
Humidity control vs Ventilation Illustration
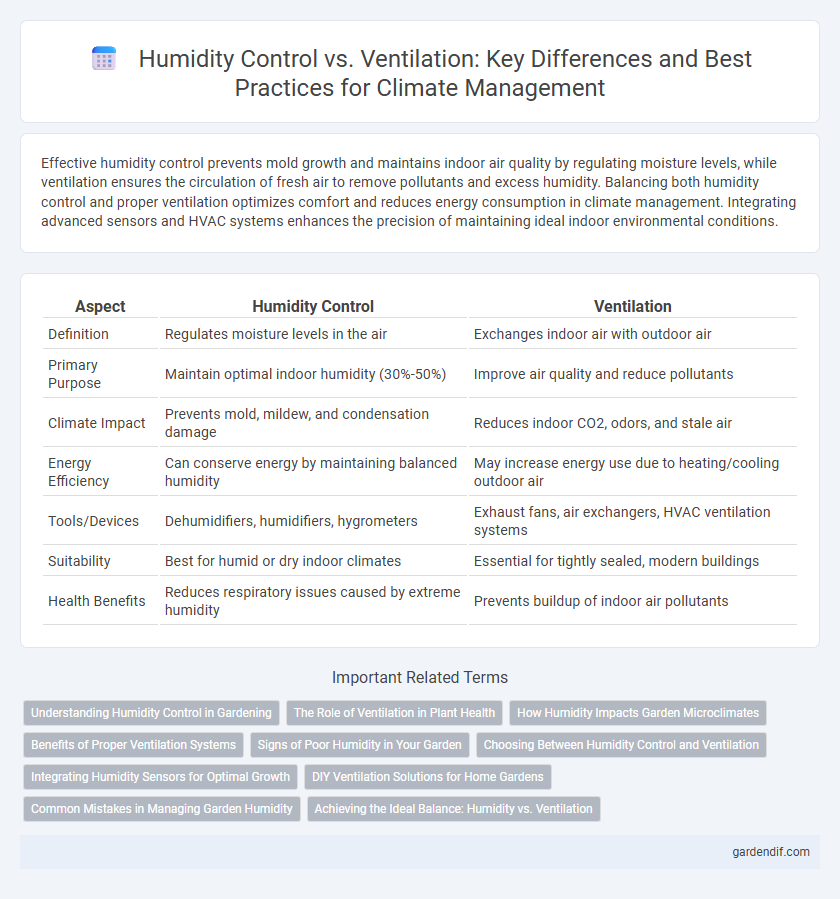
Effective humidity control prevents mold growth and maintains indoor air quality by regulating moisture levels, while ventilation ensures the circulation of fresh air to remove pollutants and excess humidity. Balancing both humidity control and proper ventilation optimizes comfort and reduces energy consumption in climate management. Integrating advanced sensors and HVAC systems enhances the precision of maintaining ideal indoor environmental conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Humidity Control | Ventilation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Regulates moisture levels in the air | Exchanges indoor air with outdoor air |
| Primary Purpose | Maintain optimal indoor humidity (30%-50%) | Improve air quality and reduce pollutants |
| Climate Impact | Prevents mold, mildew, and condensation damage | Reduces indoor CO2, odors, and stale air |
| Energy Efficiency | Can conserve energy by maintaining balanced humidity | May increase energy use due to heating/cooling outdoor air |
| Tools/Devices | Dehumidifiers, humidifiers, hygrometers | Exhaust fans, air exchangers, HVAC ventilation systems |
| Suitability | Best for humid or dry indoor climates | Essential for tightly sealed, modern buildings |
| Health Benefits | Reduces respiratory issues caused by extreme humidity | Prevents buildup of indoor air pollutants |
Understanding Humidity Control in Gardening
Effective humidity control in gardening maintains optimal moisture levels, preventing fungal growth and promoting plant health. Ventilation regulates airflow, helping to reduce excess humidity and stabilize temperature, but without precise humidity control, plants risk stress from fluctuating moisture. Combining targeted humidity control with proper ventilation ensures a balanced environment that supports photosynthesis and prevents disease.
The Role of Ventilation in Plant Health
Ventilation plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal plant health by regulating humidity levels and preventing the buildup of excess moisture that can lead to mold and fungal diseases. Proper air circulation enhances transpiration, promoting stronger cell structure and nutrient uptake in plants. Effective ventilation systems ensure a balanced microclimate, reducing the risk of pest infestations and improving overall plant growth and yield.
How Humidity Impacts Garden Microclimates
Humidity control directly influences garden microclimates by regulating moisture levels essential for plant health and disease prevention. Excessive humidity creates favorable conditions for fungal growth and pest infestations, while inadequate moisture can stress plants and reduce photosynthesis efficiency. Ventilation enhances air circulation, mitigating high humidity zones and stabilizing temperature fluctuations to maintain an optimal microclimate for diverse plant species.
Benefits of Proper Ventilation Systems
Proper ventilation systems significantly reduce indoor humidity levels, preventing mold growth and improving air quality by removing excess moisture and pollutants. They enhance thermal comfort by regulating indoor temperature and promoting air circulation, which reduces reliance on air conditioning and lowers energy costs. Effective ventilation also protects building structures from moisture damage, extending their lifespan and ensuring a healthier living environment.
Signs of Poor Humidity in Your Garden
Wilting leaves, mold growth, and persistent dampness are clear signs of poor humidity control in your garden. Insufficient ventilation exacerbates these issues by trapping moisture, creating an environment conducive to fungal diseases and pest infestations. Proper balance between humidity management and adequate airflow is essential for maintaining plant health and preventing damage.
Choosing Between Humidity Control and Ventilation
Choosing between humidity control and ventilation depends on the specific climate and indoor air quality needs. Humidity control systems regulate moisture levels to prevent mold growth and maintain comfort, while ventilation ensures a continuous supply of fresh air to reduce pollutants and carbon dioxide buildup. In environments with high moisture or risk of condensation, prioritizing humidity control is essential, whereas areas with poor air circulation require enhanced ventilation strategies.
Integrating Humidity Sensors for Optimal Growth
Integrating humidity sensors with ventilation systems enhances climate control by providing precise real-time data to adjust airflow and maintain optimal moisture levels for plant growth. Proper humidity regulation prevents fungal diseases and promotes transpiration, which is critical for photosynthesis and nutrient absorption. Combining sensor-driven humidity control with ventilation ensures a stable environment, optimizing crop yield and energy efficiency.
DIY Ventilation Solutions for Home Gardens
DIY ventilation solutions for home gardens improve air circulation, reducing excess humidity that can lead to mold and plant diseases. Simple setups, such as installing exhaust fans or creating passive vents, help maintain optimal moisture levels and promote healthy plant growth. Effective ventilation balances humidity control by preventing stagnant air and ensuring fresh oxygen flow throughout the garden space.
Common Mistakes in Managing Garden Humidity
Common mistakes in managing garden humidity include relying solely on ventilation without considering ambient moisture levels, which can lead to inconsistent humidity and stressed plants. Overventilating during high humidity periods fails to reduce moisture effectively and may cause temperature fluctuations harmful to garden health. Ignoring soil moisture monitoring while adjusting air humidity often results in poor humidity control and garden disease proliferation.
Achieving the Ideal Balance: Humidity vs. Ventilation
Achieving the ideal balance between humidity control and ventilation is essential for maintaining indoor air quality and comfort. Proper humidity control prevents mold growth and condensation, while effective ventilation removes excess moisture and pollutants, promoting a healthier environment. Integrating precise humidity sensors with adjustable ventilation systems enables optimal climate management tailored to varying outdoor and indoor conditions.
Humidity control vs Ventilation Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com