
Rain garden vs Xeriscape Illustration
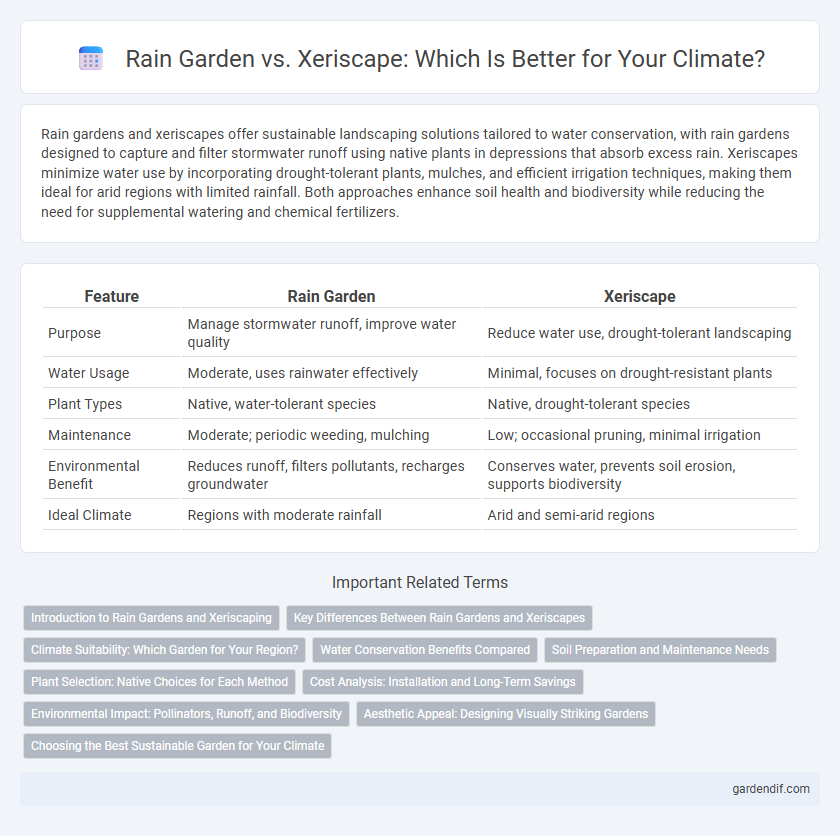
Rain gardens and xeriscapes offer sustainable landscaping solutions tailored to water conservation, with rain gardens designed to capture and filter stormwater runoff using native plants in depressions that absorb excess rain. Xeriscapes minimize water use by incorporating drought-tolerant plants, mulches, and efficient irrigation techniques, making them ideal for arid regions with limited rainfall. Both approaches enhance soil health and biodiversity while reducing the need for supplemental watering and chemical fertilizers.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Rain Garden | Xeriscape |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Manage stormwater runoff, improve water quality | Reduce water use, drought-tolerant landscaping |
| Water Usage | Moderate, uses rainwater effectively | Minimal, focuses on drought-resistant plants |
| Plant Types | Native, water-tolerant species | Native, drought-tolerant species |
| Maintenance | Moderate; periodic weeding, mulching | Low; occasional pruning, minimal irrigation |
| Environmental Benefit | Reduces runoff, filters pollutants, recharges groundwater | Conserves water, prevents soil erosion, supports biodiversity |
| Ideal Climate | Regions with moderate rainfall | Arid and semi-arid regions |
Introduction to Rain Gardens and Xeriscaping
Rain gardens are designed landscapes that capture and absorb stormwater, reducing runoff and improving water quality by utilizing native plants and engineered soils. Xeriscaping emphasizes water conservation through drought-tolerant plants, mulching, and efficient irrigation methods to minimize outdoor water use in arid climates. Both rain gardens and xeriscapes contribute to sustainable landscaping by enhancing ecosystem resilience and supporting climate adaptation efforts.
Key Differences Between Rain Gardens and Xeriscapes
Rain gardens are designed to capture and filter stormwater runoff using native, water-tolerant plants, enhancing groundwater recharge and reducing pollution. Xeriscapes emphasize water conservation by incorporating drought-resistant, low-maintenance vegetation adapted to arid conditions, minimizing irrigation needs. While both practices promote sustainable landscaping, rain gardens primarily manage excess water, whereas xeriscapes focus on reducing water consumption in dry climates.
Climate Suitability: Which Garden for Your Region?
Rain gardens are ideal for regions with moderate to heavy rainfall, effectively managing stormwater runoff and reducing flooding risk. Xeriscape is best suited for arid or drought-prone climates, emphasizing water conservation through drought-tolerant plants and minimal irrigation. Selecting between a rain garden and xeriscape depends on local precipitation patterns, soil composition, and water availability.
Water Conservation Benefits Compared
Rain gardens enhance water conservation by capturing and infiltrating stormwater, reducing runoff, and replenishing groundwater, making them highly effective in urban areas prone to flooding. Xeriscaping minimizes water use by utilizing drought-resistant plants and efficient irrigation techniques, significantly lowering outdoor water consumption in arid and semi-arid climates. Compared to rain gardens, xeriscapes offer more consistent long-term water savings, especially in regions with limited rainfall, while rain gardens provide critical stormwater management during heavy precipitation events.
Soil Preparation and Maintenance Needs
Rain gardens require well-drained soil amended with organic matter to promote infiltration and support diverse plant roots, while xeriscape landscaping demands soil preparation that enhances moisture retention through mulching and selecting drought-tolerant, deep-rooted plants. Maintenance for rain gardens involves regular removal of invasive species and monitoring for soil erosion to maintain water absorption efficiency, whereas xeriscaping necessitates minimal irrigation, pruning of drought-resistant plants, and occasional replenishment of mulch to conserve soil moisture. Both approaches contribute to sustainable water management but differ significantly in soil conditioning techniques and upkeep routines designed for specific hydrological environments.
Plant Selection: Native Choices for Each Method
Rain garden plant selection emphasizes native species that tolerate periodic flooding and wet soil, such as swamp milkweed (Asclepias incarnata) and blue flag iris (Iris versicolor). Xeriscape landscaping relies on drought-resistant natives like purple coneflower (Echinacea purpurea) and little bluestem grass (Schizachyrium scoparium) to minimize water use while thriving in arid conditions. Both methods prioritize ecological compatibility by choosing indigenous plants suited to their unique moisture requirements, enhancing biodiversity and reducing maintenance needs.
Cost Analysis: Installation and Long-Term Savings
Rain gardens typically require moderate installation costs due to soil excavation and plant selection, but they provide significant long-term savings by reducing stormwater runoff and lowering municipal water treatment expenses. Xeriscaping involves higher upfront costs for drought-tolerant plants and specialized irrigation systems, yet it minimizes water usage, leading to substantial reductions in water bills and maintenance expenses over time. Both landscaping methods contribute to climate resilience, but xeriscapes offer greater financial efficiency in arid regions where water conservation is critical.
Environmental Impact: Pollinators, Runoff, and Biodiversity
Rain gardens enhance environmental impact by improving pollinator habitats, reducing stormwater runoff, and increasing local biodiversity through diverse native plantings that support wildlife. Xeriscapes minimize water usage significantly, mitigating drought stress while providing limited but crucial shelter for drought-tolerant pollinators, and reducing runoff through permeable planting schemes. Selecting between rain gardens and xeriscapes depends on regional climate conditions and water availability, balancing ecosystem benefits with sustainable landscape water management.
Aesthetic Appeal: Designing Visually Striking Gardens
Rain gardens enhance aesthetic appeal by incorporating lush, native plants and vibrant flowers that thrive in moist conditions, creating a dynamic and colorful landscape. Xeriscape designs emphasize striking textures and drought-tolerant plants such as succulents and ornamental grasses, offering a minimalist yet visually captivating garden with low water use. Both approaches provide eco-friendly beauty, but rain gardens highlight seasonal blooms and water features, while xeriscapes focus on structural form and resilience.
Choosing the Best Sustainable Garden for Your Climate
Rain gardens efficiently manage stormwater by capturing runoff and promoting groundwater recharge, making them ideal for regions with moderate to high rainfall. Xeriscape landscaping minimizes water use by incorporating drought-tolerant plants and mulch, perfectly suited for arid or drought-prone climates. Selecting the best sustainable garden depends on local precipitation patterns, soil type, and native vegetation to optimize water conservation and ecological benefits.
Rain garden vs Xeriscape Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com