
Overwintering crops vs Annual cropping Illustration
Overwintering crops provide soil cover during winter, reducing erosion and nutrient loss while enhancing soil structure and microbial activity compared to annual cropping. This practice improves water retention and supports early-season growth, offering a more sustainable approach to land management. Annual cropping, by contrast, often leaves soil bare during off-seasons, increasing vulnerability to degradation and reducing long-term soil health.
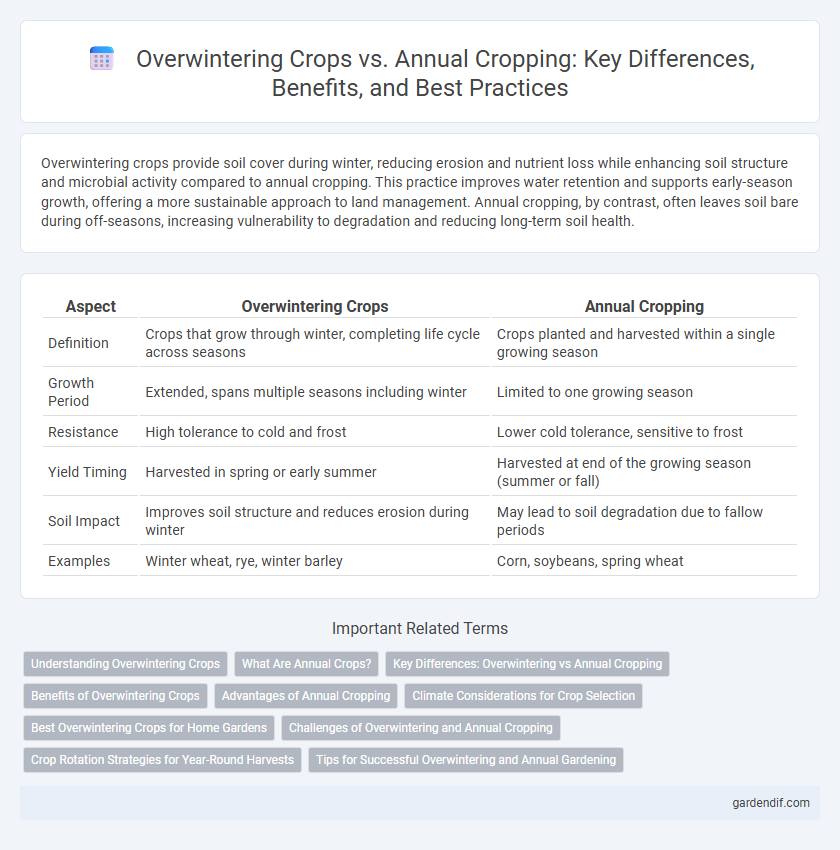
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Overwintering Crops | Annual Cropping |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Crops that grow through winter, completing life cycle across seasons | Crops planted and harvested within a single growing season |
| Growth Period | Extended, spans multiple seasons including winter | Limited to one growing season |
| Resistance | High tolerance to cold and frost | Lower cold tolerance, sensitive to frost |
| Yield Timing | Harvested in spring or early summer | Harvested at end of the growing season (summer or fall) |
| Soil Impact | Improves soil structure and reduces erosion during winter | May lead to soil degradation due to fallow periods |
| Examples | Winter wheat, rye, winter barley | Corn, soybeans, spring wheat |
Understanding Overwintering Crops
Overwintering crops, such as winter wheat and rye, are planted in the fall and remain dormant during the cold months, providing soil protection and early spring growth. These crops enhance soil structure, reduce erosion, and improve nutrient retention compared to annual cropping, which involves planting and harvesting within a single growing season. Understanding the benefits of overwintering crops helps optimize crop rotation, increase yield stability, and support sustainable agricultural practices.
What Are Annual Crops?
Annual crops complete their entire life cycle--from germination to seed production--within a single growing season, typically lasting less than a year. Common examples include wheat, maize, and soybeans, which require replanting each season due to their inability to survive harsh winter conditions. These crops offer rapid turnover and flexibility in crop rotation but lack the resilience of overwintering crops that survive multiple seasons.
Key Differences: Overwintering vs Annual Cropping
Overwintering crops, such as winter wheat and rye, survive through cold seasons by entering dormancy, providing soil cover and reducing erosion, while annual cropping involves planting and harvesting crops, like corn and soybeans, within a single growing season without surviving frost. Overwintering enhances soil health by maintaining organic matter and supporting beneficial microorganisms during winter, contrasting with annual cropping that often leaves soil bare in colder months. Yield consistency and nutrient cycling differ as overwintering crops can capture residual nitrogen and improve soil structure, whereas annual crops typically require replanting and additional soil management each year.
Benefits of Overwintering Crops
Overwintering crops enhance soil structure and increase organic matter by maintaining root systems during colder months, reducing erosion and nutrient loss. These crops improve nitrogen fixation and moisture retention, leading to higher yields and greater resilience against drought and frost compared to annual cropping systems. Farmers benefit from extended growing seasons and reduced input costs due to the natural soil conditioning provided by overwintering crops.
Advantages of Annual Cropping
Annual cropping offers distinct advantages such as faster crop turnover and the ability to cultivate a wider variety of crops within a single year, boosting overall productivity. This approach minimizes pest and disease cycles by disrupting their life stages, enhancing crop health and yield stability. Farmers benefit from flexible planting schedules and the opportunity to rotate crops more frequently, improving soil fertility and reducing the need for chemical inputs.
Climate Considerations for Crop Selection
Overwintering crops demonstrate resilience against cold temperatures and frost, enabling growth during off-season periods and reducing soil erosion risks. Annual cropping requires careful climate assessment to match crop growth cycles with favorable temperature and precipitation patterns, ensuring optimal yield. Selecting crops based on local climate data, such as chill hours and frost dates, maximizes adaptation and sustainable production.
Best Overwintering Crops for Home Gardens
Kale, garlic, and spinach are among the best overwintering crops for home gardens due to their cold tolerance and ability to thrive in low temperatures. These crops not only extend the growing season but also improve soil health by reducing erosion and enhancing nutrient cycling. Choosing hardy varieties like Siberian kale and elephant garlic ensures reliable yields through the winter months, making them ideal for sustainable home gardening.
Challenges of Overwintering and Annual Cropping
Overwintering crops face challenges such as frost damage, pest infestations during dormancy, and nutrient depletion in the soil, which can reduce yield potential. Annual cropping demands intense soil preparation and crop rotation to maintain soil fertility and manage weed pressure effectively. Both systems require careful management of water resources and timely planting to optimize growth and minimize losses.
Crop Rotation Strategies for Year-Round Harvests
Overwintering crops enhance soil health and extend the growing season by maintaining active root systems during winter, improving nutrient cycling in crop rotation strategies. Integrating these crops with annual cropping systems optimizes land use, reduces pest pressures, and ensures continuous yields throughout the year. This approach supports sustainable agriculture by balancing soil fertility management and minimizing fallow periods for consistent harvests.
Tips for Successful Overwintering and Annual Gardening
Overwintering crops like kale, spinach, and garlic thrive with proper soil preparation, mulch application, and timely planting to protect against frost damage. Annual gardening success depends on selecting region-appropriate seeds, consistent watering, and regular pest management throughout the growing season. Both methods benefit from soil testing and nutrient amendments to enhance plant resilience and yield.
Overwintering crops vs Annual cropping Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com