
Tiered raised bed vs Single-level raised bed Illustration
Tiered raised beds maximize planting space by utilizing vertical levels, allowing gardeners to grow a variety of crops in a compact footprint while improving drainage and soil depth control. In contrast, single-level raised beds offer simpler construction and easier access but may limit the diversity and quantity of plants grown. Choosing between tiered and single-level raised beds depends on available space, desired plant variety, and ease of maintenance.
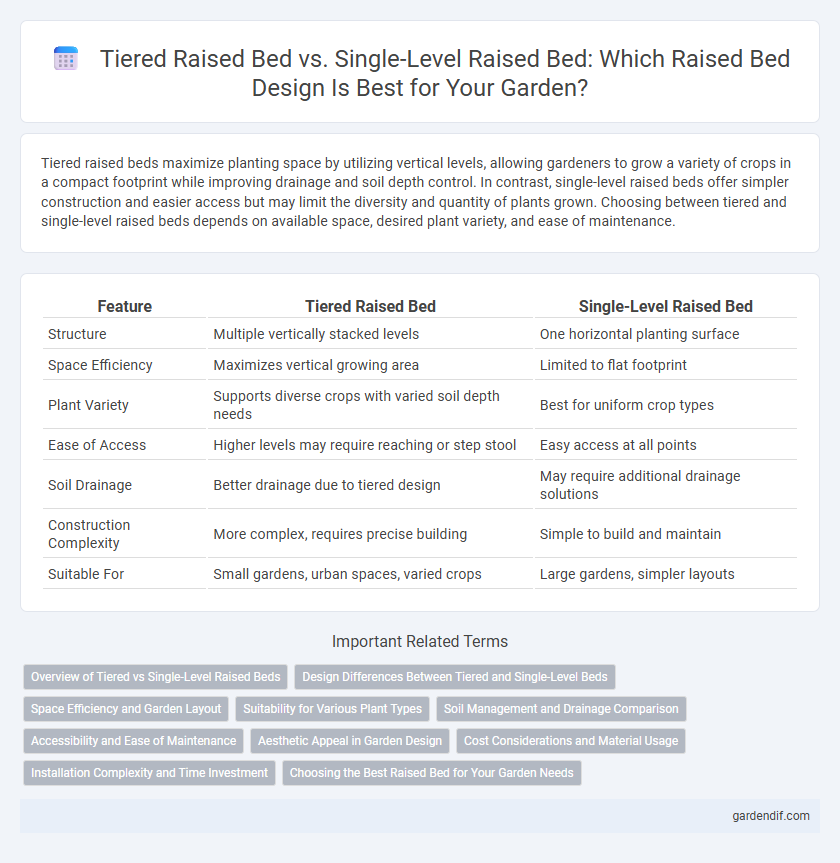
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Tiered Raised Bed | Single-Level Raised Bed |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Multiple vertically stacked levels | One horizontal planting surface |
| Space Efficiency | Maximizes vertical growing area | Limited to flat footprint |
| Plant Variety | Supports diverse crops with varied soil depth needs | Best for uniform crop types |
| Ease of Access | Higher levels may require reaching or step stool | Easy access at all points |
| Soil Drainage | Better drainage due to tiered design | May require additional drainage solutions |
| Construction Complexity | More complex, requires precise building | Simple to build and maintain |
| Suitable For | Small gardens, urban spaces, varied crops | Large gardens, simpler layouts |
Overview of Tiered vs Single-Level Raised Beds
Tiered raised beds offer multiple planting levels, maximizing vertical space and allowing for diverse crop arrangements in limited areas. Single-level raised beds provide a uniform planting surface ideal for root development and simplified maintenance. Choosing between tiered and single-level beds depends on garden size, plant variety, and space optimization needs.
Design Differences Between Tiered and Single-Level Beds
Tiered raised beds feature multiple vertical levels, maximizing growing space in compact areas and improving soil drainage by allowing gravity to assist water runoff. Single-level raised beds consist of a single horizontal planting area, providing uniform soil depth and easier access for planting and maintenance. The design choice impacts plant variety, irrigation methods, and ergonomic factors in garden layout.
Space Efficiency and Garden Layout
Tiered raised beds maximize vertical space by stacking multiple planting levels, ideal for small gardens or patios where horizontal space is limited. Single-level raised beds require more ground area but offer easier access and simpler planting arrangements, suitable for expansive garden layouts. Choosing tiered raised beds enhances space efficiency and supports diverse plant varieties in compact areas, while single-level beds favor straightforward maintenance and uniform crop spacing.
Suitability for Various Plant Types
Tiered raised beds offer distinct advantages for growing a variety of plants with differing root depths and sunlight needs by creating microclimates and improved drainage on each level. Single-level raised beds provide uniform soil conditions ideal for crops that require similar growing environments, such as leafy greens or root vegetables. Gardeners can optimize yield and plant health by matching plant types to the structure of the raised bed based on space and environmental preferences.
Soil Management and Drainage Comparison
Tiered raised beds provide enhanced soil management by allowing different soil types and moisture levels to be tailored to each tier, optimizing plant growth conditions. Their design naturally improves drainage by reducing soil compaction and facilitating water runoff between levels, preventing waterlogging. In contrast, single-level raised beds offer uniform soil conditions but may face challenges with drainage, requiring careful soil amendment and irrigation management to avoid water retention issues.
Accessibility and Ease of Maintenance
Tiered raised beds enhance accessibility by reducing the need to bend or stretch, making gardening easier for individuals with limited mobility. Single-level raised beds provide straightforward maintenance and require fewer materials, offering simplicity for traditional gardening tasks. The tiered design also allows for better organization of plants by height and sunlight needs, improving overall garden management.
Aesthetic Appeal in Garden Design
Tiered raised beds offer enhanced aesthetic appeal by creating dynamic vertical layers that add depth and visual interest to garden design. Single-level raised beds provide a clean, uniform look ideal for minimalist or traditional garden styles but lack the dimensional variety of tiered structures. Incorporating tiered beds can maximize space efficiency while transforming the garden into a visually striking landscape feature.
Cost Considerations and Material Usage
Tiered raised beds typically require more materials such as additional lumber or retaining walls, resulting in higher upfront costs compared to single-level raised beds. Single-level beds generally use fewer resources and are more cost-effective, making them ideal for budget-conscious gardeners. Material efficiency in single-level designs often leads to easier setup and less ongoing maintenance expenses.
Installation Complexity and Time Investment
Tiered raised beds require more intricate planning and construction, often involving multiple levels and secure support structures that increase installation complexity compared to single-level raised beds. The time investment for tiered designs is significantly higher due to the need for precise measurements, varied material cuts, and careful layering to ensure stability and optimal plant growth. Single-level raised beds offer a simpler, quicker setup, making them ideal for gardeners seeking efficient installation with minimal technical demands.
Choosing the Best Raised Bed for Your Garden Needs
Tiered raised beds maximize vertical space, allowing for diverse plant growth and improved accessibility, ideal for gardeners with limited area or mobility considerations. Single-level raised beds offer simpler construction and maintenance, providing uniform soil depth suitable for large-scale planting or root vegetables. Selecting the best raised bed depends on available space, plant types, and ease of care preferences tailored to your garden's specific requirements.
Tiered raised bed vs Single-level raised bed Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com