
Seed saving vs Seed swapping Illustration
Seed saving preserves genetic diversity by allowing gardeners to collect and store seeds from their own plants, ensuring adaptation to local conditions over time. Seed swapping enhances biodiversity by facilitating the exchange of unique varieties among gardeners, broadening the range of crops cultivated in different regions. Both practices promote sustainable gardening and resilience in food systems by supporting heirloom varieties and reducing reliance on commercial seed markets.
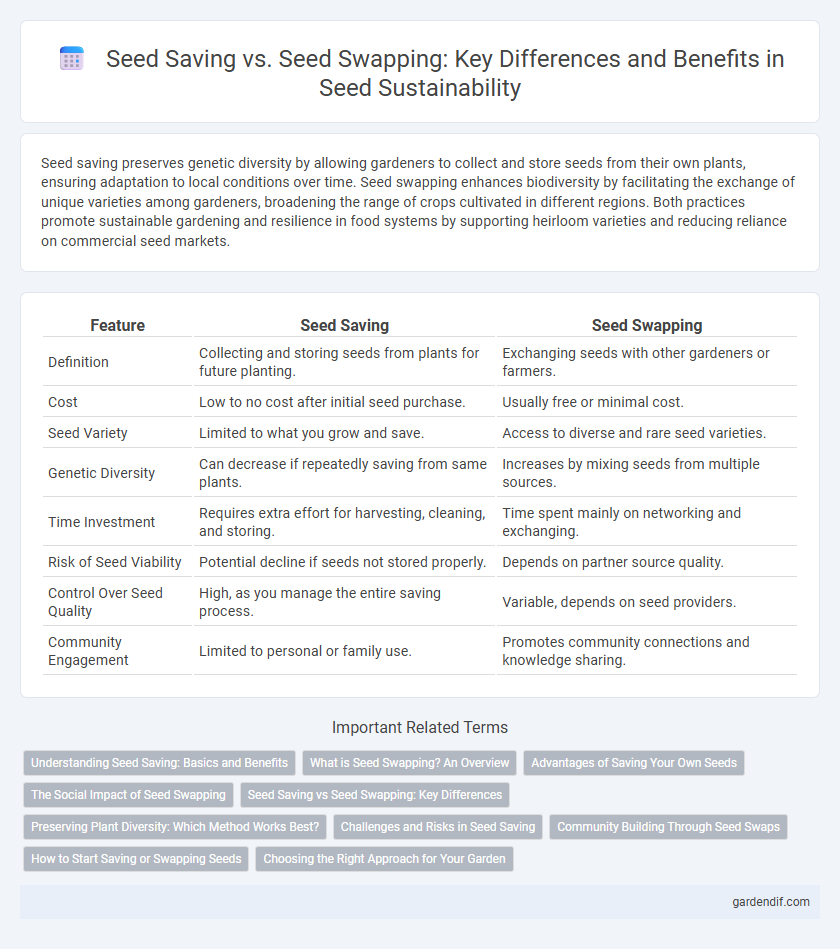
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Seed Saving | Seed Swapping |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Collecting and storing seeds from plants for future planting. | Exchanging seeds with other gardeners or farmers. |
| Cost | Low to no cost after initial seed purchase. | Usually free or minimal cost. |
| Seed Variety | Limited to what you grow and save. | Access to diverse and rare seed varieties. |
| Genetic Diversity | Can decrease if repeatedly saving from same plants. | Increases by mixing seeds from multiple sources. |
| Time Investment | Requires extra effort for harvesting, cleaning, and storing. | Time spent mainly on networking and exchanging. |
| Risk of Seed Viability | Potential decline if seeds not stored properly. | Depends on partner source quality. |
| Control Over Seed Quality | High, as you manage the entire saving process. | Variable, depends on seed providers. |
| Community Engagement | Limited to personal or family use. | Promotes community connections and knowledge sharing. |
Understanding Seed Saving: Basics and Benefits
Seed saving involves collecting and preserving seeds from open-pollinated plants to ensure genetic diversity and secure future crops. It promotes sustainability by allowing gardeners and farmers to adapt plants to local conditions while reducing dependency on commercial seed suppliers. Understanding proper techniques such as seed cleaning, drying, and storage increases germination rates and maintains seed viability across seasons.
What is Seed Swapping? An Overview
Seed swapping is the practice of exchanging seeds between gardeners and farmers to diversify plant varieties and promote agricultural biodiversity. This exchange helps preserve heirloom and rare seeds, supporting sustainable gardening and local food systems. Seed swapping fosters community engagement by sharing knowledge and resources while reducing dependence on commercial seed suppliers.
Advantages of Saving Your Own Seeds
Saving your own seeds enhances crop adaptability by preserving plant varieties suited to local climate and soil conditions. It reduces costs and dependence on commercial seed suppliers, ensuring seed availability for future planting seasons. Seed saving also promotes biodiversity by maintaining heirloom and heritage plant varieties within your garden or farm.
The Social Impact of Seed Swapping
Seed swapping fosters community resilience by promoting biodiversity and preserving heirloom varieties unique to local regions. This social practice strengthens cultural ties and encourages knowledge exchange among gardeners, creating networks that support sustainable agriculture. By democratizing seed access, seed swapping reduces dependency on commercial seed markets and enhances food sovereignty at the grassroots level.
Seed Saving vs Seed Swapping: Key Differences
Seed saving involves collecting and storing seeds from your own plants to preserve specific traits, ensuring genetic consistency and adaptability to local conditions. Seed swapping refers to the exchange of seeds between gardeners or farmers, promoting biodiversity and access to a wider variety of plant genetics. The key difference lies in seed saving's focus on conservation and self-sufficiency, while seed swapping emphasizes diversity and community sharing.
Preserving Plant Diversity: Which Method Works Best?
Seed saving preserves plant diversity by maintaining heirloom and locally adapted varieties through careful harvesting and storage. Seed swapping enhances genetic diversity by facilitating the exchange of seeds among gardeners and farmers, promoting the spread of unique traits. Combining both methods ensures robust preservation of plant biodiversity, supporting resilient ecosystems and sustainable agriculture.
Challenges and Risks in Seed Saving
Seed saving poses significant challenges such as maintaining genetic diversity and preventing cross-pollination, which can affect seed purity and plant traits. Risks include potential loss of seed viability due to improper storage conditions and susceptibility to diseases that can be carried over from parent plants. Compared to seed swapping, seed saving requires more technical knowledge and vigilant management to ensure seed quality and sustainability.
Community Building Through Seed Swaps
Seed swapping fosters community building by encouraging gardeners to exchange diverse, locally adapted seeds, enhancing genetic diversity and resilience in shared gardens. This practice strengthens social bonds and promotes collective knowledge about sustainable agriculture and heirloom varieties. Unlike seed saving, which is often individual, seed swapping creates dynamic networks of trust and cooperation among participants.
How to Start Saving or Swapping Seeds
Start saving seeds by selecting healthy, mature plants and allowing seeds to fully ripen before harvesting to ensure high viability. For seed swapping, join local gardening clubs or online platforms where gardeners exchange diverse, regionally adapted seeds to promote biodiversity. Properly label and store seeds in cool, dry conditions to maintain freshness and increase germination success during future planting seasons.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Garden
Seed saving preserves genetic diversity by maintaining heritage varieties adapted to your specific garden conditions, ensuring resilience and sustainability. Seed swapping introduces new genetics, enhancing plant variety and encouraging community collaboration among gardeners. Selecting between saving and swapping seeds depends on your garden goals, local climate, and interest in either preserving tradition or exploring innovation.
Seed saving vs Seed swapping Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com