
Tissue culture vs Clone cuttings Illustration
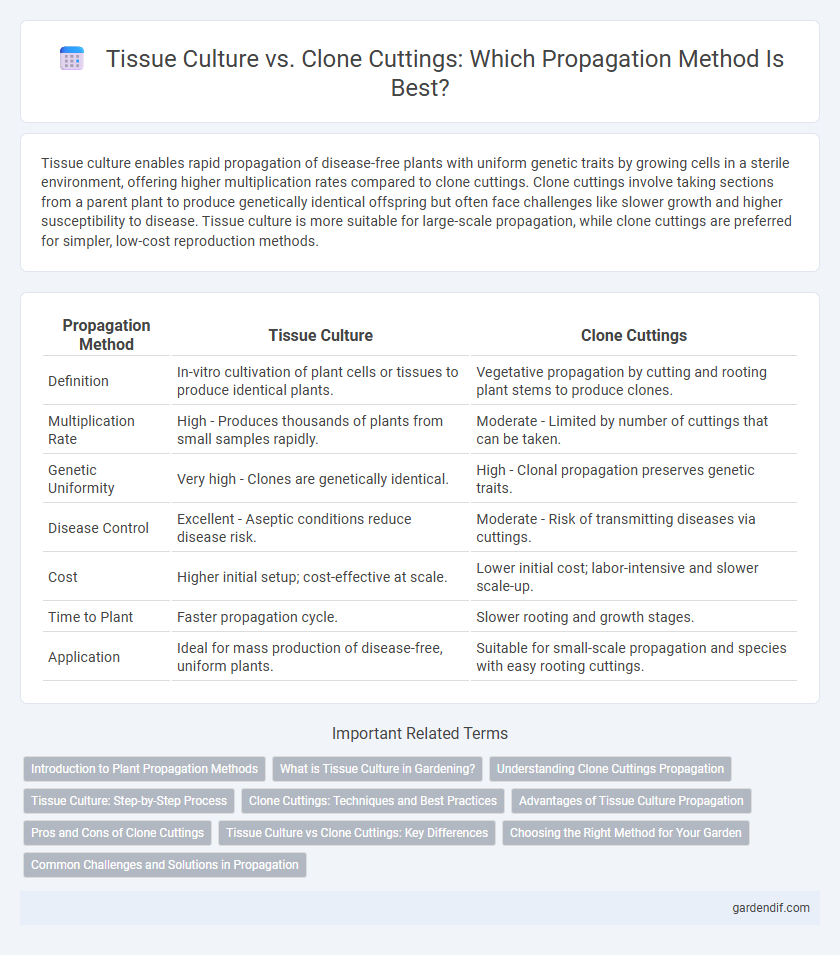
Tissue culture enables rapid propagation of disease-free plants with uniform genetic traits by growing cells in a sterile environment, offering higher multiplication rates compared to clone cuttings. Clone cuttings involve taking sections from a parent plant to produce genetically identical offspring but often face challenges like slower growth and higher susceptibility to disease. Tissue culture is more suitable for large-scale propagation, while clone cuttings are preferred for simpler, low-cost reproduction methods.
Table of Comparison
| Propagation Method | Tissue Culture | Clone Cuttings |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | In-vitro cultivation of plant cells or tissues to produce identical plants. | Vegetative propagation by cutting and rooting plant stems to produce clones. |
| Multiplication Rate | High - Produces thousands of plants from small samples rapidly. | Moderate - Limited by number of cuttings that can be taken. |
| Genetic Uniformity | Very high - Clones are genetically identical. | High - Clonal propagation preserves genetic traits. |
| Disease Control | Excellent - Aseptic conditions reduce disease risk. | Moderate - Risk of transmitting diseases via cuttings. |
| Cost | Higher initial setup; cost-effective at scale. | Lower initial cost; labor-intensive and slower scale-up. |
| Time to Plant | Faster propagation cycle. | Slower rooting and growth stages. |
| Application | Ideal for mass production of disease-free, uniform plants. | Suitable for small-scale propagation and species with easy rooting cuttings. |
Introduction to Plant Propagation Methods
Plant propagation methods include tissue culture and clone cuttings, both essential for replicating desired plant traits. Tissue culture involves growing plants in sterile, nutrient-rich media, enabling mass production from small tissue samples with genetic uniformity. Clone cuttings use parts of a parent plant, such as stems or leaves, to produce genetically identical offspring through rooting, offering a simpler and cost-effective propagation technique.
What is Tissue Culture in Gardening?
Tissue culture in gardening is a laboratory technique that involves growing plants from small tissue samples under sterile conditions to produce genetically identical clones. This method allows for rapid multiplication of disease-free and uniform plants, overcoming limitations of traditional propagation methods like clone cuttings. Tissue culture is widely used for mass production of high-quality ornamental plants, fruit trees, and vegetables, ensuring consistency and faster growth cycles.
Understanding Clone Cuttings Propagation
Clone cuttings propagation involves producing genetically identical plants by cutting parts such as stems or leaves and encouraging root development. This method ensures uniformity and rapid multiplication of desired plant traits without the need for complex lab environments required in tissue culture. Comparing both, clone cuttings offer a cost-effective, straightforward approach ideal for small-scale growers, while tissue culture suits mass propagation with strict disease control.
Tissue Culture: Step-by-Step Process
Tissue culture involves sterilizing explant tissue before placing it on a nutrient-rich culture medium under controlled environmental conditions to promote cell division and shoot proliferation. The process includes stages such as initiation, multiplication, rooting, and acclimatization, ensuring rapid and disease-free plant propagation. This method offers high multiplication rates and uniformity compared to clone cuttings, making it ideal for mass production of genetically identical plants.
Clone Cuttings: Techniques and Best Practices
Clone cuttings involve taking a section of a parent plant, such as a stem or leaf, and encouraging root growth to create a genetically identical new plant. Techniques include selecting healthy, disease-free plant material, making precise cuts at nodes, and using rooting hormones like auxins to enhance root development. Best practices emphasize maintaining optimal humidity, temperature, and sterile conditions to increase success rates and reduce contamination risks.
Advantages of Tissue Culture Propagation
Tissue culture propagation offers rapid multiplication of disease-free plants under sterile conditions, ensuring genetic uniformity across large populations. This method enables the production of plants year-round regardless of seasonal limitations, significantly accelerating crop improvement programs. High multiplication rates and space efficiency make tissue culture a cost-effective solution for mass propagation compared to traditional clone cuttings.
Pros and Cons of Clone Cuttings
Clone cuttings offer rapid propagation with genetically identical plants, ensuring uniformity and consistent crop quality, which is advantageous for commercial growers. However, clone cuttings have limitations such as vulnerability to pests and diseases due to lack of genetic diversity and slower multiplication rates compared to tissue culture. The establishment of mature plants from cuttings requires optimal environmental conditions and skilled labor, impacting overall efficiency in large-scale propagation.
Tissue Culture vs Clone Cuttings: Key Differences
Tissue culture involves the aseptic cultivation of plant cells or tissues on a nutrient medium under controlled conditions, allowing for the rapid production of genetically uniform and disease-free plants. Clone cuttings, on the other hand, rely on vegetative propagation by rooting stem or leaf cuttings from a parent plant, which may carry pathogens and exhibit genetic variability. Tissue culture offers higher multiplication rates and better quality control compared to clone cuttings, making it ideal for commercial propagation of elite cultivars.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Garden
Tissue culture offers rapid multiplication of disease-free plants by using sterile laboratory techniques, ideal for mass propagation of rare or high-value species. Clone cuttings provide a cost-effective and straightforward approach for maintaining genetic consistency in familiar plants through stem or leaf cuttings rooted in soil or water. Selecting between tissue culture and clone cuttings depends on factors like plant type, scale of propagation, disease control needs, and available resources in your garden.
Common Challenges and Solutions in Propagation
Tissue culture propagation faces contamination risks and high initial setup costs, while clone cuttings often encounter rooting difficulties and variable success rates. Sterile techniques and optimized nutrient media are essential solutions for tissue culture contamination, and applying rooting hormones with controlled environmental conditions improves clone cutting success. Both methods benefit from precise monitoring to enhance propagation efficiency and plant quality.
Tissue culture vs Clone cuttings Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com