
Chemical weed control vs organic weed control Illustration
Chemical weed control uses synthetic herbicides to effectively eliminate weeds, providing rapid and targeted results with minimal labor. Organic weed control relies on natural methods such as mulching, hand weeding, and biological agents, promoting soil health and reducing environmental impact. While chemical control offers convenience and efficiency, organic methods support sustainable agriculture and long-term ecosystem balance.
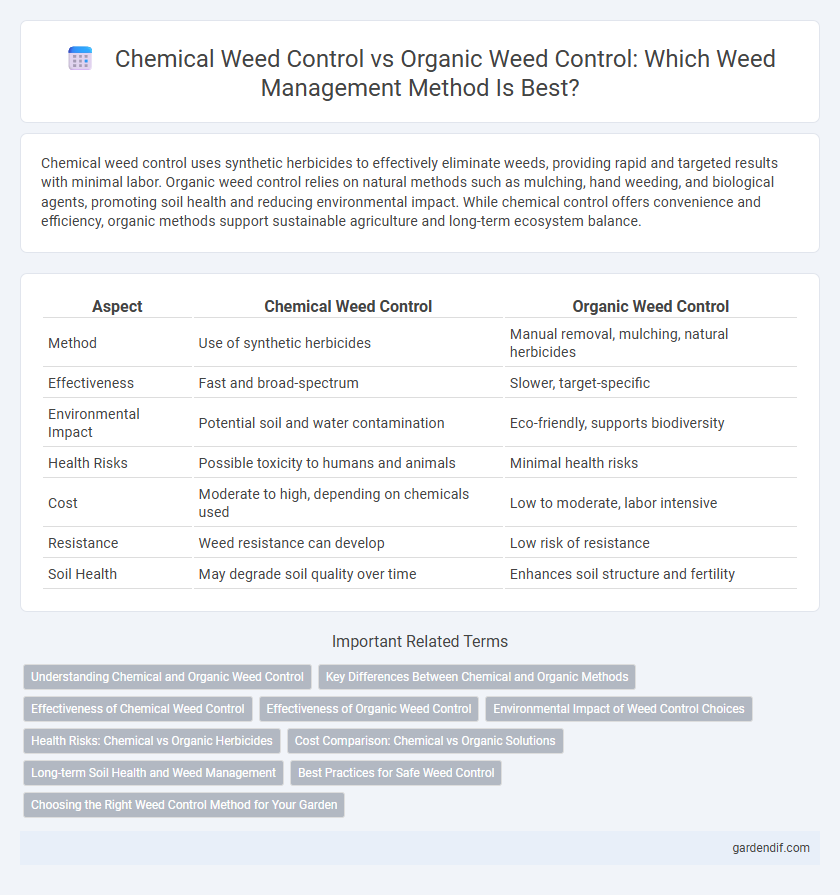
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Chemical Weed Control | Organic Weed Control |
|---|---|---|
| Method | Use of synthetic herbicides | Manual removal, mulching, natural herbicides |
| Effectiveness | Fast and broad-spectrum | Slower, target-specific |
| Environmental Impact | Potential soil and water contamination | Eco-friendly, supports biodiversity |
| Health Risks | Possible toxicity to humans and animals | Minimal health risks |
| Cost | Moderate to high, depending on chemicals used | Low to moderate, labor intensive |
| Resistance | Weed resistance can develop | Low risk of resistance |
| Soil Health | May degrade soil quality over time | Enhances soil structure and fertility |
Understanding Chemical and Organic Weed Control
Chemical weed control utilizes synthetic herbicides targeting specific plant enzymes or pathways to effectively eliminate unwanted weeds, offering rapid results and precise application. Organic weed control relies on natural methods such as mulching, manual removal, and the use of bioherbicides like corn gluten meal, promoting soil health and reducing chemical residues. Understanding the balance between these approaches involves evaluating factors like environmental impact, persistence, and weed resistance management.
Key Differences Between Chemical and Organic Methods
Chemical weed control relies on synthetic herbicides that target specific plant processes for rapid and effective weed elimination, often resulting in quicker results but with potential environmental and health risks. Organic weed control utilizes natural substances like mulch, manual removal, and bioherbicides, promoting soil health and biodiversity while reducing chemical residue. Key differences include the speed of action, environmental impact, and sustainability, with chemical methods focusing on immediate results and organic methods emphasizing long-term ecosystem balance.
Effectiveness of Chemical Weed Control
Chemical weed control demonstrates high effectiveness by targeting specific weed species with herbicides that inhibit essential biological processes, resulting in rapid and thorough weed elimination. The use of selective herbicides allows for minimal impact on desired crops while maximizing weed suppression, leading to increased agricultural productivity. Consistent application under recommended guidelines reduces weed resistance and maintains long-term field hygiene, making chemical control a reliable option for large-scale agriculture.
Effectiveness of Organic Weed Control
Organic weed control relies on natural methods such as mulching, crop rotation, and the use of bioherbicides derived from plant extracts, effectively reducing weed growth without harmful chemicals. Although it may require more frequent application and careful management, organic control minimizes environmental impact and supports soil health. Research indicates that integrating organic practices with mechanical removal enhances long-term weed suppression and biodiversity in agricultural systems.
Environmental Impact of Weed Control Choices
Chemical weed control often relies on synthetic herbicides that can contaminate soil and water, disrupting ecosystems and harming non-target species. Organic weed control methods, such as manual weeding or natural mulches, promote soil health and biodiversity by avoiding harmful chemicals. Choosing organic approaches reduces chemical runoff and preserves environmental integrity, supporting sustainable agriculture and ecosystem balance.
Health Risks: Chemical vs Organic Herbicides
Chemical weed control relies on synthetic herbicides such as glyphosate, which can pose significant health risks including endocrine disruption and carcinogenic potential. Organic weed control methods use natural substances like vinegar or corn gluten meal, generally associated with lower toxicity and reduced long-term health hazards. Choosing organic herbicides minimizes exposure to harmful chemicals and supports safer agricultural and residential environments.
Cost Comparison: Chemical vs Organic Solutions
Chemical weed control generally offers a lower upfront cost compared to organic methods due to mass production and availability of synthetic herbicides. Organic weed control often requires higher labor and material expenses, including frequent manual removal and natural herbicide applications, increasing overall cost. Long-term expenses may favor organic solutions by enhancing soil health and reducing environmental damage costs associated with chemical herbicide use.
Long-term Soil Health and Weed Management
Chemical weed control often provides immediate weed suppression but can degrade long-term soil health by disrupting microbial communities and reducing organic matter. Organic weed control methods, such as mulching and crop rotation, promote soil biodiversity and enhance soil structure, supporting sustainable weed management. Integrating organic practices with minimal chemical use can balance effective weed suppression and maintain soil resilience over time.
Best Practices for Safe Weed Control
Chemical weed control relies on herbicides like glyphosate to target and eradicate weeds efficiently, but it requires careful application to minimize risks to non-target plants and soil health. Organic weed control emphasizes mechanical methods, mulching, and natural herbicides derived from plant extracts, promoting biodiversity and reducing chemical residues. Integrating both approaches through precise timing, spot treatment, and adherence to safety guidelines ensures effective weed management while protecting the environment and human health.
Choosing the Right Weed Control Method for Your Garden
Chemical weed control offers fast, effective eradication of invasive plants by using herbicides targeted at specific weed species, making it ideal for large or heavily infested gardens. Organic weed control relies on natural methods such as mulching, manual removal, and biological agents to promote long-term soil health and biodiversity while minimizing environmental impact. Evaluating garden size, infestation severity, and eco-sustainability goals helps determine the optimal weed control strategy for maintaining a healthy, thriving garden ecosystem.
Chemical weed control vs organic weed control Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com