
Sheet mulching vs Soil replacement Illustration
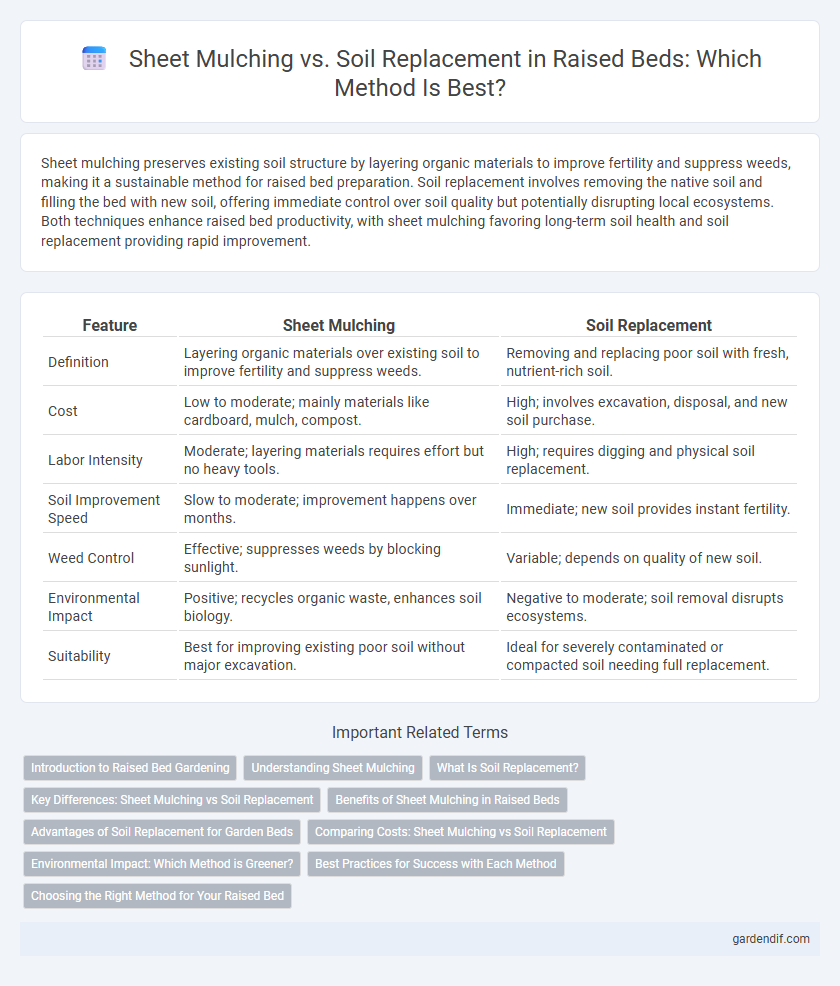
Sheet mulching preserves existing soil structure by layering organic materials to improve fertility and suppress weeds, making it a sustainable method for raised bed preparation. Soil replacement involves removing the native soil and filling the bed with new soil, offering immediate control over soil quality but potentially disrupting local ecosystems. Both techniques enhance raised bed productivity, with sheet mulching favoring long-term soil health and soil replacement providing rapid improvement.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Sheet Mulching | Soil Replacement |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Layering organic materials over existing soil to improve fertility and suppress weeds. | Removing and replacing poor soil with fresh, nutrient-rich soil. |
| Cost | Low to moderate; mainly materials like cardboard, mulch, compost. | High; involves excavation, disposal, and new soil purchase. |
| Labor Intensity | Moderate; layering materials requires effort but no heavy tools. | High; requires digging and physical soil replacement. |
| Soil Improvement Speed | Slow to moderate; improvement happens over months. | Immediate; new soil provides instant fertility. |
| Weed Control | Effective; suppresses weeds by blocking sunlight. | Variable; depends on quality of new soil. |
| Environmental Impact | Positive; recycles organic waste, enhances soil biology. | Negative to moderate; soil removal disrupts ecosystems. |
| Suitability | Best for improving existing poor soil without major excavation. | Ideal for severely contaminated or compacted soil needing full replacement. |
Introduction to Raised Bed Gardening
Raised bed gardening enhances soil quality and plant growth by creating a controlled environment. Sheet mulching improves soil fertility by layering organic materials, promoting beneficial microbial activity and moisture retention. Soil replacement involves removing poor soil and filling beds with nutrient-rich soil, providing immediate improved conditions for healthier root development.
Understanding Sheet Mulching
Sheet mulching is an eco-friendly gardening technique that suppresses weeds, improves soil fertility, and enhances moisture retention by layering organic materials like cardboard, compost, and mulch directly on top of existing soil. Unlike soil replacement, which removes and replaces the native soil entirely, sheet mulching revitalizes the current soil ecosystem through natural decomposition and microbial activity. This method promotes sustainable raised bed preparation by preserving soil structure and boosting long-term soil health.
What Is Soil Replacement?
Soil replacement involves removing the existing soil from a raised bed and substituting it with a fresh, nutrient-rich soil mix to improve plant growth and drainage. This method is ideal for beds contaminated by pests, disease, or poor soil structure, providing immediate access to optimal growing conditions. Unlike sheet mulching, which improves soil gradually by layering organic materials, soil replacement offers a direct and rapid enhancement of soil quality for raised bed gardening.
Key Differences: Sheet Mulching vs Soil Replacement
Sheet mulching improves soil fertility and moisture retention by layering organic materials directly on top of the existing soil, promoting natural decomposition and microbial activity. Soil replacement involves removing the native soil entirely and substituting it with new soil, which can quickly establish ideal growing conditions but may disrupt existing soil biology. Key differences include the minimal disturbance and gradual nutrient enhancement of sheet mulching versus the immediate but more invasive process of soil replacement.
Benefits of Sheet Mulching in Raised Beds
Sheet mulching in raised beds enhances soil health by improving moisture retention, suppressing weeds, and increasing organic matter through natural decomposition. This method reduces labor and material costs compared to full soil replacement, making it an eco-friendly and sustainable gardening practice. Additionally, sheet mulching fosters beneficial microbial activity, leading to healthier plant growth and increased nutrient availability.
Advantages of Soil Replacement for Garden Beds
Soil replacement in garden beds provides immediate improvement in soil quality by introducing nutrient-rich, well-draining soil tailored to plant needs, enhancing root growth and moisture retention. This method reduces the risk of weed infestations and soil-borne diseases commonly associated with existing soil layers. Unlike sheet mulching, soil replacement offers a long-term, stable foundation for healthy plant development without the gradual decomposition process.
Comparing Costs: Sheet Mulching vs Soil Replacement
Sheet mulching typically costs less upfront, averaging $0.50 to $1 per square foot, due to use of organic materials like cardboard and compost, whereas soil replacement can range from $2 to $5 per square foot because of excavation, removal, and new soil purchase. Labor expenses are generally higher for soil replacement given the need for heavy equipment and disposal fees, while sheet mulching relies on manual layering processes. Long-term maintenance costs favor sheet mulching as it improves soil health gradually, reducing fertilizer and irrigation expenses compared to immediate but costly soil replacement.
Environmental Impact: Which Method is Greener?
Sheet mulching enhances soil health by recycling organic waste, reducing landfill burden and minimizing carbon emissions associated with transporting and manufacturing new soil, making it an environmentally sustainable choice. Soil replacement involves significant carbon footprint due to excavation, transportation, and potential depletion of native topsoil resources, contributing to habitat disruption and increased greenhouse gas emissions. Thus, sheet mulching is the greener option, supporting biodiversity and promoting sustainable gardening practices in raised bed construction.
Best Practices for Success with Each Method
Sheet mulching involves layering organic materials like cardboard, compost, and mulch directly over the existing soil to suppress weeds and enrich soil fertility, making it ideal for improving soil structure without excavation. Soil replacement requires removing the original soil and filling the bed with a carefully balanced mix of topsoil, compost, and amendments, ensuring optimal nutrient levels and drainage for plant health. Best practices for sheet mulching include thorough weed removal before layering and maintaining adequate moisture, while soil replacement demands proper soil testing and avoiding compaction during installation for long-term success.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Raised Bed
Sheet mulching enhances soil health by layering organic materials that suppress weeds and improve moisture retention, making it ideal for nutrient-poor or compacted areas. Soil replacement offers immediate soil quality improvement by completely removing and substituting existing soil, which suits heavily contaminated or poor-texture sites. Selecting the appropriate method depends on the existing soil condition, budget, and long-term garden goals for optimized raised bed productivity.
Sheet mulching vs Soil replacement Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com