
Humidity Tolerance vs Aridity Tolerance Illustration
Humidity tolerance refers to an organism's ability to survive and thrive in environments with high moisture levels, while aridity tolerance defines its capacity to withstand dry, low-humidity conditions. Species adapted to high humidity often possess mechanisms to manage excess water and prevent fungal infections, whereas those with aridity tolerance develop strategies like water retention and reduced transpiration. Understanding these adaptations is crucial for predicting the impacts of climate change on biodiversity and ecosystem stability.
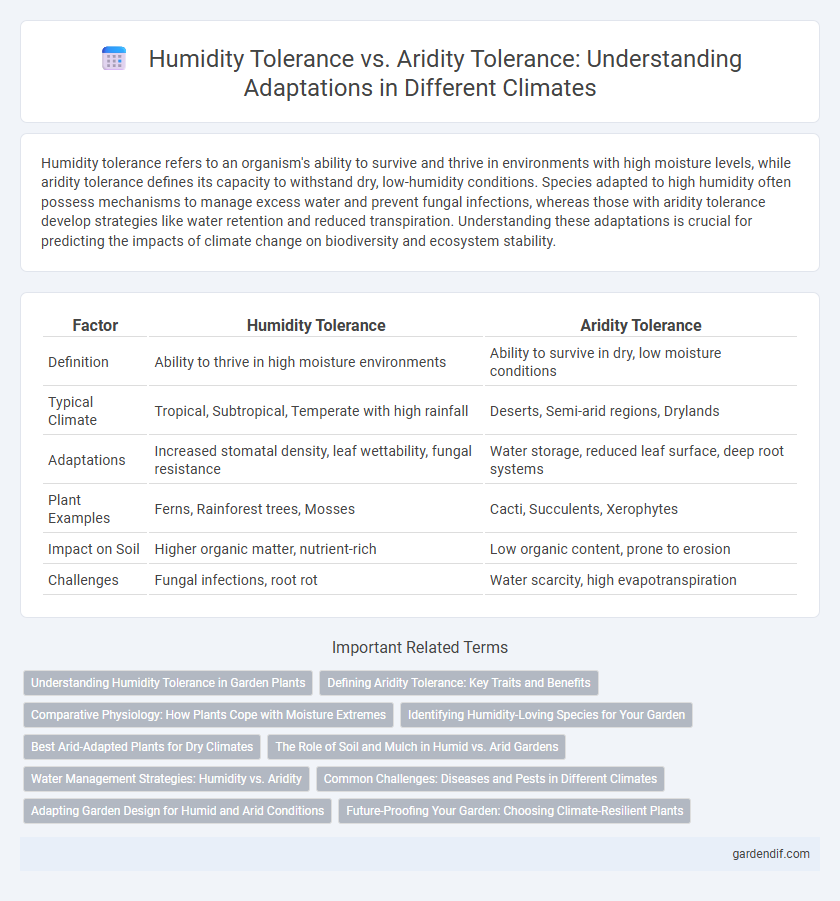
Table of Comparison
| Factor | Humidity Tolerance | Aridity Tolerance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ability to thrive in high moisture environments | Ability to survive in dry, low moisture conditions |
| Typical Climate | Tropical, Subtropical, Temperate with high rainfall | Deserts, Semi-arid regions, Drylands |
| Adaptations | Increased stomatal density, leaf wettability, fungal resistance | Water storage, reduced leaf surface, deep root systems |
| Plant Examples | Ferns, Rainforest trees, Mosses | Cacti, Succulents, Xerophytes |
| Impact on Soil | Higher organic matter, nutrient-rich | Low organic content, prone to erosion |
| Challenges | Fungal infections, root rot | Water scarcity, high evapotranspiration |
Understanding Humidity Tolerance in Garden Plants
Humidity tolerance in garden plants refers to their ability to thrive in environments with high moisture levels in the air, which affects transpiration rates and disease susceptibility. Plants with high humidity tolerance often possess adaptations like waxy leaf coatings or stomatal regulation to minimize water loss and prevent fungal infections. Understanding these traits helps gardeners select species suited to humid climates, ensuring optimal growth and reduced plant stress.
Defining Aridity Tolerance: Key Traits and Benefits
Aridity tolerance refers to an organism's ability to withstand prolonged periods of low water availability and extreme moisture deficits in desert or semi-arid environments. Key traits include efficient water retention mechanisms, reduced transpiration rates, and metabolic adaptations to minimize water loss. These traits enhance survival and productivity in ecosystems with limited precipitation and high evaporative demand.
Comparative Physiology: How Plants Cope with Moisture Extremes
Plants exhibit distinct physiological strategies to manage humidity tolerance and aridity tolerance, optimizing water use efficiency in fluctuating moisture conditions. Humidity-tolerant species often develop specialized stomatal regulation and leaf morphology to prevent excess water loss and optimize gas exchange in saturated environments. Conversely, aridity-tolerant plants enhance root depth, accumulate osmoprotectants, and adjust cellular water retention mechanisms to survive prolonged drought and minimize desiccation stress.
Identifying Humidity-Loving Species for Your Garden
Selecting plants with high humidity tolerance enhances garden resilience in moist climates by ensuring species can thrive in consistently damp conditions, such as ferns and calatheas. Identifying humidity-loving species involves examining native habitats and moisture preferences, favoring those adapted to tropical or subtropical environments with high atmospheric moisture. Prioritizing these plants improves growth rates, foliage vitality, and reduces stress from fungal diseases common in less suitable species under humid conditions.
Best Arid-Adapted Plants for Dry Climates
Best arid-adapted plants for dry climates exhibit remarkable aridity tolerance, thriving in environments with minimal moisture and extreme temperature fluctuations. Succulents like cacti and agave store water in their tissues, enabling survival during prolonged droughts, while desert shrubs such as creosote bush possess deep root systems that access rare underground moisture. These species outcompete humidity-tolerant plants by minimizing water loss through reduced leaf surface area and specialized stomatal control, ensuring resilience in harsh arid ecosystems.
The Role of Soil and Mulch in Humid vs. Arid Gardens
Soil composition and mulch types critically influence humidity tolerance in humid gardens by retaining moisture and regulating temperature, thereby supporting plant health. In arid gardens, soil with high sand content and organic mulch enhances aridity tolerance by maximizing water infiltration and reducing evaporation rates. Effective management of soil texture and appropriate mulch selection optimizes plant resilience against varying moisture conditions in both humid and arid climates.
Water Management Strategies: Humidity vs. Aridity
Plants exhibit distinct water management strategies to cope with humidity tolerance versus aridity tolerance, optimizing survival in contrasting climates. In high-humidity environments, species regulate excess water through enhanced transpiration and stomatal control to prevent fungal infections and maintain gas exchange. Conversely, aridity-tolerant plants employ adaptations like deep root systems, reduced leaf surface area, and CAM photosynthesis to maximize water uptake and minimize evaporation under prolonged drought conditions.
Common Challenges: Diseases and Pests in Different Climates
Humidity tolerance and aridity tolerance influence how plants and animals manage disease and pest pressures in varying climates. High humidity environments promote fungal infections, mold growth, and insect proliferation, creating challenges for ecosystems and agriculture. In contrast, arid climates limit moisture-dependent pathogens but encourage pests adapted to dry conditions, leading to unique stressors on biodiversity and crop resilience.
Adapting Garden Design for Humid and Arid Conditions
Adapting garden design for humid conditions emphasizes selecting moisture-loving plants with efficient drainage systems to prevent root rot and promote healthy growth. In contrast, aridity tolerance requires incorporating drought-resistant species, mulching for moisture retention, and using soil amendments that enhance water absorption. Strategic plant placement and irrigation techniques tailored to each climate optimize garden resilience and sustainability.
Future-Proofing Your Garden: Choosing Climate-Resilient Plants
Selecting plants with high humidity tolerance and aridity tolerance ensures a garden resilient to climate variability and extreme weather patterns. Species like succulents, native grasses, and certain Mediterranean herbs adapt well to low moisture, while tropical plants and ferns thrive in humid conditions. Integrating diverse, climate-resilient plants enhances water efficiency, reduces maintenance, and future-proofs gardens against increasing droughts and unpredictable rainfall.
Humidity Tolerance vs Aridity Tolerance Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com