
Broadcast seeding vs Precision seeding Illustration
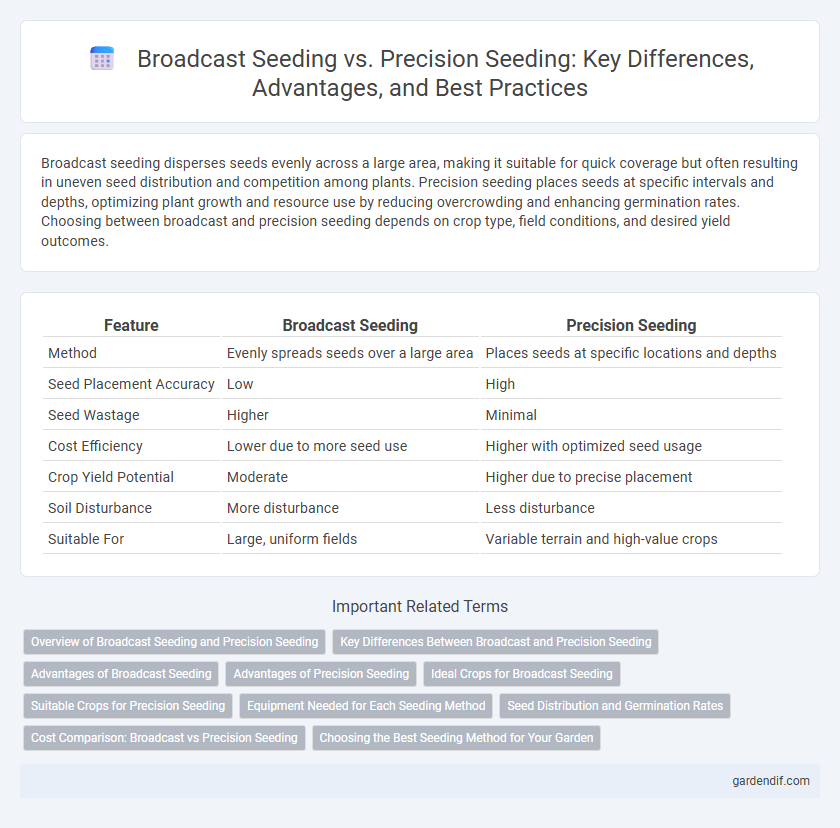
Broadcast seeding disperses seeds evenly across a large area, making it suitable for quick coverage but often resulting in uneven seed distribution and competition among plants. Precision seeding places seeds at specific intervals and depths, optimizing plant growth and resource use by reducing overcrowding and enhancing germination rates. Choosing between broadcast and precision seeding depends on crop type, field conditions, and desired yield outcomes.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Broadcast Seeding | Precision Seeding |
|---|---|---|
| Method | Evenly spreads seeds over a large area | Places seeds at specific locations and depths |
| Seed Placement Accuracy | Low | High |
| Seed Wastage | Higher | Minimal |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower due to more seed use | Higher with optimized seed usage |
| Crop Yield Potential | Moderate | Higher due to precise placement |
| Soil Disturbance | More disturbance | Less disturbance |
| Suitable For | Large, uniform fields | Variable terrain and high-value crops |
Overview of Broadcast Seeding and Precision Seeding
Broadcast seeding distributes seeds evenly across a large area, ensuring rapid ground coverage but often resulting in uneven seed placement and waste. Precision seeding places seeds individually at specific depths and intervals, maximizing germination rates and crop uniformity. This targeted approach enhances resource efficiency and yield potential by optimizing soil contact and minimizing competition among seedlings.
Key Differences Between Broadcast and Precision Seeding
Broadcast seeding involves scattering seeds broadly and unevenly across the soil surface, promoting rapid ground coverage but often resulting in variable plant density and potential seed wastage. Precision seeding places individual seeds at exact intervals and depths using specialized equipment, ensuring uniform plant spacing and maximizing germination rates. These key differences impact resource efficiency, crop uniformity, and overall yield potential in agricultural production.
Advantages of Broadcast Seeding
Broadcast seeding improves planting efficiency by covering large areas quickly, making it ideal for erosion control and lawn establishment. This method enhances seed-to-soil contact, promoting uniform germination and reducing labor costs compared to precision seeding. Broadcast seeding also accommodates a wide range of seed types and sizes, increasing flexibility in diverse agricultural and landscaping applications.
Advantages of Precision Seeding
Precision seeding enhances crop uniformity and optimizes seed spacing, resulting in better resource utilization and higher yield potential. It reduces seed waste and lowers input costs by placing seeds accurately at ideal depths and intervals. This targeted approach improves germination rates and supports sustainable farming through precise nutrient and water management.
Ideal Crops for Broadcast Seeding
Broadcast seeding is ideally suited for small grains such as wheat, barley, and rye due to their ability to establish quickly and tolerate denser plant populations. This method is also effective for forage crops like clover and alfalfa, which benefit from the uniform seed distribution it provides. Crops with small, lightweight seeds and fast germination rates perform best under broadcast seeding, optimizing soil coverage and minimizing seed waste.
Suitable Crops for Precision Seeding
Precision seeding is particularly suitable for high-value crops such as vegetables, maize, and sunflower, where uniform plant spacing and optimized seed placement significantly enhance yield and resource efficiency. This method supports crops requiring precise depth control and population management, improving germination rates and overall crop performance. It is less ideal for densely planted cereals like wheat and barley, which tolerate variable spacing and are often suited to broadcast seeding.
Equipment Needed for Each Seeding Method
Broadcast seeding requires equipment such as broadcast spreaders or rotary seeders that disperse seeds uniformly over a wide area, making it ideal for large fields but less precise seed placement. Precision seeding involves machinery like seed drills or precision planters that place seeds at exact depths and intervals, optimizing seed-to-soil contact and enhancing germination rates. The choice of equipment impacts seeding efficiency, seed wastage, and overall crop yield potential.
Seed Distribution and Germination Rates
Broadcast seeding disperses seeds broadly and unevenly, often leading to variable seed distribution that can reduce germination rates due to overcrowding or gaps. Precision seeding places seeds at uniform intervals and depth, optimizing seed-to-soil contact and improving germination rates by ensuring consistent resource availability for each seed. Enhanced seed distribution accuracy in precision seeding promotes stronger seedling emergence and higher crop uniformity compared to broadcast methods.
Cost Comparison: Broadcast vs Precision Seeding
Broadcast seeding distributes seeds over a wide area quickly but often results in higher seed wastage and uneven plant density, increasing overall costs. Precision seeding targets specific planting spots, optimizing seed use, reducing waste, and improving germination rates, which lowers input expenses despite higher equipment investment. Over time, precision seeding offers better cost-efficiency by maximizing yield potential and minimizing seed and labor costs compared to broadcast methods.
Choosing the Best Seeding Method for Your Garden
Broadcast seeding distributes seeds evenly across a large area, ideal for lawns or wildflower meadows where uniform coverage is desired, while precision seeding places seeds individually at optimal spacing, maximizing plant growth and reducing competition. Selecting the best seeding method depends on garden size, plant type, and desired density, with precision seeding often preferred for vegetable gardens and high-value crops. Understanding soil conditions and seed characteristics ensures efficient germination and healthier plant development regardless of the chosen technique.
Broadcast seeding vs Precision seeding Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com