
Renewal pruning vs corrective pruning Illustration
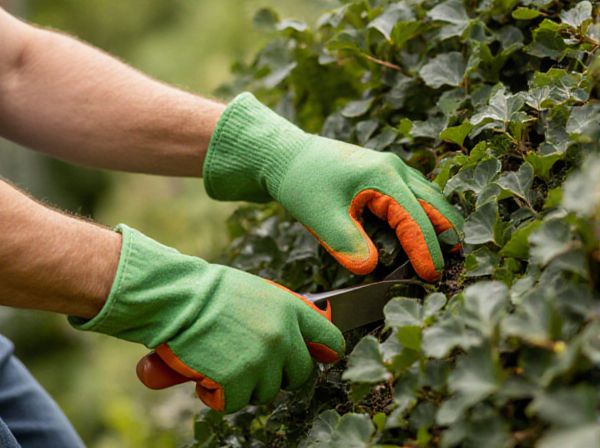
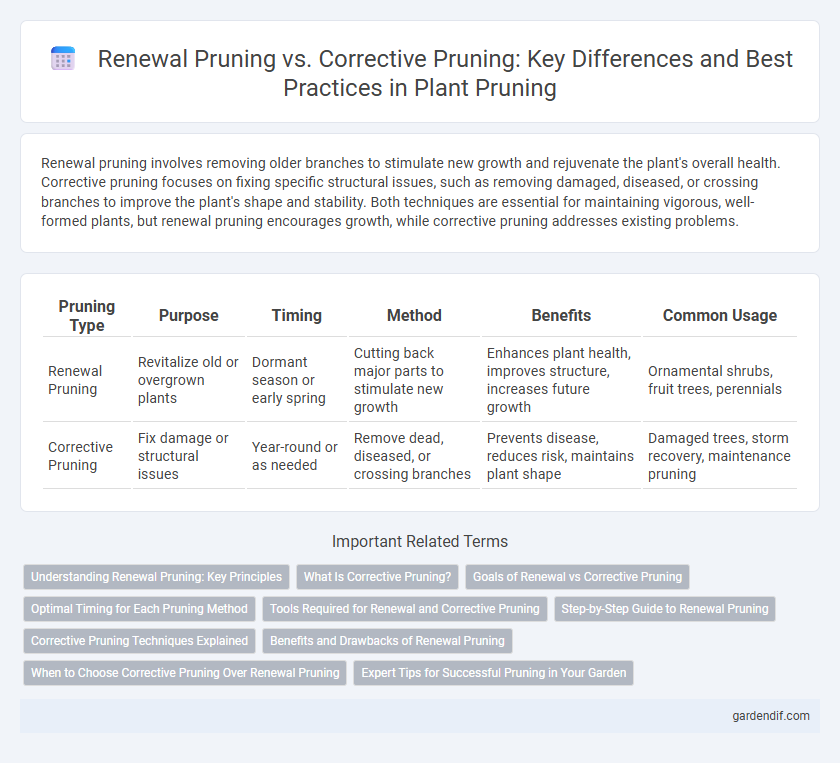
Renewal pruning involves removing older branches to stimulate new growth and rejuvenate the plant's overall health. Corrective pruning focuses on fixing specific structural issues, such as removing damaged, diseased, or crossing branches to improve the plant's shape and stability. Both techniques are essential for maintaining vigorous, well-formed plants, but renewal pruning encourages growth, while corrective pruning addresses existing problems.
Table of Comparison
| Pruning Type | Purpose | Timing | Method | Benefits | Common Usage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Renewal Pruning | Revitalize old or overgrown plants | Dormant season or early spring | Cutting back major parts to stimulate new growth | Enhances plant health, improves structure, increases future growth | Ornamental shrubs, fruit trees, perennials |
| Corrective Pruning | Fix damage or structural issues | Year-round or as needed | Remove dead, diseased, or crossing branches | Prevents disease, reduces risk, maintains plant shape | Damaged trees, storm recovery, maintenance pruning |
Understanding Renewal Pruning: Key Principles
Renewal pruning involves strategically cutting back old branches to stimulate healthy new growth, enhancing the overall structure and vitality of a plant. Key principles include removing older, less productive wood while preserving younger, vigorous shoots to promote a balanced canopy and improve light penetration. This method contrasts with corrective pruning, which primarily addresses specific damage or structural flaws without aiming to rejuvenate the entire plant.
What Is Corrective Pruning?
Corrective pruning involves removing damaged, diseased, or structurally unsound branches to improve overall tree health and prevent potential hazards. This type of pruning targets specific defects, such as dead limbs or crossing branches, to restore proper form and function. Corrective pruning differs from renewal pruning, which focuses on stimulating new growth by cutting back entire sections.
Goals of Renewal vs Corrective Pruning
Renewal pruning aims to revitalize aging trees by stimulating new growth and improving overall structure, promoting long-term health and vitality. Corrective pruning focuses on removing damaged, diseased, or structurally unsound branches to prevent hazards and maintain tree safety. Both techniques enhance tree longevity but differ in their primary goals of fostering growth versus mitigating risk.
Optimal Timing for Each Pruning Method
Renewal pruning is most effective during late winter or early spring, just before new growth begins, to stimulate vigorous shoot development and maintain tree health. Corrective pruning should be performed promptly when structural defects or damage are identified, often in late winter or early summer, to prevent further decline and improve tree structure. Timing each pruning method according to the tree species and growth cycle maximizes pruning benefits and supports long-term vitality.
Tools Required for Renewal and Corrective Pruning
Renewal pruning requires specialized tools such as loppers, pruning saws, and pole pruners to remove older branches and stimulate new growth effectively. Corrective pruning involves precise equipment like hand pruners, bypass shears, and disinfectants to address disease, damage, or structural issues without harming healthy parts. Proper maintenance of tools, including sharpening and sterilizing, is crucial for both pruning types to ensure clean cuts and prevent pathogen spread.
Step-by-Step Guide to Renewal Pruning
Renewal pruning involves systematically removing older branches to stimulate healthy new growth, typically starting with identifying and cutting out dead, damaged, or overcrowded limbs. The process includes gradually thinning the canopy over several growing seasons, ensuring the tree maintains structural integrity and vitality. This method contrasts with corrective pruning, which addresses immediate issues like removing hazardous or diseased branches without focusing on overall rejuvenation.
Corrective Pruning Techniques Explained
Corrective pruning focuses on removing damaged, diseased, or structurally unsound branches to improve tree health and safety. Techniques include thinning cuts to reduce branch density, heading cuts to eliminate problematic growth, and removing crossing or rubbing limbs that cause wounds. Proper use of corrective pruning promotes canopy balance, reduces risk of decay, and enhances tree longevity.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Renewal Pruning
Renewal pruning promotes the growth of healthy, productive branches by systematically removing older wood, enhancing air circulation and light penetration essential for plant vigor. Its benefits include revitalizing plant structure and extending lifespan, but the drawbacks involve a temporary reduction in yield and increased labor intensity during execution. The careful balance of renewal pruning helps maintain optimal plant health while avoiding excessive stress caused by over-pruning.
When to Choose Corrective Pruning Over Renewal Pruning
Choose corrective pruning over renewal pruning when addressing specific structural issues or damage in a tree, such as broken branches, disease, or crossing limbs that hinder healthy growth. Corrective pruning targets problem areas to restore the tree's natural form and improve safety without removing large sections of healthy growth. This method is essential for maintaining tree stability and preventing further deterioration when immediate intervention is required.
Expert Tips for Successful Pruning in Your Garden
Expert tips for successful pruning emphasize the importance of renewal pruning to stimulate vigorous new growth by removing older, less productive branches, while corrective pruning focuses on addressing damage, structural issues, or disease. Proper timing and technique tailored to each plant species enhance health and aesthetics, with clean cuts promoting faster healing and reducing the risk of infection. Using sharp, sterilized tools and understanding plant-specific growth patterns ensures effective renewal and corrective pruning results in a thriving, well-maintained garden.
Renewal pruning vs corrective pruning Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com