
Mulched beds vs Unmulched beds Illustration
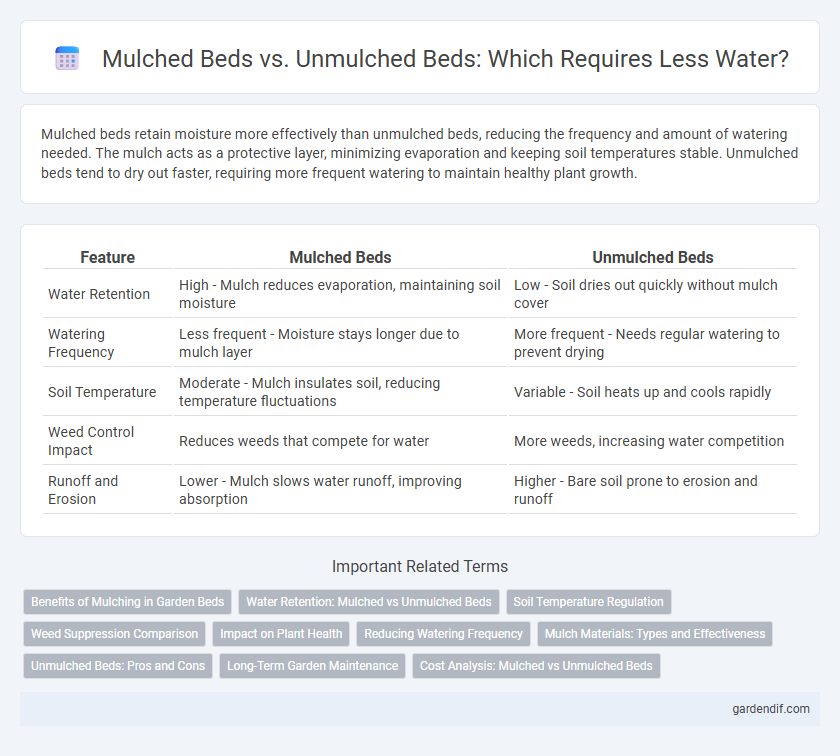
Mulched beds retain moisture more effectively than unmulched beds, reducing the frequency and amount of watering needed. The mulch acts as a protective layer, minimizing evaporation and keeping soil temperatures stable. Unmulched beds tend to dry out faster, requiring more frequent watering to maintain healthy plant growth.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Mulched Beds | Unmulched Beds |
|---|---|---|
| Water Retention | High - Mulch reduces evaporation, maintaining soil moisture | Low - Soil dries out quickly without mulch cover |
| Watering Frequency | Less frequent - Moisture stays longer due to mulch layer | More frequent - Needs regular watering to prevent drying |
| Soil Temperature | Moderate - Mulch insulates soil, reducing temperature fluctuations | Variable - Soil heats up and cools rapidly |
| Weed Control Impact | Reduces weeds that compete for water | More weeds, increasing water competition |
| Runoff and Erosion | Lower - Mulch slows water runoff, improving absorption | Higher - Bare soil prone to erosion and runoff |
Benefits of Mulching in Garden Beds
Mulched beds conserve soil moisture by reducing evaporation, which leads to more efficient watering and less frequent irrigation. The mulch layer also regulates soil temperature, protecting roots from extreme heat and promoting healthier plant growth. Enhanced moisture retention in mulched garden beds supports strong root development and reduces water runoff, optimizing water use in the garden.
Water Retention: Mulched vs Unmulched Beds
Mulched beds significantly enhance water retention by reducing evaporation and maintaining soil moisture levels compared to unmulched beds. The organic layer in mulched beds acts as a barrier, minimizing water runoff and promoting deeper infiltration into the soil. Unmulched beds often experience faster drying, leading to frequent watering needs and increased water waste.
Soil Temperature Regulation
Mulched beds significantly stabilize soil temperature by insulating it from extreme heat and cold, maintaining a consistent environment that promotes healthy root development. Unmulched beds experience greater temperature fluctuations, which can stress plants and slow growth due to exposure to direct sunlight and cooler night temperatures. Consistent soil temperature regulation in mulched beds improves moisture retention and nutrient availability, enhancing overall plant resilience and productivity.
Weed Suppression Comparison
Mulched beds significantly reduce weed growth by blocking sunlight and creating an inhospitable environment for weed seeds to germinate, leading to decreased competition for water and nutrients. In contrast, unmulched beds allow more weed seeds to sprout, increasing the need for frequent watering and manual weeding. Studies show mulched beds retain moisture better, contributing to healthier plant roots and less water waste due to reduced weed proliferation.
Impact on Plant Health
Mulched beds improve plant health by retaining soil moisture, reducing water evaporation, and regulating soil temperature, which promotes stronger root development and reduces plant stress. In contrast, unmulched beds often experience rapid soil drying and temperature fluctuations, leading to increased water needs and vulnerability to diseases. Consistent moisture levels in mulched beds enhance nutrient uptake and overall plant vigor, resulting in healthier, more resilient plants.
Reducing Watering Frequency
Mulched beds retain soil moisture by reducing evaporation, significantly decreasing the need for frequent watering compared to unmulched beds. Organic mulch materials like wood chips or straw improve soil structure and increase water absorption efficiency, leading to longer-lasting soil moisture. Unmulched beds often dry out faster, requiring more frequent irrigation to maintain plant health and growth.
Mulch Materials: Types and Effectiveness
Organic mulches such as wood chips, straw, and compost improve water retention by reducing evaporation and moderating soil temperature in mulched beds. Inorganic mulches like gravel and landscape fabric primarily prevent weed growth but have limited impact on moisture conservation compared to organic alternatives. Selecting mulch materials with high water-holding capacity enhances irrigation efficiency and promotes healthier plant growth in mulched garden beds.
Unmulched Beds: Pros and Cons
Unmulched beds allow for quicker soil warming in early spring, which can promote faster seed germination and plant growth. However, these beds are more prone to moisture evaporation, soil erosion, and weed growth, requiring more frequent watering and maintenance. The lack of mulch also means reduced insulation, making soil temperatures more variable and potentially stressing plant roots.
Long-Term Garden Maintenance
Mulched beds retain soil moisture up to 50% longer than unmulched beds, reducing watering frequency and conserving water resources. Mulch also suppresses weed growth, minimizing competition for water and nutrients, which promotes healthier plant development over time. Consistent moisture levels in mulched beds lead to improved root systems and increased resilience during drought conditions, enhancing long-term garden sustainability.
Cost Analysis: Mulched vs Unmulched Beds
Mulched beds reduce water evaporation by up to 50%, significantly lowering irrigation costs over time compared to unmulched beds that require more frequent watering. Initial mulching expenses average $1 to $3 per square foot, but these are offset by decreased water bills and reduced labor for watering throughout the growing season. Unmulched beds often lead to higher water consumption and increased weed control costs, resulting in a less economical option for sustainable landscaping.
Mulched beds vs Unmulched beds Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com