USDA Hardiness Zones vs Sunset Zones Illustration
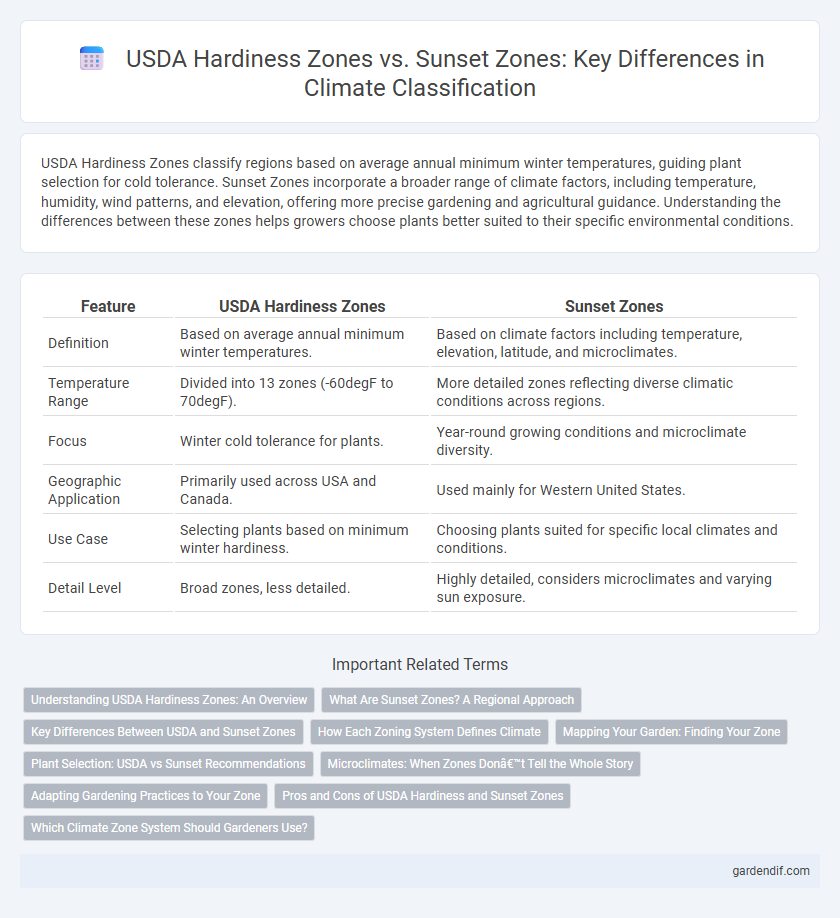
USDA Hardiness Zones classify regions based on average annual minimum winter temperatures, guiding plant selection for cold tolerance. Sunset Zones incorporate a broader range of climate factors, including temperature, humidity, wind patterns, and elevation, offering more precise gardening and agricultural guidance. Understanding the differences between these zones helps growers choose plants better suited to their specific environmental conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | USDA Hardiness Zones | Sunset Zones |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Based on average annual minimum winter temperatures. | Based on climate factors including temperature, elevation, latitude, and microclimates. |
| Temperature Range | Divided into 13 zones (-60degF to 70degF). | More detailed zones reflecting diverse climatic conditions across regions. |
| Focus | Winter cold tolerance for plants. | Year-round growing conditions and microclimate diversity. |
| Geographic Application | Primarily used across USA and Canada. | Used mainly for Western United States. |
| Use Case | Selecting plants based on minimum winter hardiness. | Choosing plants suited for specific local climates and conditions. |
| Detail Level | Broad zones, less detailed. | Highly detailed, considers microclimates and varying sun exposure. |
Understanding USDA Hardiness Zones: An Overview
USDA Hardiness Zones categorize regions based on average annual minimum winter temperatures, aiding gardeners in selecting plants suited to survive local cold conditions. These zones range from 1 to 13, with lower numbers indicating colder climates and higher numbers indicating warmer ones. Understanding USDA Hardiness Zones helps predict plant resilience and optimize garden planning for climate-specific survival.
What Are Sunset Zones? A Regional Approach
Sunset Zones provide a detailed regional approach to climate classification by considering factors such as elevation, proximity to oceans, and microclimates, unlike USDA Hardiness Zones which focus primarily on average minimum winter temperatures. These zones help gardeners and landscapers select plants that are better adapted to local environmental conditions, promoting healthier growth and sustainability. By integrating data on seasonal weather patterns and geographical nuances, Sunset Zones offer a more comprehensive guide for successful regional planting decisions.
Key Differences Between USDA and Sunset Zones
USDA Hardiness Zones classify regions based on average annual minimum winter temperatures, providing gardeners with guidance on plant cold tolerance. Sunset Zones incorporate a more complex range of climate factors, including temperature, humidity, rainfall, and wind patterns, reflecting local microclimates more accurately. This multidimensional approach in Sunset Zones offers a finer scale for selecting suitable plants compared to the temperature-focused USDA system.
How Each Zoning System Defines Climate
USDA Hardiness Zones categorize climate based on average annual minimum winter temperatures, providing a clear guide for plant survival during cold periods. Sunset Zones incorporate a broader range of factors including temperature, precipitation, wind patterns, humidity, and elevation, offering a more detailed and localized climate profile. Each system's unique approach affects gardening and agricultural decisions by emphasizing different climate variables essential for plant growth.
Mapping Your Garden: Finding Your Zone
USDA Hardiness Zones categorize regions based on minimum winter temperatures, providing gardeners with essential information for plant survival through cold seasons. Sunset Zones incorporate additional climate factors such as elevation, latitude, ocean influence, and seasonal temperature variations, offering a more detailed and localized gardening guide. Mapping your garden using both USDA and Sunset Zones ensures accurate plant selection tailored to the complexities of your specific regional climate.
Plant Selection: USDA vs Sunset Recommendations
USDA Hardiness Zones categorize plants based on average annual minimum winter temperatures, helping gardeners select species suitable for cold tolerance. Sunset Zones incorporate climate factors beyond temperature, including elevation, rainfall, and microclimates, offering a more nuanced guide for plant selection. Combining USDA and Sunset recommendations enables more precise landscaping choices tailored to both temperature extremes and local environmental conditions.
Microclimates: When Zones Don’t Tell the Whole Story
USDA Hardiness Zones categorize regions based on average annual minimum temperatures, providing a general guide for plant survival, but they often overlook localized temperature variations caused by microclimates. Sunset Zones incorporate factors like latitude, elevation, proximity to the coast, and seasonal temperature shifts, offering a more nuanced understanding of climate influences on plant growth. Microclimates created by features such as buildings, bodies of water, and terrain can significantly impact temperature and moisture levels, making Sunset Zones more reliable for gardeners aiming to match plants with precise environmental conditions.
Adapting Gardening Practices to Your Zone
USDA Hardiness Zones classify regions based on average winter temperatures, guiding plant selection for cold tolerance, while Sunset Zones incorporate a broader range of climate factors such as elevation, rainfall, and microclimates, offering more precise gardening guidance. Adapting gardening practices to your zone involves choosing plants suited not only to minimum temperatures but also to local environmental conditions reflected in Sunset Zones. Utilizing Sunset Zones can enhance plant survival and growth by matching species to specific regional climates beyond temperature alone.
Pros and Cons of USDA Hardiness and Sunset Zones
USDA Hardiness Zones provide detailed temperature-based climate data ideal for selecting plants based on minimum winter temperatures, ensuring survival during cold spells. Sunset Zones incorporate additional factors like microclimates, coastal influences, and elevation, offering a more comprehensive guide for plant adaptability in varied environments, but their complexity can make them harder to interpret. While USDA zones are widely recognized and simple, they may overlook local climate nuances that Sunset Zones capture, leading to better tailored gardening decisions.
Which Climate Zone System Should Gardeners Use?
USDA Hardiness Zones categorize regions based on average annual minimum winter temperatures, guiding gardeners on plant cold tolerance. Sunset Zones incorporate temperature ranges, precipitation patterns, elevation, and microclimates, offering a more nuanced approach tailored to West Coast and diverse U.S. regions. Gardeners seeking precise planting guidance should use Sunset Zones for comprehensive climate factors, while USDA Zones remain useful for general cold-hardiness information.
USDA Hardiness Zones vs Sunset Zones Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com