
Hardiness Zone vs Sunset Zone Illustration
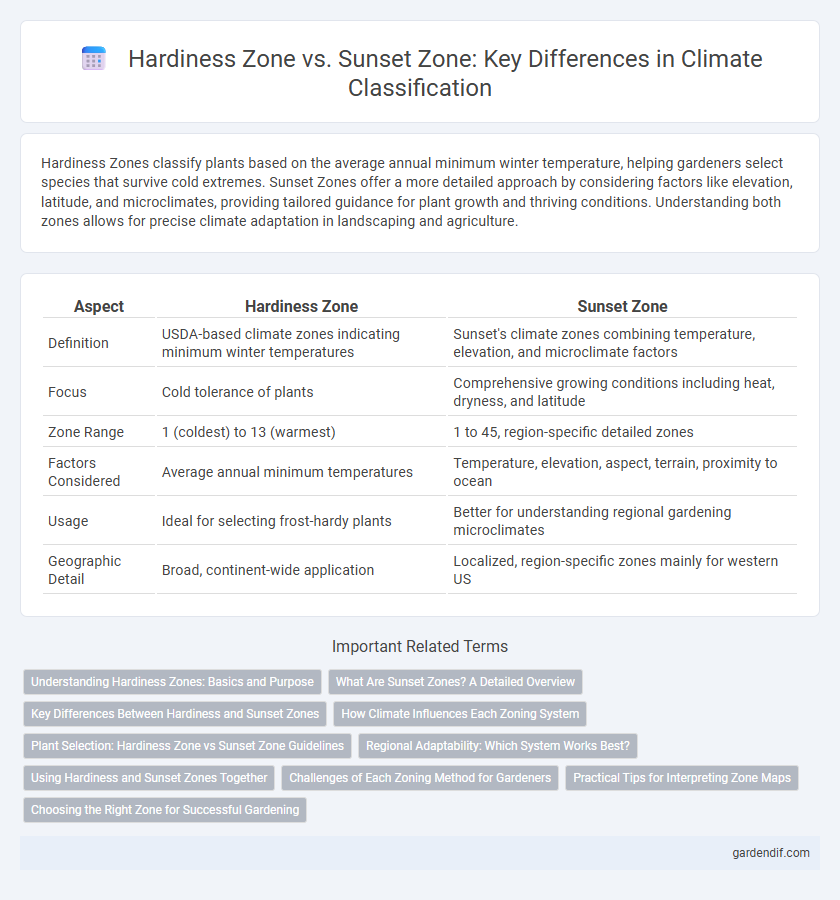
Hardiness Zones classify plants based on the average annual minimum winter temperature, helping gardeners select species that survive cold extremes. Sunset Zones offer a more detailed approach by considering factors like elevation, latitude, and microclimates, providing tailored guidance for plant growth and thriving conditions. Understanding both zones allows for precise climate adaptation in landscaping and agriculture.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Hardiness Zone | Sunset Zone |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | USDA-based climate zones indicating minimum winter temperatures | Sunset's climate zones combining temperature, elevation, and microclimate factors |
| Focus | Cold tolerance of plants | Comprehensive growing conditions including heat, dryness, and latitude |
| Zone Range | 1 (coldest) to 13 (warmest) | 1 to 45, region-specific detailed zones |
| Factors Considered | Average annual minimum temperatures | Temperature, elevation, aspect, terrain, proximity to ocean |
| Usage | Ideal for selecting frost-hardy plants | Better for understanding regional gardening microclimates |
| Geographic Detail | Broad, continent-wide application | Localized, region-specific zones mainly for western US |
Understanding Hardiness Zones: Basics and Purpose
Hardiness zones classify regions based on minimum winter temperatures to guide plant selection and ensure survival through cold seasons. These zones help gardeners and farmers determine which plants are most likely to thrive in their specific climatic conditions, minimizing crop failure and maximizing growth success. Unlike Sunset Zones, which consider a broader range of environmental factors like temperature ranges, elevation, and microclimates, hardiness zones focus solely on temperature thresholds critical for plant cold tolerance.
What Are Sunset Zones? A Detailed Overview
Sunset Zones are a unique climate classification system developed by Sunset Magazine that considers a combination of geographical factors including latitude, elevation, ocean influence, and rainfall patterns, providing more effective gardening guidance than traditional USDA Hardiness Zones. Unlike Hardiness Zones, which focus primarily on average minimum winter temperatures, Sunset Zones capture seasonal weather variation, soil types, and microclimates to help gardeners select plants best suited to specific regional conditions. This comprehensive approach makes Sunset Zones highly valuable for optimizing plant health, growth, and sustainability across diverse climates in North America.
Key Differences Between Hardiness and Sunset Zones
Hardiness Zones classify regions based on average annual minimum winter temperatures, guiding plant cold tolerance, while Sunset Zones incorporate local climate nuances such as elevation, proximity to coastlines, and microclimates, offering more detailed gardening insights. Sunset Zones are divided into 45 distinct categories reflecting regional climate variations throughout the year, whereas Hardiness Zones use a simpler 13-zone system based solely on temperature thresholds. This makes Sunset Zones more precise for selecting plants that thrive in specific environmental conditions beyond just cold tolerance.
How Climate Influences Each Zoning System
Hardiness Zones primarily consider average annual minimum winter temperatures, providing guidance on plant survival during cold periods, while Sunset Zones integrate additional climate factors such as temperature fluctuations, humidity, rainfall patterns, and microclimates to offer a more nuanced perspective for gardeners. Climate influences Hardiness Zones by defining the extreme low-temperature thresholds that determine plant hardiness, whereas Sunset Zones reflect a broader spectrum of climatic conditions that affect plant growth cycles and stress tolerance. Understanding these differing climatic influences enables more precise plant selection and landscape planning tailored to specific regional environments.
Plant Selection: Hardiness Zone vs Sunset Zone Guidelines
Hardiness Zones classify regions based on minimum winter temperatures, guiding gardeners on the cold tolerance of plants. Sunset Zones provide a more detailed climate profile by considering factors like temperature ranges, day length, and elevation, offering localized planting advice. Choosing plants using Sunset Zone guidelines often results in better growth and survival compared to relying solely on Hardiness Zones.
Regional Adaptability: Which System Works Best?
Hardiness Zones are primarily based on minimum winter temperatures, offering a general guide to plant survival in cold climates, while Sunset Zones incorporate a broader range of climatic factors including temperature, precipitation, and humidity, tailored to specific regions. Regional adaptability favors Sunset Zones in diverse climates like the western United States, where microclimates significantly affect plant growth. In contrast, Hardiness Zones remain useful for broader, temperature-centric regions, making Sunset Zones more effective for precise gardening decisions in varied environments.
Using Hardiness and Sunset Zones Together
Using Hardiness Zones alongside Sunset Zones provides a comprehensive understanding of plant suitability by combining minimum temperature data with microclimate factors such as sun exposure, wind, and humidity. Hardiness Zones, defined by USDA based on average annual minimum winter temperatures, help determine plant survival in cold temperatures, while Sunset Zones consider regional climate variations and local weather patterns, offering more precise gardening guidance. Integrating both systems allows gardeners to select plants that thrive in their specific environment, optimizing growth and resilience.
Challenges of Each Zoning Method for Gardeners
Hardiness Zones primarily gauge average minimum winter temperatures, limiting their ability to reflect microclimates and seasonal variations that affect plant survival. Sunset Zones incorporate factors like latitude, elevation, and rainfall, offering a nuanced climate profile but complicating plant selection due to overlapping zones. Gardeners must navigate these challenges by combining both systems with local knowledge to optimize plant health and garden longevity.
Practical Tips for Interpreting Zone Maps
Hardiness Zone maps are based primarily on average annual minimum winter temperatures, helping gardeners select plants that survive cold winters, while Sunset Zone maps incorporate additional factors such as temperature ranges, elevation, rainfall patterns, and microclimates, offering a more detailed guide for regional gardening. When interpreting these maps, prioritize Sunset Zones for nuanced climate understanding, especially in transitional areas, since they reflect local environmental variations beyond just temperature lows. Cross-referencing both maps ensures a comprehensive approach to plant selection by combining cold tolerance with broader climate adaptability.
Choosing the Right Zone for Successful Gardening
Hardiness Zones classify regions based on average annual minimum temperatures, guiding plant selection for cold tolerance, while Sunset Zones incorporate additional climatic factors such as elevation, rainfall, and wind patterns for more precise gardening success. Selecting the appropriate zone involves understanding both temperature extremes and local microclimates to match plants with their ideal growing conditions. Utilizing Sunset Zones alongside Hardiness Zones enhances accuracy in predicting plant performance and optimizing garden productivity.
Hardiness Zone vs Sunset Zone Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com