
Mulch-covered soil vs Bare soil watering Illustration
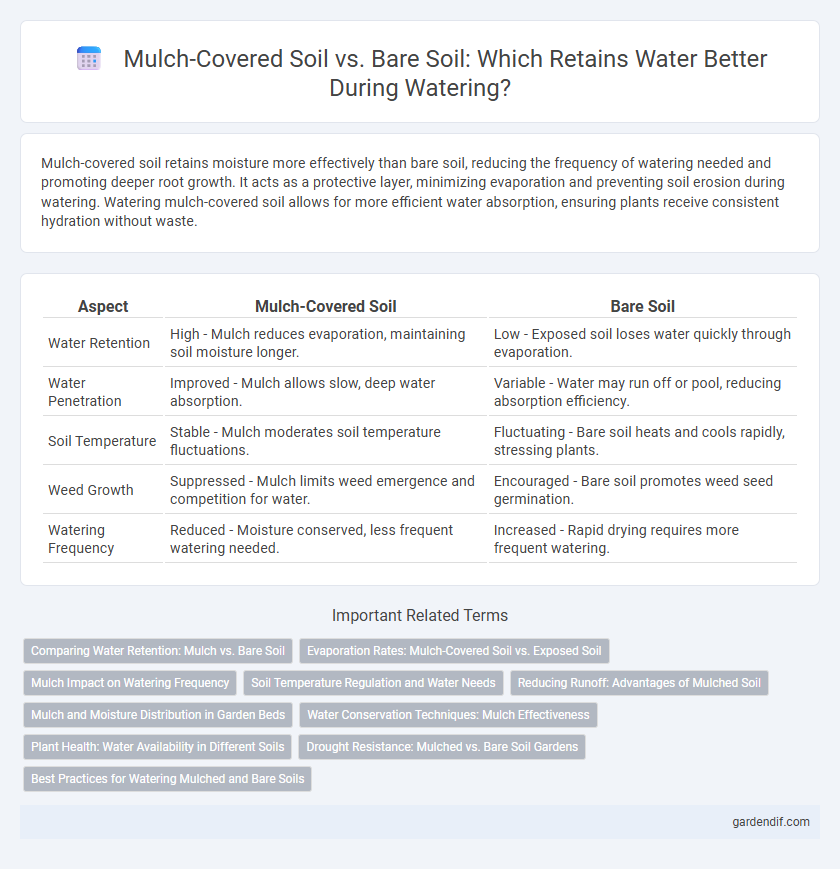
Mulch-covered soil retains moisture more effectively than bare soil, reducing the frequency of watering needed and promoting deeper root growth. It acts as a protective layer, minimizing evaporation and preventing soil erosion during watering. Watering mulch-covered soil allows for more efficient water absorption, ensuring plants receive consistent hydration without waste.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Mulch-Covered Soil | Bare Soil |
|---|---|---|
| Water Retention | High - Mulch reduces evaporation, maintaining soil moisture longer. | Low - Exposed soil loses water quickly through evaporation. |
| Water Penetration | Improved - Mulch allows slow, deep water absorption. | Variable - Water may run off or pool, reducing absorption efficiency. |
| Soil Temperature | Stable - Mulch moderates soil temperature fluctuations. | Fluctuating - Bare soil heats and cools rapidly, stressing plants. |
| Weed Growth | Suppressed - Mulch limits weed emergence and competition for water. | Encouraged - Bare soil promotes weed seed germination. |
| Watering Frequency | Reduced - Moisture conserved, less frequent watering needed. | Increased - Rapid drying requires more frequent watering. |
Comparing Water Retention: Mulch vs. Bare Soil
Mulch-covered soil retains water significantly better than bare soil, reducing evaporation and maintaining consistent moisture levels essential for plant health. Studies show that mulch can reduce soil water loss by up to 50%, promoting deeper root growth and minimizing irrigation frequency. In contrast, bare soil experiences rapid drying due to direct exposure to sun and wind, leading to inefficient water usage and increased plant stress.
Evaporation Rates: Mulch-Covered Soil vs. Exposed Soil
Mulch-covered soil significantly reduces evaporation rates by creating a barrier that retains moisture and maintains soil temperature, resulting in up to 50% less water loss compared to bare soil. This moisture conservation enhances plant hydration efficiency and reduces irrigation frequency. Exposed soil, lacking this protective layer, experiences faster water evaporation, leading to drier soil conditions and increased water demand.
Mulch Impact on Watering Frequency
Mulch-covered soil significantly reduces the need for frequent watering by retaining moisture and minimizing evaporation compared to bare soil. Studies show that mulched areas can require up to 50% less watering over the same period, promoting efficient water use in gardens and landscapes. The insulating properties of mulch also help maintain consistent soil temperature, further supporting moisture retention and reducing plant stress.
Soil Temperature Regulation and Water Needs
Mulch-covered soil significantly reduces soil temperature fluctuations, maintaining a cooler and more stable environment compared to bare soil, which heats up quickly and cools down faster. This temperature regulation decreases water evaporation rates, resulting in lower water requirements for plants grown in mulched areas. Bare soil typically demands more frequent watering due to higher evaporation and less moisture retention.
Reducing Runoff: Advantages of Mulched Soil
Mulch-covered soil significantly reduces water runoff by enhancing moisture retention and promoting deeper water absorption. The organic layer acts as a protective barrier, minimizing soil erosion and improving infiltration rates compared to bare soil surfaces. This results in more efficient water use and healthier plant growth due to consistent soil hydration.
Mulch and Moisture Distribution in Garden Beds
Mulch-covered soil significantly improves moisture retention in garden beds by reducing evaporation and promoting even water distribution across the root zone. The organic layer acts as an insulating barrier, maintaining consistent soil temperature and allowing water to penetrate deeper, which supports healthier plant growth. Compared to bare soil, mulched beds exhibit enhanced moisture conservation, reduce runoff, and minimize soil erosion, making them a superior choice for efficient garden watering.
Water Conservation Techniques: Mulch Effectiveness
Mulch-covered soil significantly enhances water conservation by reducing evaporation rates by up to 70%, maintaining consistent soil moisture levels essential for plant health. The organic layer acts as a barrier, minimizing runoff and promoting deeper water penetration into the root zone, which improves water use efficiency. In contrast, bare soil exposes moisture to direct sunlight and wind, accelerating drying and necessitating more frequent watering to sustain optimal hydration.
Plant Health: Water Availability in Different Soils
Mulch-covered soil retains moisture significantly better than bare soil, reducing evaporation rates by up to 30%, which ensures more consistent water availability for plant roots. This consistent moisture level promotes healthier root development and enhances plant resilience during dry periods. In contrast, bare soil experiences rapid water loss, leading to frequent watering needs and increased plant stress due to inconsistent hydration.
Drought Resistance: Mulched vs. Bare Soil Gardens
Mulch-covered soil significantly enhances drought resistance by reducing evaporation and retaining soil moisture longer than bare soil, which quickly loses water due to direct exposure. Studies show that mulched gardens can use up to 50% less water during dry periods compared to bare soil gardens. This moisture retention supports healthier plant roots and reduces the frequency of watering needed in drought-prone areas.
Best Practices for Watering Mulched and Bare Soils
Mulch-covered soil retains moisture more effectively by reducing evaporation, allowing for less frequent but deeper watering compared to bare soil, which requires more frequent irrigation to prevent drying out. Best practices for watering mulched soil include targeting the root zone and applying water slowly to maximize absorption, while bare soil benefits from shallow, more frequent watering to maintain consistent moisture levels. Using drip irrigation or soaker hoses can improve water efficiency in both mulched and bare soil settings, promoting healthy plant growth and conserving water.
Mulch-covered soil vs Bare soil watering Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com