
Frost-hardy plants vs Frost-tender plants Illustration
Frost-hardy plants withstand freezing temperatures and continue to thrive during cold seasons, making them ideal for winter gardens. Frost-tender plants, on the other hand, are susceptible to frost damage and require protection or indoor relocation when temperatures drop. Selecting the appropriate plant type based on frost tolerance ensures successful growth and seasonal resilience.
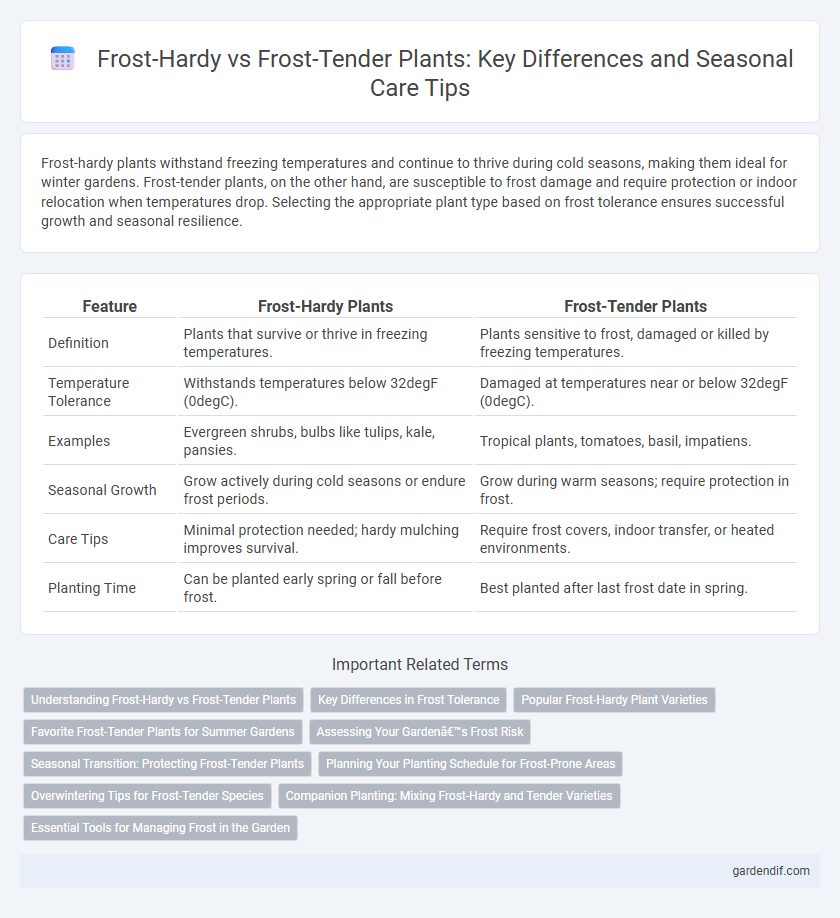
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Frost-Hardy Plants | Frost-Tender Plants |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Plants that survive or thrive in freezing temperatures. | Plants sensitive to frost, damaged or killed by freezing temperatures. |
| Temperature Tolerance | Withstands temperatures below 32degF (0degC). | Damaged at temperatures near or below 32degF (0degC). |
| Examples | Evergreen shrubs, bulbs like tulips, kale, pansies. | Tropical plants, tomatoes, basil, impatiens. |
| Seasonal Growth | Grow actively during cold seasons or endure frost periods. | Grow during warm seasons; require protection in frost. |
| Care Tips | Minimal protection needed; hardy mulching improves survival. | Require frost covers, indoor transfer, or heated environments. |
| Planting Time | Can be planted early spring or fall before frost. | Best planted after last frost date in spring. |
Understanding Frost-Hardy vs Frost-Tender Plants
Frost-hardy plants possess cellular adaptations and protective mechanisms that enable them to survive freezing temperatures and frost exposure without significant damage, making them suitable for cultivation in colder climates or during early spring and late autumn. Frost-tender plants lack these protective traits, causing their tissues to be highly susceptible to frost injury, which can lead to wilting, blackened foliage, or plant death when temperatures drop below freezing. Understanding the difference between frost-hardy and frost-tender plants is essential for gardeners and farmers to select appropriate species for seasonal planting schedules and frost risk management.
Key Differences in Frost Tolerance
Frost-hardy plants, such as pansies and kale, possess cellular structures and antifreeze proteins that enable them to survive temperatures below freezing by preventing ice crystal formation within their tissues. In contrast, frost-tender plants like tomatoes and impatiens lack these protective adaptations, making their cells susceptible to damage and death at frost onset. Understanding these key differences in frost tolerance guides effective seasonal planting and garden management to protect vulnerable species from cold stress.
Popular Frost-Hardy Plant Varieties
Popular frost-hardy plant varieties such as hellebores, ornamental cabbages, and pansies thrive in cold temperatures, making them ideal for winter gardens. These resilient plants tolerate frost and can survive sub-freezing conditions without damage, extending garden color and texture through the colder months. In contrast, frost-tender plants like impatiens and begonias require protection or indoor environments to avoid frost damage and ensure continued growth.
Favorite Frost-Tender Plants for Summer Gardens
Favorite frost-tender plants for summer gardens include tender annuals like impatiens, begonias, and petunias, which thrive in warm temperatures and vibrant sunlight. These plants require protection from late spring and early fall frosts, as their delicate leaves and blooms are vulnerable to cold damage. Gardeners often use frost cloths or plant containers indoors to extend their growing season for these colorful, heat-loving species.
Assessing Your Garden’s Frost Risk
Assessing your garden's frost risk involves understanding the distinction between frost-hardy plants, which can withstand temperatures below freezing, and frost-tender plants, which are vulnerable to frost damage. Key factors include your region's average last frost date, microclimates within your garden, and soil moisture levels, all crucial for predicting frost exposure. Protecting frost-tender species with mulch, frost cloths, or relocating pots minimizes damage and ensures garden vitality during cold spells.
Seasonal Transition: Protecting Frost-Tender Plants
During the seasonal transition from autumn to winter, protecting frost-tender plants is crucial to prevent damage from dropping temperatures and frost. Frost-hardy plants, such as kale and rosemary, can withstand freezing conditions, while frost-tender plants like basil and impatiens require mulching, covering with frost cloths, or moving indoors to maintain their health. Implementing these protective measures ensures frost-tender plants survive until warmer spring temperatures return.
Planning Your Planting Schedule for Frost-Prone Areas
Frost-hardy plants such as kale, spinach, and pansies withstand temperatures below freezing, making them ideal for early spring or late fall planting in frost-prone areas. In contrast, frost-tender plants like tomatoes, peppers, and basil require waiting until after the last expected frost date to avoid damage. Careful planning using local frost zone data maximizes growth potential and minimizes crop loss in gardens exposed to cold snaps.
Overwintering Tips for Frost-Tender Species
Frost-tender plants require careful overwintering strategies to survive cold temperatures, including mulching to insulate roots and using frost cloths or protective covers during freezing nights. Indoor relocation or placing containers in unheated greenhouses can provide a controlled environment to prevent frost damage. Monitoring soil moisture and avoiding waterlogged conditions is essential to reduce stress on frost-sensitive species during winter dormancy.
Companion Planting: Mixing Frost-Hardy and Tender Varieties
Companion planting combines frost-hardy plants like kale and Brussels sprouts with frost-tender varieties such as tomatoes and peppers to extend the growing season. Frost-hardy plants provide natural protection by creating microclimates that shield tender crops from early frosts. Proper spacing and strategic arrangement optimize temperature regulation and moisture retention, enhancing overall garden resilience against cold stress.
Essential Tools for Managing Frost in the Garden
Frost-hardy plants like pansies and kale withstand low temperatures with minimal protection, while frost-tender plants such as tomatoes and impatiens require more careful management. Essential tools for protecting these plants include frost cloths, cold frames, and garden blankets, which insulate against freezing temperatures and prevent frost damage. Portable heaters and soil thermometers also help monitor and maintain optimal growing conditions during frost-prone nights.
Frost-hardy plants vs Frost-tender plants Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com