
Continental climate vs Maritime climate Illustration
Continental climates experience more extreme temperature variations with hot summers and cold winters due to their distance from large bodies of water. Maritime climates have milder temperatures year-round, influenced by the proximity to oceans which moderate seasonal changes. Precipitation patterns also vary, with maritime climates generally receiving more consistent rainfall compared to the often drier continental climates.
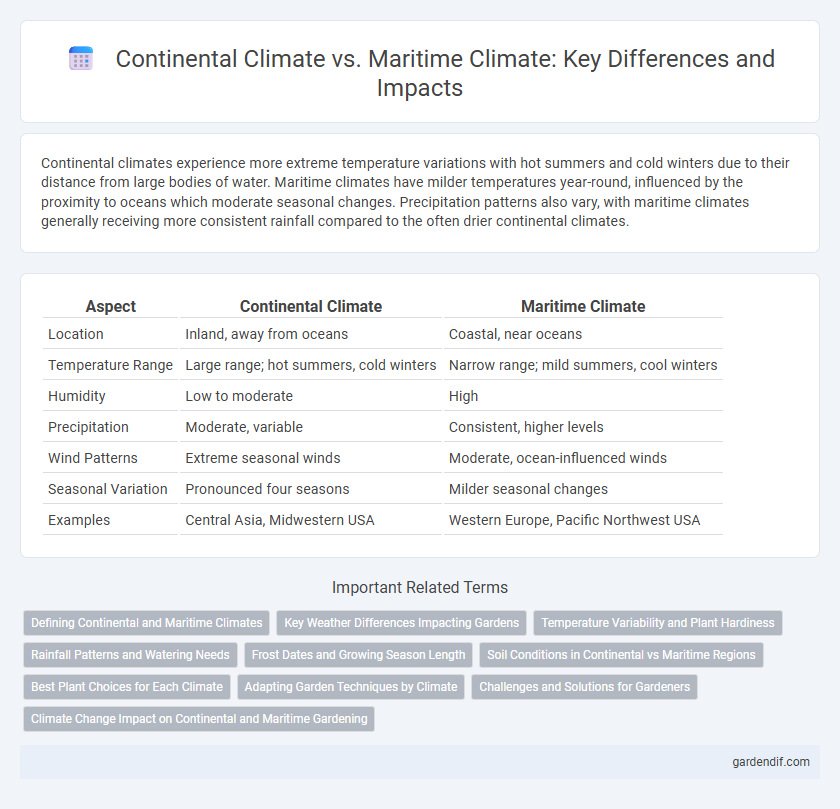
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Continental Climate | Maritime Climate |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Inland, away from oceans | Coastal, near oceans |
| Temperature Range | Large range; hot summers, cold winters | Narrow range; mild summers, cool winters |
| Humidity | Low to moderate | High |
| Precipitation | Moderate, variable | Consistent, higher levels |
| Wind Patterns | Extreme seasonal winds | Moderate, ocean-influenced winds |
| Seasonal Variation | Pronounced four seasons | Milder seasonal changes |
| Examples | Central Asia, Midwestern USA | Western Europe, Pacific Northwest USA |
Defining Continental and Maritime Climates
Continental climates are characterized by significant temperature variations between summer and winter due to their inland location, typically found in regions far from large water bodies. Maritime climates experience mild temperature fluctuations year-round because of the moderating influence of nearby oceans or seas, resulting in cooler summers and warmer winters. These distinct temperature patterns shape regional ecosystems and human activities, making the understanding of continental versus maritime climates essential for climate adaptation strategies.
Key Weather Differences Impacting Gardens
Continental climates feature hot summers and cold winters with significant temperature fluctuations that stress plant roots and shorten growing seasons. Maritime climates maintain mild temperatures year-round with higher humidity and stable rainfall, promoting consistent soil moisture and reducing drought stress in gardens. These key weather differences influence plant selection and care, as gardens in continental zones require drought-resistant species and frost protection, while maritime gardens thrive with moisture-loving, frost-sensitive plants.
Temperature Variability and Plant Hardiness
Continental climates exhibit high temperature variability with hot summers and cold winters, impacting plant hardiness by necessitating species that can withstand extreme temperature fluctuations. Maritime climates maintain moderate temperature ranges year-round, promoting greater plant diversity due to milder winter conditions and reduced frost risk. Understanding these climatic differences is crucial for agriculture and horticulture, as plant growth and survival directly depend on temperature stability and seasonal extremes.
Rainfall Patterns and Watering Needs
Continental climates experience more extreme seasonal temperature variations and typically receive lower annual rainfall, leading to irregular and often insufficient moisture for consistent watering needs. Maritime climates benefit from stable temperatures and higher, evenly distributed rainfall throughout the year, reducing supplemental irrigation requirements. Understanding these rainfall patterns is crucial for optimizing watering strategies in agriculture and landscaping depending on the climate zone.
Frost Dates and Growing Season Length
Continental climates exhibit a shorter growing season with later last frost dates in spring and earlier first frost dates in autumn compared to maritime climates. Maritime climates benefit from moderated temperatures due to proximity to large bodies of water, resulting in longer frost-free periods and extended growing seasons. Frost date variability in continental regions can significantly impact agriculture, while maritime regions typically experience more stable growing conditions.
Soil Conditions in Continental vs Maritime Regions
Continental climates typically feature soil with lower moisture content due to greater temperature fluctuations and reduced precipitation, resulting in drier and often more acidic soil conditions. Maritime climates benefit from higher humidity and consistent rainfall, producing soils rich in organic matter with better moisture retention and nutrient availability. These soil differences significantly influence vegetation types and agricultural practices in each region.
Best Plant Choices for Each Climate
Continental climates with their large temperature fluctuations are ideal for cold-hardy plants like maples, oaks, and perennial wildflowers that can withstand harsh winters and hot summers. Maritime climates offer milder, more stable temperatures and higher humidity, favoring moisture-loving plants such as rhododendrons, camellias, and ferns, which thrive in cool, damp environments. Selecting plants adapted to their respective temperature ranges and moisture levels ensures optimal growth and resilience in continental or maritime environments.
Adapting Garden Techniques by Climate
Garden techniques vary significantly between continental and maritime climates due to temperature extremes and humidity differences. In continental climates, gardeners prioritize drought-resistant plants and mulching to retain soil moisture during hot summers and insulating methods to protect roots from harsh winters. Conversely, maritime climates allow for a broader variety of moisture-loving plants, requiring well-draining soil and windbreaks to mitigate salty sea breezes and prevent root rot.
Challenges and Solutions for Gardeners
Continental climates present challenges such as extreme temperature fluctuations and shorter growing seasons, requiring gardeners to select hardy, cold-tolerant plant varieties and utilize protective measures like mulching and windbreaks. Maritime climates offer milder temperatures and consistent moisture but can lead to fungal diseases and root rot, prompting gardeners to improve soil drainage and choose disease-resistant plants. Implementing season extension techniques such as greenhouses and raised beds helps adapt gardening practices to both climate types.
Climate Change Impact on Continental and Maritime Gardening
Continental climates, characterized by greater temperature extremes and lower humidity, experience more pronounced stress from climate change effects such as increased drought frequency and heatwaves, impacting plant growth and requiring adaptive gardening practices like drought-resistant species and mulching. Maritime climates benefit from milder temperatures and higher humidity but face challenges from rising sea levels, saltwater intrusion, and altered precipitation patterns, demanding salt-tolerant plants and improved soil drainage techniques. Both climate types must address shifting seasonal patterns and invasive species proliferation, making climate-resilient horticulture essential for sustainable gardening in the face of global warming.
Continental climate vs Maritime climate Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com