
Surface watering vs Subsurface watering Illustration
Surface watering involves delivering water directly to the soil surface, allowing it to seep downward and hydrate plant roots, which can lead to evaporation losses and uneven distribution. Subsurface watering targets the root zone by delivering water below the soil surface, reducing evaporation and promoting deeper root growth for enhanced drought resistance. This method is often more efficient for water conservation and supports healthier plant development compared to traditional surface watering techniques.
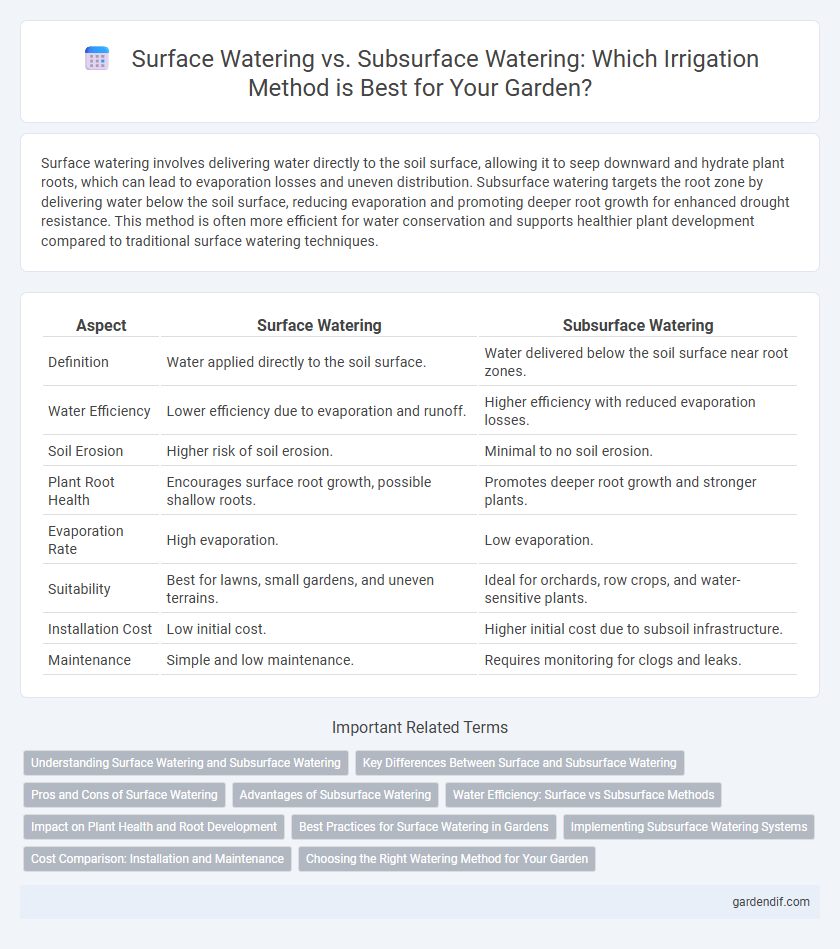
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Surface Watering | Subsurface Watering |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Water applied directly to the soil surface. | Water delivered below the soil surface near root zones. |
| Water Efficiency | Lower efficiency due to evaporation and runoff. | Higher efficiency with reduced evaporation losses. |
| Soil Erosion | Higher risk of soil erosion. | Minimal to no soil erosion. |
| Plant Root Health | Encourages surface root growth, possible shallow roots. | Promotes deeper root growth and stronger plants. |
| Evaporation Rate | High evaporation. | Low evaporation. |
| Suitability | Best for lawns, small gardens, and uneven terrains. | Ideal for orchards, row crops, and water-sensitive plants. |
| Installation Cost | Low initial cost. | Higher initial cost due to subsoil infrastructure. |
| Maintenance | Simple and low maintenance. | Requires monitoring for clogs and leaks. |
Understanding Surface Watering and Subsurface Watering
Surface watering involves applying water directly to the soil or plant leaves, promoting quick absorption but increasing evaporation and runoff risks. Subsurface watering delivers moisture below the soil surface, enhancing water efficiency by targeting root zones and reducing surface evaporation. Understanding these methods helps optimize irrigation strategies to improve plant health and conserve water resources effectively.
Key Differences Between Surface and Subsurface Watering
Surface watering applies water directly to the soil surface, promoting quick hydration but often leading to higher evaporation losses and surface runoff. Subsurface watering delivers water below the soil surface, enhancing root zone moisture retention and reducing evaporation while minimizing weed growth on the soil surface. The key differences include water application depth, efficiency in water use, and impact on plant root development and soil erosion.
Pros and Cons of Surface Watering
Surface watering allows easy visual monitoring and is cost-effective with minimal installation requirements, making it suitable for various garden sizes. It can lead to higher evaporation rates and potential water runoff, reducing efficiency and increasing water waste. Surface watering may also promote weed growth and surface soil erosion, requiring careful management to prevent these issues.
Advantages of Subsurface Watering
Subsurface watering delivers water directly to the root zone, reducing evaporation loss and promoting deeper root growth for healthier plants. This method conserves water by minimizing runoff and surface evaporation compared to surface watering. Enhanced soil moisture retention and decreased weed growth are additional advantages of subsurface watering systems.
Water Efficiency: Surface vs Subsurface Methods
Subsurface watering delivers water directly to plant roots, reducing evaporation and runoff, which improves water efficiency compared to surface watering. Surface watering often results in significant water loss through evaporation and surface runoff, particularly in dry or windy conditions. By minimizing water waste, subsurface irrigation systems enhance water conservation and promote healthier plant growth in water-scarce environments.
Impact on Plant Health and Root Development
Surface watering often leads to shallow root development and increased risk of fungal diseases due to prolonged leaf wetness, while subsurface watering promotes deeper root growth by delivering moisture directly to the root zone. Improved root depth enhances plant stability and drought resistance, making subsurface irrigation more effective for long-term plant health. Efficient water delivery through subsurface systems reduces water loss from evaporation and runoff, optimizing soil moisture levels critical for nutrient uptake.
Best Practices for Surface Watering in Gardens
Effective surface watering in gardens involves applying water evenly at the soil surface to promote deep root growth and prevent runoff. Watering should be done early in the morning or late in the evening to reduce evaporation and maximize absorption. Using drip irrigation or soaker hoses helps deliver water precisely to plant roots, improving water efficiency and minimizing weed growth.
Implementing Subsurface Watering Systems
Implementing subsurface watering systems involves installing drip irrigation lines below the soil surface to deliver water directly to plant roots, enhancing water efficiency and reducing evaporation. These systems promote deeper root growth and minimize weed proliferation by limiting surface moisture. Proper design requires understanding soil type, crop needs, and precise emitter spacing for optimal performance.
Cost Comparison: Installation and Maintenance
Surface watering typically incurs lower initial installation costs due to simpler equipment and layout, while subsurface watering demands higher upfront investment for specialized drip lines and soil sensors. Maintenance expenses for surface watering are generally higher because of increased vulnerability to evaporation, runoff, and clogging, whereas subsurface systems benefit from reduced water loss and less frequent repairs despite complex monitoring requirements. Over time, subsurface watering proves more cost-effective for water conservation and efficiency despite the steeper installation expense.
Choosing the Right Watering Method for Your Garden
Surface watering delivers water directly to the soil surface, providing quick hydration ideal for shallow-rooted plants and reducing water loss from evaporation. Subsurface watering targets the root zone more efficiently by delivering moisture below the soil surface, promoting deeper root growth and conserving water in drought-prone areas. Selecting the right watering method depends on plant type, soil composition, and environmental conditions to maximize water use efficiency and support healthy garden growth.
Surface watering vs Subsurface watering Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com