | Generally odorless when maintained well. |
| Pest Issues | Potential for attracting pests like rodents and flies. | Less pest attraction due to enclosed system. |
| Ideal For | Homeowners with outdoor space and yard waste. | Urban gardeners, small-space composters, those seeking fast results. |
Understanding Backyard Composting
Backyard composting utilizes aerobic decomposition of organic waste through microorganism activity in a controlled environment, producing nutrient-rich humus ideal for soil enrichment. This method accommodates a variety of compostable materials, including kitchen scraps, yard waste, and paper products, promoting sustainable waste reduction and soil health. Proper aeration, moisture control, and balance of green and brown materials are essential factors for efficient backyard compost breakdown and odor prevention.
What is Vermicomposting?
Vermicomposting is the process of using specific earthworms, usually red wigglers (Eisenia fetida), to decompose organic waste into nutrient-rich compost known as worm castings. This method accelerates the breakdown of kitchen scraps, paper, and garden waste while improving soil structure and fertility with beneficial microorganisms. Vermicomposting is ideal for small spaces and produces compost faster than traditional backyard composting techniques.
Materials Used in Both Methods
Backyard composting primarily uses a mix of green materials such as fruit and vegetable scraps, coffee grounds, and grass clippings, combined with brown materials like dry leaves, straw, and cardboard to maintain a balanced carbon-to-nitrogen ratio. Vermicomposting relies mainly on organic kitchen waste, paper products, and shredded cardboard, focusing on materials that are easily digestible by earthworms like red wigglers. Both methods avoid meat, dairy, and oily foods to prevent odors and pests, but vermicomposting requires finer, softer materials to support worm activity and maintain optimal moisture levels.
Composting Process: Backyard vs Vermicomposting
Backyard composting involves aerobic decomposition of organic waste through microbial activity, requiring regular turning to maintain oxygen levels and manage moisture. Vermicomposting utilizes specific earthworm species, such as Eisenia fetida, to accelerate the breakdown of organic matter, producing nutrient-rich castings with minimal odor and less space. Both methods recycle kitchen and garden waste into valuable soil amendments, but vermicomposting offers faster processing and higher nutrient retention.
Benefits of Backyard Composting
Backyard composting enriches soil with essential nutrients, improving plant growth and soil structure through natural decomposition of kitchen scraps and yard waste. It reduces household waste sent to landfills, cutting methane emissions and promoting environmental sustainability. This method requires minimal cost and effort, making it accessible for homeowners to create rich, organic compost efficiently.
Advantages of Vermicomposting
Vermicomposting accelerates organic waste decomposition through the activity of earthworms, resulting in nutrient-rich castings that enhance soil fertility and plant growth more effectively than backyard composting. It produces compost faster, typically within 2 to 3 months, compared to traditional methods that may take 6 months or longer. Vermicomposting systems operate efficiently in smaller spaces and generate minimal odor, making them ideal for urban or indoor environments.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Backyard composting often faces challenges such as slow decomposition and odor issues caused by improper balance of green and brown materials, which can be mitigated by regularly turning the pile and maintaining adequate aeration. Vermicomposting encounters difficulties like worm escape and moisture imbalance, solvable through careful temperature regulation and ensuring the bedding remains damp but not waterlogged. Both methods benefit from monitoring pH levels and avoiding non-compostable items to optimize nutrient-rich organic waste breakdown.
Maintenance Requirements Compared
Backyard composting requires regular turning and monitoring of moisture levels to ensure proper aeration and decomposition, often demanding more space and occasional temperature checks. Vermicomposting involves maintaining a stable environment with consistent moisture, temperature, and feeding of worms, typically needing less physical effort but consistent care to prevent odor and pests. Both methods benefit from routine attention, but vermicomposting generally involves lower daily maintenance and faster organic waste breakdown.
Compost Quality and Nutrient Value
Backyard composting produces nutrient-rich, organic matter with a balanced carbon-to-nitrogen ratio, supporting soil health and plant growth, though it may have longer decomposition times and less consistent nutrient profiles. Vermicomposting uses earthworms to accelerate decomposition, producing finely textured, high-quality worm castings that are rich in nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and beneficial microbes, resulting in superior nutrient value and improved soil fertility. Both methods enhance soil structure and nutrient availability, but vermicomposting typically yields faster, more nutrient-dense compost.
Choosing the Best Method for Your Garden
Backyard composting efficiently processes yard waste and fruit scraps into nutrient-rich soil, ideal for larger gardens with space and varied organic material. Vermicomposting uses earthworms to rapidly break down kitchen scraps into fine, high-quality humus, perfect for small spaces or indoor setups requiring odor control and faster nutrient cycling. Assess garden size, waste type, and composting goals to determine whether aerobic backyard heaps or worm-driven vermiculture best supports your plant growth and soil health.
Backyard composting vs vermicomposting Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com