
Shade gardening vs Full sun gardening Illustration
Shade gardening thrives in cooler, indirect light environments, supporting plants that require protection from intense sunlight and reducing water evaporation from soil. Full sun gardening demands plants that tolerate or prefer direct sunlight for at least six hours a day, promoting robust growth and vibrant blooms. Understanding the specific light needs and microclimate of your garden helps optimize plant health and water efficiency seasonally.
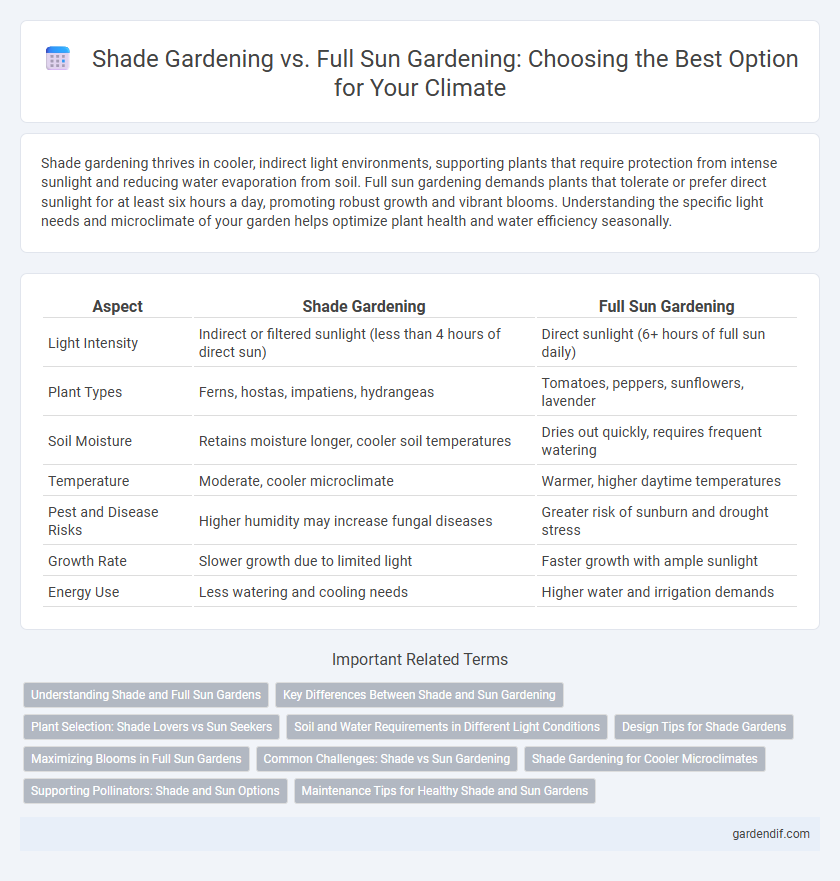
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Shade Gardening | Full Sun Gardening |
|---|---|---|
| Light Intensity | Indirect or filtered sunlight (less than 4 hours of direct sun) | Direct sunlight (6+ hours of full sun daily) |
| Plant Types | Ferns, hostas, impatiens, hydrangeas | Tomatoes, peppers, sunflowers, lavender |
| Soil Moisture | Retains moisture longer, cooler soil temperatures | Dries out quickly, requires frequent watering |
| Temperature | Moderate, cooler microclimate | Warmer, higher daytime temperatures |
| Pest and Disease Risks | Higher humidity may increase fungal diseases | Greater risk of sunburn and drought stress |
| Growth Rate | Slower growth due to limited light | Faster growth with ample sunlight |
| Energy Use | Less watering and cooling needs | Higher water and irrigation demands |
Understanding Shade and Full Sun Gardens
Shade gardening thrives in areas receiving less than four hours of direct sunlight daily, favoring plants like hostas, ferns, and astilbes that adapt to lower light levels and cooler soil. Full sun gardening requires at least six hours of uninterrupted sunlight, supporting sun-loving species such as tomatoes, lavender, and sunflowers that need intense light for optimal growth. Understanding the light requirements, soil moisture, and temperature variations is crucial for selecting appropriate plant species and ensuring a thriving garden environment in both shade and full sun conditions.
Key Differences Between Shade and Sun Gardening
Shade gardening thrives in low light environments, favoring plants like ferns, hostas, and impatiens that require minimal direct sunlight. Full sun gardening demands at least six hours of direct sunlight daily and suits sun-loving plants such as tomatoes, lavender, and marigolds that need intense light for photosynthesis. Soil moisture retention and temperature regulation differ significantly, with shade gardens typically cooler and more humid while sun gardens experience higher evaporation rates and warmer soil temperatures.
Plant Selection: Shade Lovers vs Sun Seekers
Shade gardening favors plants like hostas, ferns, and astilbes that thrive in low-light conditions and high humidity, adapting well to cooler microclimates. Full sun gardening requires sun-loving species such as tomatoes, lavender, and sunflowers, which need at least six hours of direct sunlight for optimal growth and flowering. Selecting plants based on their light tolerance ensures robust development, disease resistance, and sustained photosynthesis efficiency in diverse climate zones.
Soil and Water Requirements in Different Light Conditions
Shade gardening requires soil that retains moisture well, as lower light levels reduce evaporation and transpiration, allowing plants to thrive with less frequent watering. Full sun gardening demands well-draining soil to prevent waterlogging, coupled with more frequent irrigation to compensate for higher evaporation rates and soil drying under intense sunlight. Adjusting soil composition and watering schedules according to light conditions optimizes plant health and resource use efficiency in both shade and full sun gardens.
Design Tips for Shade Gardens
Shade gardening thrives with plants adapted to low-light conditions like hostas, ferns, and astilbes, creating lush, textured landscapes. Incorporate layers of various foliage shapes and shades of green to add depth and interest, while using reflective surfaces or light-colored mulch to brighten dim areas. Position shade-tolerant flowers strategically near walkways or seating areas to enhance color contrast and attract pollinators despite limited sunlight.
Maximizing Blooms in Full Sun Gardens
Full sun gardens provide optimal conditions for sun-loving plants such as sunflowers, marigolds, and lavender, which maximize bloom production through ample sunlight exposure. Selecting heat-tolerant and drought-resistant varieties enhances flower longevity and vibrancy in intense sunlight. Proper soil preparation and consistent watering further support robust growth and abundant blossoms in full sun settings.
Common Challenges: Shade vs Sun Gardening
Shade gardening often struggles with limited sunlight, which can lead to slower plant growth, increased moisture retention, and higher susceptibility to fungal diseases. Full sun gardening faces challenges such as intense heat, rapid soil drying, and higher water requirements, increasing the risk of plant stress and wilting. Both environments demand careful plant selection and irrigation management to optimize growth and minimize environmental stress factors.
Shade Gardening for Cooler Microclimates
Shade gardening thrives in cooler microclimates by utilizing plants adapted to lower light levels and reduced temperatures, which helps conserve moisture and reduce heat stress. Selecting shade-tolerant species such as ferns, hostas, and astilbes can optimize growth while minimizing water usage. Shade gardens create microhabitats that moderate temperature fluctuations, supporting biodiversity and enhancing climate resilience in hotter regions.
Supporting Pollinators: Shade and Sun Options
Shade gardening supports pollinators by providing cooler habitats and flowering plants like ferns, hostas, and impatiens that attract shade-tolerant bees and butterflies. Full sun gardening offers abundant nectar sources with sun-loving plants such as lavender, coneflowers, and milkweed, which are essential for bees, butterflies, and hummingbirds. Creating a diverse garden with both shade and sun options maximizes pollinator support by accommodating a wide range of pollinator species and their varying habitat needs.
Maintenance Tips for Healthy Shade and Sun Gardens
Shade gardens require regular monitoring of soil moisture and the use of mulch to retain humidity, preventing root dryness and promoting healthy plant growth. Full sun gardens benefit from deep watering early in the morning to reduce evaporation and heat stress, along with periodic fertilization to maintain nutrient levels. Both gardening styles demand tailored pruning techniques to enhance air circulation and prevent disease, ensuring vibrant and resilient plants.
Shade gardening vs Full sun gardening Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com