
wicking bed vs conventional raised bed Illustration
Wicking beds offer efficient water management by using a water reservoir that allows plants to draw moisture as needed, reducing water waste compared to conventional raised beds. Conventional raised beds rely on surface watering, which can lead to uneven moisture distribution and more frequent irrigation. Wicking beds promote healthier root growth and conserve water, making them ideal for dry climates and sustainable gardening.
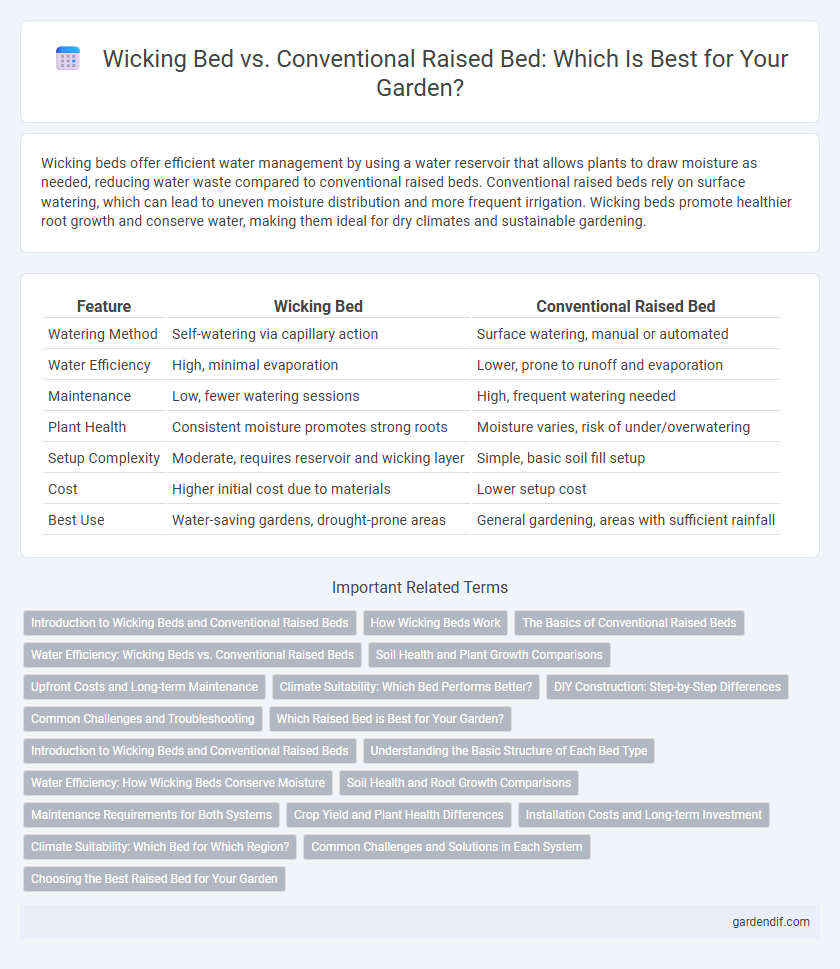
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Wicking Bed | Conventional Raised Bed |
|---|---|---|
| Watering Method | Self-watering via capillary action | Surface watering, manual or automated |
| Water Efficiency | High, minimal evaporation | Lower, prone to runoff and evaporation |
| Maintenance | Low, fewer watering sessions | High, frequent watering needed |
| Plant Health | Consistent moisture promotes strong roots | Moisture varies, risk of under/overwatering |
| Setup Complexity | Moderate, requires reservoir and wicking layer | Simple, basic soil fill setup |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to materials | Lower setup cost |
| Best Use | Water-saving gardens, drought-prone areas | General gardening, areas with sufficient rainfall |
Introduction to Wicking Beds and Conventional Raised Beds
Wicking beds use a self-watering system where water is stored in a reservoir below the soil, allowing moisture to wick upward directly to plant roots, enhancing water efficiency and reducing watering frequency. Conventional raised beds rely on traditional soil beds elevated above ground level without built-in water reservoirs, requiring regular surface watering which can lead to uneven moisture distribution. The wicking bed design is particularly effective in arid climates and for water conservation, while conventional raised beds offer simplicity and flexibility for a variety of soil and plant types.
How Wicking Beds Work
Wicking beds use a water reservoir beneath the soil that allows plants to draw moisture upward through capillary action, ensuring consistent hydration directly to the roots. This self-watering mechanism reduces water waste and promotes healthier plant growth compared to conventional raised beds, which rely on surface watering and often lead to uneven moisture distribution. The design of wicking beds enhances efficiency by maintaining optimal soil moisture levels, reducing the need for frequent irrigation.
The Basics of Conventional Raised Beds
Conventional raised beds consist of elevated soil beds typically framed with wood, stone, or metal, designed to improve drainage and soil aeration for optimal plant growth. They require regular watering since water retention depends on soil composition and climate, making irrigation frequency critical for healthy crops. These beds promote better root development and soil warmth but lack the self-watering capabilities inherent in wicking beds.
Water Efficiency: Wicking Beds vs. Conventional Raised Beds
Wicking beds significantly enhance water efficiency by using a self-watering reservoir that delivers moisture directly to plant roots, reducing evaporation and runoff commonly seen in conventional raised beds. This system can reduce water usage by up to 50% compared to traditional methods, making it ideal for drought-prone areas or water-restricted gardens. Conventional raised beds rely heavily on surface watering, which often leads to uneven moisture distribution and increased water loss.
Soil Health and Plant Growth Comparisons
Wicking beds maintain consistent soil moisture through capillary action, promoting deeper root development and improved nutrient uptake, which enhances overall plant growth compared to conventional raised beds. Conventional raised beds often experience fluctuating moisture levels, leading to increased soil dryness and potential nutrient stress that can hinder optimal soil microbial activity and plant health. Enhanced aeration and moisture retention in wicking beds create an ideal environment for beneficial soil organisms, improving soil structure and fertility over time.
Upfront Costs and Long-term Maintenance
Wicking beds typically require higher upfront costs due to the need for waterproof liners, irrigation components, and specialized soil layering compared to conventional raised beds made from basic wood or metal frames filled with standard soil. Long-term maintenance of wicking beds is generally lower because the self-watering system conserves water and reduces the frequency of manual watering, while conventional raised beds often demand more frequent irrigation and soil replenishment. Over time, wicking beds can offer cost savings through improved water efficiency and minimized labor, despite the initial investment.
Climate Suitability: Which Bed Performs Better?
Wicking beds outperform conventional raised beds in arid and drought-prone climates due to their self-watering system that maintains consistent soil moisture levels, reducing water stress on plants. Conventional raised beds may require more frequent irrigation and can face challenges with uneven water distribution, especially in hot or dry conditions. Wicking beds are better suited for water conservation and sustained plant growth in climates with limited rainfall.
DIY Construction: Step-by-Step Differences
DIY construction of a wicking bed involves creating a water reservoir beneath the soil layer using waterproof liner and perforated piping, enabling self-watering compared to a conventional raised bed that relies solely on surface watering. The wicking bed requires precise layering, including a reservoir base, capillary barrier, and soil mix designed for water retention, while a conventional raised bed consists mainly of soil contained within wooden or metal frames. Installing an overflow outlet is a critical step in wicking beds to prevent waterlogging, a feature absent in standard raised bed construction.
Common Challenges and Troubleshooting
Wicking beds often face challenges with maintaining optimal water levels, as excessive moisture can lead to root rot while insufficient water reduces efficiency, unlike conventional raised beds that require frequent manual watering. Troubleshooting wicking beds involves monitoring the water reservoir carefully, ensuring the wicking mechanism remains unobstructed, and checking for proper soil aeration to prevent waterlogging. Conventional raised beds commonly struggle with inconsistent moisture distribution and soil erosion, necessitating regular irrigation adjustments and mulching to retain soil structure.
Which Raised Bed is Best for Your Garden?
A wicking bed offers superior water efficiency by utilizing a self-watering reservoir that delivers moisture directly to plant roots, reducing irrigation frequency compared to a conventional raised bed. Conventional raised beds provide excellent soil control and drainage but often require more frequent watering and can lead to uneven moisture distribution. Choosing the best raised bed depends on your garden's water availability, climate, and maintenance preferences, with wicking beds being ideal for water conservation and conventional beds suited for crops needing well-drained soil.
wicking bed vs conventional raised bed Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com