
Epsom salt vs Gypsum Illustration
Epsom salt and gypsum serve different roles in soil amendment, with Epsom salt providing magnesium and sulfur essential for plant growth and gypsum supplying calcium and sulfur to improve soil structure. Epsom salt is often used to correct magnesium deficiencies, enhancing chlorophyll production and nutrient uptake. Gypsum helps alleviate soil compaction and reduce aluminum toxicity, promoting better root development in clay and acidic soils.
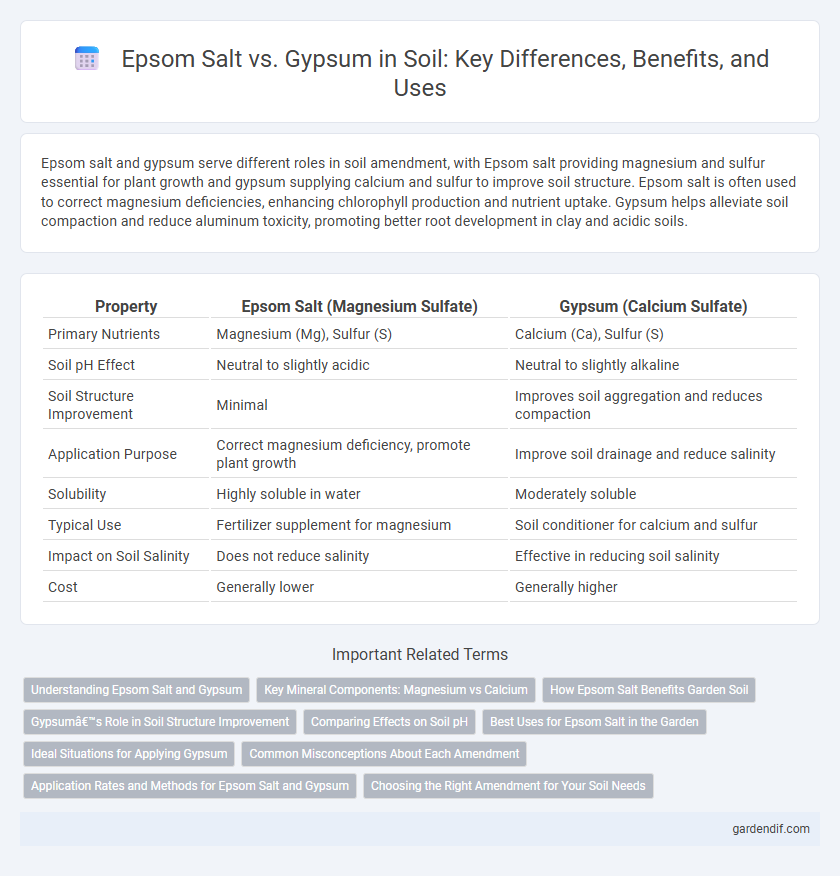
Table of Comparison
| Property | Epsom Salt (Magnesium Sulfate) | Gypsum (Calcium Sulfate) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Nutrients | Magnesium (Mg), Sulfur (S) | Calcium (Ca), Sulfur (S) |
| Soil pH Effect | Neutral to slightly acidic | Neutral to slightly alkaline |
| Soil Structure Improvement | Minimal | Improves soil aggregation and reduces compaction |
| Application Purpose | Correct magnesium deficiency, promote plant growth | Improve soil drainage and reduce salinity |
| Solubility | Highly soluble in water | Moderately soluble |
| Typical Use | Fertilizer supplement for magnesium | Soil conditioner for calcium and sulfur |
| Impact on Soil Salinity | Does not reduce salinity | Effective in reducing soil salinity |
| Cost | Generally lower | Generally higher |
Understanding Epsom Salt and Gypsum
Epsom salt, chemically known as magnesium sulfate, supplies essential magnesium and sulfur that promote chlorophyll production and improve nutrient absorption in plants. Gypsum, or calcium sulfate, primarily enhances soil structure by improving water infiltration and reducing compaction while supplying calcium and sulfur to the soil. Understanding the distinct nutrient contributions and soil benefits of Epsom salt versus gypsum helps optimize plant growth and soil health management.
Key Mineral Components: Magnesium vs Calcium
Epsom salt primarily contains magnesium sulfate, which supplies essential magnesium and sulfur to the soil, enhancing chlorophyll production and improving plant nutrient uptake. Gypsum, on the other hand, is rich in calcium sulfate, providing calcium important for cell wall strength and soil structure without altering soil pH significantly. Both minerals play distinct roles in soil health; magnesium from Epsom salt aids in enzymatic functions while calcium from gypsum promotes soil aggregation and reduces compaction.
How Epsom Salt Benefits Garden Soil
Epsom salt provides essential magnesium and sulfur, which improve nutrient uptake and promote chlorophyll production in garden soil. This enhances plant growth, leading to greener leaves and stronger stems, especially for magnesium-deficient soils. Unlike gypsum, which primarily adds calcium and sulfur, Epsom salt specifically targets magnesium deficiencies crucial for photosynthesis and overall plant health.
Gypsum’s Role in Soil Structure Improvement
Gypsum enhances soil structure by improving soil aggregation and porosity, which facilitates better water infiltration and root penetration. It supplies calcium without altering soil pH significantly, promoting the flocculation of clay particles and reducing soil compaction. Unlike Epsom salt, which primarily provides magnesium and sulfur, gypsum is favored for reclaiming sodic soils and enhancing overall soil aeration and drainage.
Comparing Effects on Soil pH
Epsom salt primarily provides magnesium and sulfur without significantly altering soil pH, making it ideal for correcting magnesium deficiencies without affecting acidity. Gypsum supplies calcium and sulfur and can help improve soil structure while slightly lowering soil pH in alkaline conditions. For soils with pH balance issues, gypsum is more effective in modifying pH, whereas Epsom salt is beneficial for nutrient supplementation without pH alteration.
Best Uses for Epsom Salt in the Garden
Epsom salt is best used in gardens to provide magnesium and sulfur, essential nutrients that promote healthy plant growth, improve seed germination, and enhance nutrient uptake. It is particularly effective for correcting magnesium deficiencies in tomatoes, peppers, and roses, leading to greener leaves and increased flower production. Unlike gypsum, which primarily adds calcium and improves soil structure, Epsom salt directly targets magnesium levels, making it ideal for foliar feeding and boosting specific plant health.
Ideal Situations for Applying Gypsum
Gypsum is ideal for improving soil structure in heavy clay soils by promoting better drainage and reducing compaction. It effectively supplies calcium and sulfur without altering soil pH, making it suitable for alkaline or saline soils. Gypsum is also beneficial for correcting sodium toxicity and enhancing root growth in waterlogged conditions.
Common Misconceptions About Each Amendment
Epsom salt is often mistakenly believed to improve soil structure, but its primary function is supplying magnesium and sulfur, essential for chlorophyll production and plant growth, rather than altering soil pH or texture. Gypsum is commonly thought to be a fertilizer, yet it mainly provides calcium and sulfate to improve soil structure, reduce compaction, and mitigate sodium toxicity in sodic soils without significantly changing soil pH. Both amendments serve distinct roles in soil management and are not interchangeable for correcting nutrient deficiencies or soil physical properties.
Application Rates and Methods for Epsom Salt and Gypsum
Epsom salt is typically applied at rates of 1 to 2 pounds per 100 square feet to supply magnesium and sulfur, often dissolved in water for foliar or soil drench applications, ensuring rapid nutrient uptake. Gypsum application rates range from 20 to 50 pounds per 1,000 square feet, used primarily to improve soil structure and calcium levels, with recommended methods including surface broadcasting followed by light irrigation to facilitate soil penetration. Both materials require soil testing to tailor application rates and maximize nutrient availability while preventing over-application and environmental impact.
Choosing the Right Amendment for Your Soil Needs
Epsom salt provides magnesium and sulfur, essential for chlorophyll production and nutrient absorption, making it ideal for magnesium-deficient soils. Gypsum improves soil structure by supplying calcium and sulfur, reducing soil compaction and salt buildup without altering pH levels. Selecting between Epsom salt and gypsum depends on correcting specific nutrient deficiencies versus enhancing soil texture and drainage.
Epsom salt vs Gypsum Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com