
Potting Mix vs Garden Soil Illustration
Potting mix is a lightweight, well-draining medium designed specifically for container plants, enriched with organic matter and nutrients to support root growth. Garden soil contains native soil from the ground, often denser and less aerated, making it suitable for outdoor beds but less ideal for pots. Choosing the right medium depends on plant type and growing environment to promote healthy development.
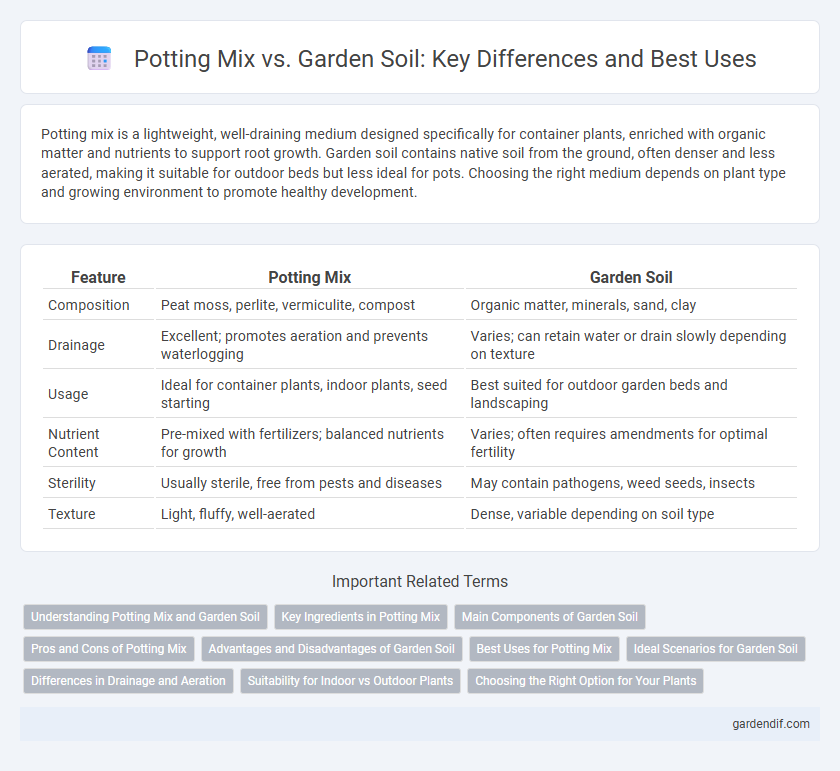
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Potting Mix | Garden Soil |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Peat moss, perlite, vermiculite, compost | Organic matter, minerals, sand, clay |
| Drainage | Excellent; promotes aeration and prevents waterlogging | Varies; can retain water or drain slowly depending on texture |
| Usage | Ideal for container plants, indoor plants, seed starting | Best suited for outdoor garden beds and landscaping |
| Nutrient Content | Pre-mixed with fertilizers; balanced nutrients for growth | Varies; often requires amendments for optimal fertility |
| Sterility | Usually sterile, free from pests and diseases | May contain pathogens, weed seeds, insects |
| Texture | Light, fluffy, well-aerated | Dense, variable depending on soil type |
Understanding Potting Mix and Garden Soil
Potting mix is a lightweight, well-draining medium specifically formulated for container plants, often containing peat moss, vermiculite, and perlite to enhance aeration and moisture retention. Garden soil is a heavier blend composed mainly of natural soil enriched with organic matter, designed for use in outdoor garden beds to support plant roots and improve soil structure. Understanding the distinct compositions and purposes of potting mix and garden soil is crucial for selecting the appropriate growing medium to promote healthy plant growth.
Key Ingredients in Potting Mix
Potting mix contains a blend of key ingredients such as peat moss, coconut coir, perlite, and vermiculite that provide excellent aeration, moisture retention, and drainage for container plants. Unlike garden soil, which is denser and contains more clay and silt, potting mix is lightweight and sterile, reducing the risk of pests and diseases. The inclusion of organic matter and often added fertilizers in potting mix ensures optimal nutrient availability for potted plants' growth and health.
Main Components of Garden Soil
Garden soil primarily consists of a balanced mixture of sand, silt, and clay particles, which create its texture and drainage properties. It also contains organic matter such as decomposed leaves, roots, and microorganisms that enhance nutrient availability and soil structure. Essential minerals like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium in garden soil support healthy plant growth by providing necessary nutrients.
Pros and Cons of Potting Mix
Potting mix offers excellent drainage and aeration, making it ideal for container plants that require controlled moisture and nutrient levels. Its lightweight composition allows for easy root growth and reduces the risk of soil compaction compared to garden soil. However, potting mix often lacks the natural microorganisms and organic matter found in garden soil, which can limit long-term soil fertility and microbial activity.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Garden Soil
Garden soil offers superior nutrient content and natural microbial activity, which enhances plant growth and root development. Its dense texture provides excellent moisture retention but can lead to poor drainage and compaction, limiting aeration for some plants. Compared to potting mix, garden soil is less sterile and may contain pests or weed seeds, presenting potential challenges for container gardening.
Best Uses for Potting Mix
Potting mix is specially formulated for container gardening, offering excellent drainage and aeration to support healthy root growth in potted plants. It typically contains peat moss, perlite, and vermiculite, which provide a lightweight, nutrient-rich medium ideal for indoor plants, seedlings, and container vegetables. Unlike garden soil, potting mix reduces the risk of soil-borne diseases and pests, making it the best choice for plants grown in pots and hanging baskets.
Ideal Scenarios for Garden Soil
Garden soil is ideal for outdoor landscaping projects, raised beds, and large-scale garden beds where natural soil conditions need improvement. It provides a balanced mix of nutrients and organic matter, supporting established plants and promoting root development in open ground environments. Using garden soil in these scenarios helps enhance soil structure and fertility, making it suitable for perennial plants, shrubs, and trees.
Differences in Drainage and Aeration
Potting mix is specifically formulated with materials like peat moss, perlite, and vermiculite to provide superior drainage and aeration, essential for container plants. Garden soil contains a denser mixture of sand, silt, and clay, which often results in slower drainage and reduced aeration compared to potting mix. Proper drainage in potting mix prevents root rot, while enhanced aeration promotes healthy root growth, making it ideal for potted plants versus the compact nature of garden soil.
Suitability for Indoor vs Outdoor Plants
Potting mix is specifically formulated for indoor plants, offering excellent drainage, aeration, and lightweight properties ideal for container growth. Garden soil, richer in organic matter and denser, is best suited for outdoor plants thriving in natural ground conditions. Choosing the correct medium enhances root health, moisture retention, and nutrient availability tailored to the plant's environment.
Choosing the Right Option for Your Plants
Potting mix is specially formulated for container plants with excellent drainage, aeration, and nutrient retention, making it ideal for indoor or potted plants. Garden soil, enriched with organic matter and native minerals, suits outdoor garden beds where plants benefit from natural soil ecosystems. Selecting the right option depends on plant type, container use, and growing environment to ensure optimal growth and root health.
Potting Mix vs Garden Soil Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com