
El Niño patterns vs La Niña patterns Illustration
El Nino patterns cause warmer-than-average sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern Pacific Ocean, leading to altered weather conditions such as increased rainfall in the Americas and droughts in Australia and Southeast Asia. La Nina patterns produce cooler-than-average sea surface temperatures in the same regions, often resulting in opposite climate effects like enhanced monsoon activity in Asia and dry conditions in the southwestern United States. Both phenomena significantly impact global climate systems by disrupting typical atmospheric circulation patterns and influencing extreme weather events worldwide.
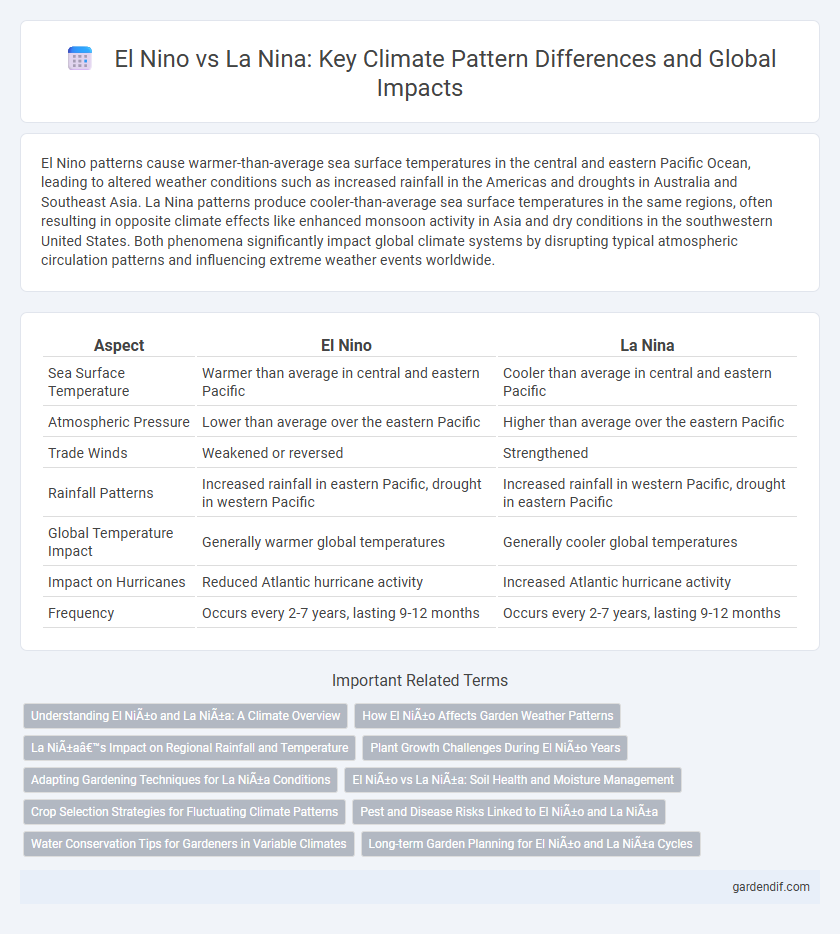
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | El Nino | La Nina |
|---|---|---|
| Sea Surface Temperature | Warmer than average in central and eastern Pacific | Cooler than average in central and eastern Pacific |
| Atmospheric Pressure | Lower than average over the eastern Pacific | Higher than average over the eastern Pacific |
| Trade Winds | Weakened or reversed | Strengthened |
| Rainfall Patterns | Increased rainfall in eastern Pacific, drought in western Pacific | Increased rainfall in western Pacific, drought in eastern Pacific |
| Global Temperature Impact | Generally warmer global temperatures | Generally cooler global temperatures |
| Impact on Hurricanes | Reduced Atlantic hurricane activity | Increased Atlantic hurricane activity |
| Frequency | Occurs every 2-7 years, lasting 9-12 months | Occurs every 2-7 years, lasting 9-12 months |
Understanding El Niño and La Niña: A Climate Overview
El Nino patterns are characterized by the warming of the central and eastern Pacific Ocean, leading to disrupted weather systems such as increased rainfall in the Americas and droughts in Asia and Australia. La Nina patterns involve the cooling of the same Pacific regions, often resulting in opposite climate effects like enhanced hurricane activity in the Atlantic and wetter conditions in Southeast Asia. Both phenomena significantly influence global atmospheric circulation, impacting agriculture, water resources, and disaster preparedness worldwide.
How El Niño Affects Garden Weather Patterns
El Nino disrupts garden weather patterns by causing warmer-than-average temperatures and increased rainfall in many regions, which can lead to early plant blooming and increased pest activity. This phenomenon often brings prolonged wet conditions that promote fungal diseases and root rot in sensitive plants. Gardeners must adjust watering schedules and select resilient plant varieties to mitigate the adverse effects of El Nino-driven climate changes.
La Niña’s Impact on Regional Rainfall and Temperature
La Nina patterns typically cause below-average sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern Pacific Ocean, leading to significant impacts on regional rainfall and temperature. This phenomenon often results in wetter conditions in Southeast Asia and Australia, while parts of the southern United States and northern South America experience droughts. Temperature anomalies during La Nina events generally include cooler-than-average conditions in the equatorial Pacific and warmer-than-average temperatures in the northern regions of North America.
Plant Growth Challenges During El Niño Years
El Nino patterns cause warmer ocean temperatures and altered rainfall that disrupt normal plant growth cycles by increasing drought stress and reducing nutrient availability. La Nina patterns, characterized by cooler ocean temperatures, often bring wetter conditions that enhance soil moisture but can also lead to flooding and root diseases in crops. Plant growth challenges during El Nino years include heightened vulnerability to water scarcity, increased pest outbreaks, and nutrient imbalances that reduce agricultural productivity globally.
Adapting Gardening Techniques for La Niña Conditions
La Nina conditions bring cooler ocean temperatures and increased rainfall, requiring gardeners to adjust soil drainage and select water-tolerant plants to prevent root rot. Mulching and raised beds enhance moisture management, reducing the risk of fungal diseases common in humid conditions. Emphasizing native, resilient plant varieties supports garden health and productivity during prolonged wet spells characteristic of La Nina patterns.
El Niño vs La Niña: Soil Health and Moisture Management
El Nino patterns typically cause warmer sea surface temperatures, leading to altered precipitation that can induce drought conditions and reduce soil moisture, negatively impacting soil health and crop productivity. In contrast, La Nina often brings cooler ocean temperatures and increased rainfall, enhancing soil moisture levels but potentially causing waterlogging and nutrient leaching in agricultural soils. Effective moisture management strategies must adapt to these contrasting climate phenomena to maintain soil structure, nutrient availability, and overall soil health.
Crop Selection Strategies for Fluctuating Climate Patterns
El Nino patterns typically bring warmer and drier conditions that favor drought-resistant crops such as sorghum and millet, while La Nina often results in cooler, wetter climates suitable for water-intensive crops like rice and sugarcane. Crop selection strategies must incorporate climate prediction data to adjust planting schedules and optimize yield stability during these fluctuating patterns. Utilizing climate-resilient varieties and diversifying crops enhances adaptation to the cyclical shifts between El Nino and La Nina events.
Pest and Disease Risks Linked to El Niño and La Niña
El Nino patterns typically increase the risk of pest outbreaks and crop diseases due to warmer ocean temperatures and altered rainfall, which create favorable conditions for pests like locusts and fungal diseases such as rusts. In contrast, La Nina often brings cooler, wetter conditions that can exacerbate soil-borne diseases and lead to higher incidences of pests like aphids and mites in affected agricultural regions. Both phenomena disrupt normal climatic conditions, intensifying risks to food security through varying pest and disease dynamics.
Water Conservation Tips for Gardeners in Variable Climates
El Nino patterns typically bring warmer, wetter conditions, increasing the importance of water-efficient irrigation and rainwater harvesting for gardeners. La Nina phases often cause cooler, drier weather, making mulching and soil moisture retention techniques critical to reduce evaporation. Utilizing drought-tolerant plant species and timing watering schedules around weather forecasts can optimize water usage amid these variable climate cycles.
Long-term Garden Planning for El Niño and La Niña Cycles
El Nino cycles typically bring warmer temperatures and increased rainfall, requiring gardeners to select drought-tolerant plants and invest in efficient drainage systems for long-term garden planning. La Nina cycles often result in cooler, wetter conditions, encouraging the use of moisture-loving plants and elevated beds to prevent root rot. Anticipating these patterns helps optimize plant health and water management strategies in garden maintenance.
El Niño patterns vs La Niña patterns Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com