
Open-bottom raised beds vs closed-bottom raised beds Illustration
Open-bottom raised beds provide superior drainage and root access to existing soil, promoting healthier plant growth by allowing roots to expand naturally. Closed-bottom raised beds offer greater control over soil quality and reduce weed intrusion but may require more careful watering and drainage management to prevent waterlogging. Choosing between the two depends on your garden's soil conditions, drainage needs, and plant preferences.
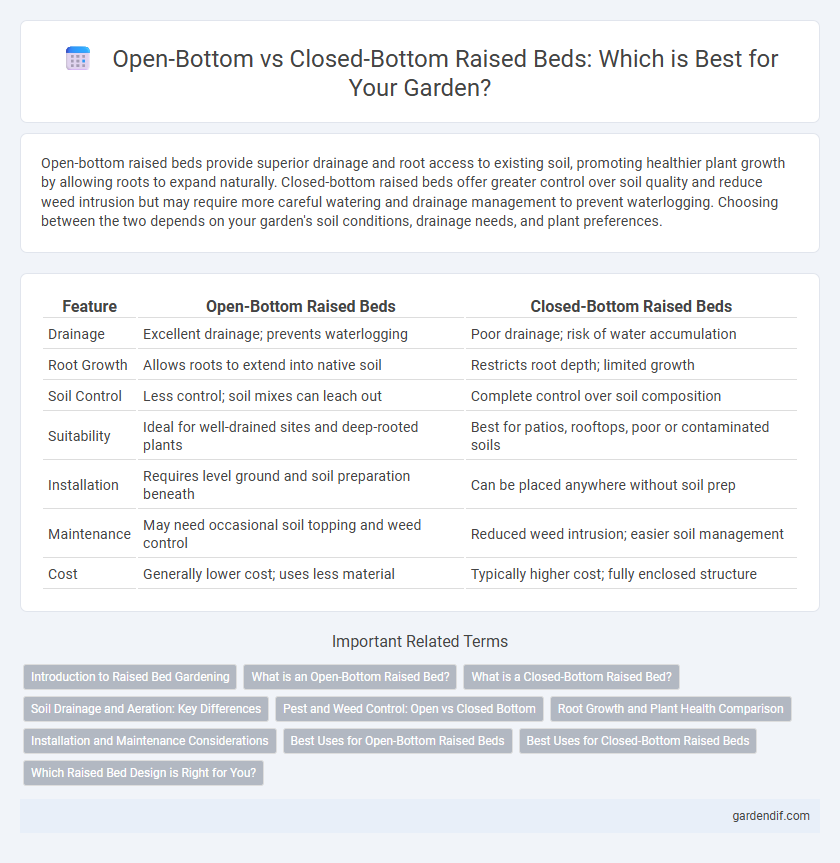
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Open-Bottom Raised Beds | Closed-Bottom Raised Beds |
|---|---|---|
| Drainage | Excellent drainage; prevents waterlogging | Poor drainage; risk of water accumulation |
| Root Growth | Allows roots to extend into native soil | Restricts root depth; limited growth |
| Soil Control | Less control; soil mixes can leach out | Complete control over soil composition |
| Suitability | Ideal for well-drained sites and deep-rooted plants | Best for patios, rooftops, poor or contaminated soils |
| Installation | Requires level ground and soil preparation beneath | Can be placed anywhere without soil prep |
| Maintenance | May need occasional soil topping and weed control | Reduced weed intrusion; easier soil management |
| Cost | Generally lower cost; uses less material | Typically higher cost; fully enclosed structure |
Introduction to Raised Bed Gardening
Open-bottom raised beds allow roots to extend directly into the native soil, promoting natural drainage and soil microorganism interaction, which enhances plant health and growth. Closed-bottom raised beds provide complete soil control, reducing weed intrusion and soil compaction, ideal for areas with poor or contaminated soil. Choosing between open and closed bottom designs depends on site conditions, soil quality, and specific gardening goals.
What is an Open-Bottom Raised Bed?
An open-bottom raised bed is a gardening structure with no base, allowing direct soil contact beneath it for natural drainage and root expansion. This design promotes healthier plant growth by enabling roots to access native soil nutrients and microorganisms, enhancing soil aeration and water absorption. Open-bottom raised beds are ideal for areas with well-draining soil and provide flexibility in garden layout and soil management.
What is a Closed-Bottom Raised Bed?
A closed-bottom raised bed is a gardening structure with a solid base that prevents soil from directly contacting the ground beneath, often made from wood, metal, or composite materials. This design helps control soil quality, prevents weed intrusion, and limits drainage, which can be beneficial for growing specific plants requiring consistent moisture. Closed-bottom raised beds are ideal for areas with poor or contaminated soil, providing a controlled environment for healthy root development.
Soil Drainage and Aeration: Key Differences
Open-bottom raised beds enhance soil drainage and aeration by allowing excess water to escape freely and air to circulate through the soil profile, preventing waterlogging and root suffocation. Closed-bottom raised beds restrict water flow, potentially causing poor drainage and reduced oxygen availability, which can lead to root rot and stunted plant growth. Proper soil structure in open-bottom beds supports healthy microbial activity and robust root systems essential for optimal plant development.
Pest and Weed Control: Open vs Closed Bottom
Open-bottom raised beds enhance natural pest control by allowing beneficial soil organisms to access the root zone, improving microbial activity and reducing pest populations. Closed-bottom raised beds prevent weed invasion from below but can trap moisture, potentially promoting root diseases and requiring more intensive management to prevent pests. Weed control in open-bottom beds relies on soil health and natural predators, whereas closed-bottom beds need regular monitoring and physical barriers to maintain pest and weed exclusion.
Root Growth and Plant Health Comparison
Open-bottom raised beds promote superior root growth by allowing roots to expand freely into the native soil, enhancing nutrient absorption and water drainage. In contrast, closed-bottom raised beds restrict root development, potentially leading to limited access to soil microbes and nutrients, which can affect overall plant health. Optimal root establishment in open-bottom designs supports stronger, healthier plants with improved resilience against drought and soil-borne diseases.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Open-bottom raised beds allow natural soil drainage and root expansion, simplifying installation by eliminating the need for a base layer or drainage setup. Maintenance is easier with open bottoms as soil organisms can access the bed, enhancing soil health and reducing the risk of waterlogging. Closed-bottom raised beds require installing drainage materials and may need frequent monitoring to prevent water buildup, increasing maintenance complexity over time.
Best Uses for Open-Bottom Raised Beds
Open-bottom raised beds excel in promoting natural drainage and healthy root development by allowing roots to penetrate the native soil beneath, making them ideal for areas with well-draining soil or existing fertile ground. These beds are best suited for growing vegetables, herbs, and flowers that require good aeration and access to deep soil nutrients. Gardeners aiming to improve soil structure and encourage beneficial microbial activity often prefer open-bottom designs for sustainable, productive gardening.
Best Uses for Closed-Bottom Raised Beds
Closed-bottom raised beds are ideal for gardeners seeking enhanced soil control and moisture retention, especially in areas with poor or contaminated ground soil. These beds prevent weed intrusion and pests from below, making them suitable for growing delicate vegetables, herbs, and flowers. They also offer better insulation, promoting root health and consistent growth in cooler climates.
Which Raised Bed Design is Right for You?
Open-bottom raised beds provide superior drainage and root expansion by allowing direct contact with native soil, ideal for gardeners with well-draining ground and natural soil fertility. Closed-bottom raised beds offer better control over soil quality and pest management, suitable for areas with poor or contaminated soil requiring a custom growing medium. Selecting the right design depends on your soil conditions, drainage needs, and gardening goals to optimize plant health and crop yield.
Open-bottom raised beds vs closed-bottom raised beds Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com