
Soil structure vs Soil texture Illustration
Soil texture refers to the proportion of sand, silt, and clay particles within the soil, influencing its water retention, drainage, and nutrient availability. Soil structure describes the arrangement and aggregation of these particles into clusters or clumps, affecting aeration, root penetration, and microbial activity. Understanding the differences between soil texture and soil structure is essential for effective soil management and optimizing plant growth.
Table of Comparison
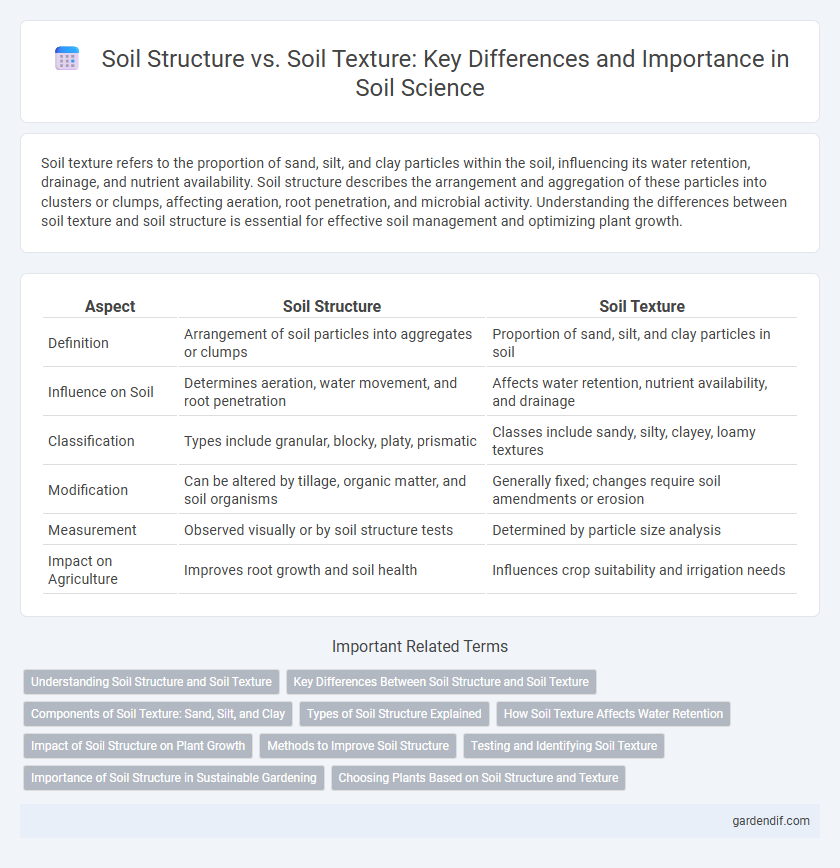
| Aspect | Soil Structure | Soil Texture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Arrangement of soil particles into aggregates or clumps | Proportion of sand, silt, and clay particles in soil |
| Influence on Soil | Determines aeration, water movement, and root penetration | Affects water retention, nutrient availability, and drainage |
| Classification | Types include granular, blocky, platy, prismatic | Classes include sandy, silty, clayey, loamy textures |
| Modification | Can be altered by tillage, organic matter, and soil organisms | Generally fixed; changes require soil amendments or erosion |
| Measurement | Observed visually or by soil structure tests | Determined by particle size analysis |
| Impact on Agriculture | Improves root growth and soil health | Influences crop suitability and irrigation needs |
Understanding Soil Structure and Soil Texture
Soil structure refers to the arrangement of soil particles into aggregates or clumps that influence water movement, root growth, and aeration, while soil texture describes the proportion of sand, silt, and clay particles affecting water retention and nutrient availability. Understanding soil structure helps in managing soil compaction and erosion, whereas soil texture determines drainage capacity and fertility potential. Both soil structure and texture are critical for optimizing soil health and plant productivity in agricultural and ecological systems.
Key Differences Between Soil Structure and Soil Texture
Soil structure refers to the arrangement of soil particles into aggregates or clumps, influencing aeration, water infiltration, and root penetration, while soil texture describes the relative proportion of sand, silt, and clay particles determining soil's feel and nutrient retention. Soil structure is dynamic and can change with cultivation and moisture conditions, whereas soil texture remains constant because it is inherent to the soil's mineral composition. Understanding the key differences between soil structure and soil texture is essential for effective soil management and optimizing plant growth.
Components of Soil Texture: Sand, Silt, and Clay
Soil texture is determined by the relative proportions of sand, silt, and clay particles, each influencing water retention, aeration, and nutrient availability. Sand particles are the largest, promoting drainage and root penetration, while silt particles are medium-sized, offering moderate water retention and fertility. Clay particles are the smallest, holding nutrients efficiently but potentially restricting airflow and water movement in the soil structure.
Types of Soil Structure Explained
Soil structure refers to the arrangement of soil particles into aggregates or clumps, influencing water retention, aeration, and root penetration, whereas soil texture describes the relative proportions of sand, silt, and clay particles. Types of soil structure include granular, blocky, prismatic, platy, and columnar, each affecting soil behavior and plant growth differently. Granular structure improves aeration and drainage, blocky enhances nutrient retention, prismatic and columnar structures impact water movement, and platy can restrict root development.
How Soil Texture Affects Water Retention
Soil texture, determined by the relative proportions of sand, silt, and clay particles, directly influences water retention capacity, with clay soils holding more water due to smaller particle sizes and greater surface area. In contrast, sandy soils have larger particles and pore spaces, causing quicker drainage and lower water retention. Proper understanding of soil texture helps optimize irrigation practices and improve plant water availability for better crop growth.
Impact of Soil Structure on Plant Growth
Soil structure significantly influences plant growth by affecting root penetration, water retention, and aeration. Well-aggregated soil promotes better root development and nutrient uptake, enhancing overall plant health. Poor soil structure, characterized by compaction or crusting, restricts root expansion and reduces oxygen availability, negatively impacting crop yields.
Methods to Improve Soil Structure
Improving soil structure involves practices such as incorporating organic matter like compost or cover crops to enhance aggregation and porosity. Techniques like reduced tillage minimize soil disruption, preserving natural crumb formation and promoting beneficial microbial activity. Applying gypsum in sodic soils reduces dispersion and improves soil aggregation, leading to better water infiltration and root penetration.
Testing and Identifying Soil Texture
Testing and identifying soil texture involves analyzing the relative proportions of sand, silt, and clay particles, typically through methods such as the feel test, sedimentation analysis, or hydrometer method. Soil texture directly influences water retention, aeration, and nutrient availability, making accurate identification essential for effective soil management. Understanding texture variations assists in assessing soil structure, but texture itself is determined solely by particle size distribution rather than aggregate arrangement.
Importance of Soil Structure in Sustainable Gardening
Soil structure refers to the arrangement of soil particles into aggregates, influencing aeration, water retention, and root penetration, which are critical for plant health in sustainable gardening. Unlike soil texture, determined by the proportion of sand, silt, and clay, soil structure can be improved through organic matter addition and reduced tillage, enhancing microbial activity and nutrient cycling. Well-developed soil structure supports sustainable gardening by promoting soil resilience, reducing erosion, and increasing water infiltration and retention efficiency.
Choosing Plants Based on Soil Structure and Texture
Soil structure influences root penetration and water retention, guiding plant selection for optimal growth. Soil texture, defined by sand, silt, and clay proportions, affects drainage and nutrient availability, crucial for matching plants to suitable soil conditions. Selecting plants adapted to both soil structure and texture ensures enhanced health and productivity in garden or agricultural settings.
Soil structure vs Soil texture Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com