
Heel Cuttings vs Tip Cuttings Illustration
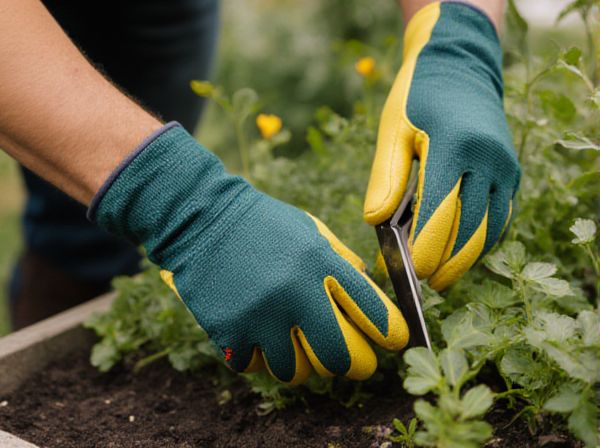
Heel cuttings retain a portion of the older stem, offering higher chances of successful rooting due to their existing mature tissue and better nutrient supply. Tip cuttings consist of the young, tender shoot tips, which root faster but may be more vulnerable to environmental stress and require more careful handling. Choosing between heel and tip cuttings depends on the plant species and propagation goals, balancing speed with rooting reliability.
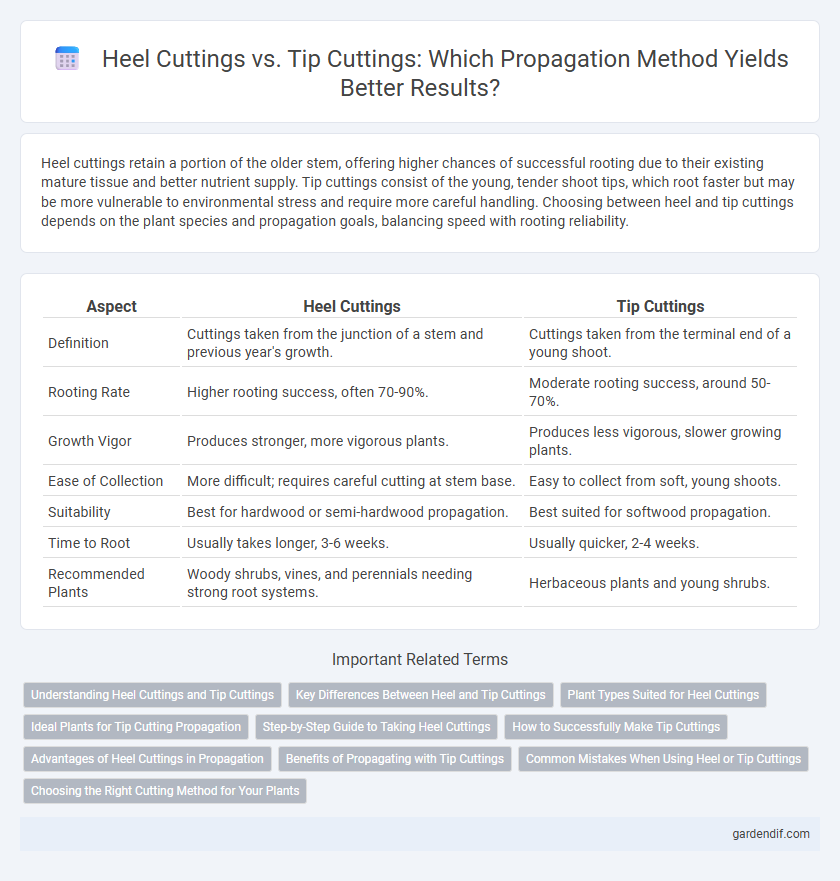
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Heel Cuttings | Tip Cuttings |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cuttings taken from the junction of a stem and previous year's growth. | Cuttings taken from the terminal end of a young shoot. |
| Rooting Rate | Higher rooting success, often 70-90%. | Moderate rooting success, around 50-70%. |
| Growth Vigor | Produces stronger, more vigorous plants. | Produces less vigorous, slower growing plants. |
| Ease of Collection | More difficult; requires careful cutting at stem base. | Easy to collect from soft, young shoots. |
| Suitability | Best for hardwood or semi-hardwood propagation. | Best suited for softwood propagation. |
| Time to Root | Usually takes longer, 3-6 weeks. | Usually quicker, 2-4 weeks. |
| Recommended Plants | Woody shrubs, vines, and perennials needing strong root systems. | Herbaceous plants and young shrubs. |
Understanding Heel Cuttings and Tip Cuttings
Heel cuttings retain a portion of the original stem base, providing a larger surface area for rooting hormones and moisture absorption, which enhances root development and increases propagation success rates. Tip cuttings consist of the terminal part of the stem, typically more tender and faster growing, but they may require more careful handling due to their fragile nature and lower initial nutrient reserves. Understanding the structural differences between heel and tip cuttings is crucial for selecting the appropriate method based on plant species and propagation goals.
Key Differences Between Heel and Tip Cuttings
Heel cuttings retain a portion of the older stem tissue, providing a woody base that often enhances rooting success, while tip cuttings consist of the soft, young shoot apex and typically root faster but may be less robust. Heel cuttings generally exhibit higher survival rates due to the presence of mature tissue, whereas tip cuttings are preferred for plants that root easily and require quicker propagation. The choice between heel and tip cuttings depends on the plant species and desired propagation speed, with heel cuttings favored for difficult-to-root plants and tip cuttings for fast-growing varieties.
Plant Types Suited for Heel Cuttings
Heel cuttings are particularly suited for woody plants such as hardwood shrubs, vines, and some trees that have mature wood with established tissues. These cuttings maintain a portion of old stem, enhancing rooting success in species like grapevines, camellias, and rhododendrons. Compared to tip cuttings, heel cuttings provide a more robust propagation method for plants requiring stable, lignified stems.
Ideal Plants for Tip Cutting Propagation
Tip cuttings are ideal for propagating plants with soft, flexible stems such as herbs (basil, mint), houseplants like pothos and philodendrons, and certain shrubs including hibiscus and hydrangea. These cuttings often root faster and develop healthier roots compared to heel cuttings due to the presence of active growth cells near the shoot tip. Selecting plants with vigorous apical growth ensures higher success rates when using tip cutting propagation techniques.
Step-by-Step Guide to Taking Heel Cuttings
Take heel cuttings by selecting mature, healthy shoots about 4-6 inches long, ensuring the heel is intact at the base for optimal rooting. Use a sharp, sterile knife to make a clean cut just below a leaf node, including a small portion of the older wood known as the heel, which promotes faster root development. Plant the heel cutting in a well-draining propagation medium, maintain consistent moisture and humidity, and place it in indirect light to encourage successful rooting within 4-6 weeks.
How to Successfully Make Tip Cuttings
To successfully make tip cuttings, select healthy, disease-free shoots with fully developed leaves and cut just below a node to encourage root development. Use a sharp, sterilized blade to create a clean cut, and dip the tip cutting in rooting hormone to enhance root initiation. Place the cuttings in a moist, well-draining propagation medium with high humidity and indirect light to maximize survival and growth rates.
Advantages of Heel Cuttings in Propagation
Heel cuttings offer superior rooting success compared to tip cuttings due to the inclusion of a small portion of mature stem tissue, which contains more developed vascular structures essential for water and nutrient transport. This mature tissue enhances hormone absorption and accelerates root initiation, resulting in faster and more robust root development. Consequently, heel cuttings exhibit higher survival rates and greater vigor during early plant growth stages in propagation.
Benefits of Propagating with Tip Cuttings
Propagating with tip cuttings offers higher rooting success rates compared to heel cuttings due to the abundance of actively growing meristematic tissue at the shoot apex. Tip cuttings often result in faster root development and more vigorous plant growth, enhancing the overall establishment of the new plant. This method also reduces the risk of disease transmission and mechanical damage commonly associated with heel cuttings.
Common Mistakes When Using Heel or Tip Cuttings
Common mistakes when using heel cuttings include failing to retain the small portion of wood attached to the base of the leaf, which provides essential nutrients and hormones for root development. With tip cuttings, a frequent error is not including enough of the stem tissue, leading to insufficient rooting potential and weaker plants. Both cutting types require careful attention to maintain moisture and avoid desiccation, as drying out can severely reduce propagation success rates.
Choosing the Right Cutting Method for Your Plants
Heel cuttings retain a portion of the parent stem, promoting faster rooting and greater nutrient uptake, making them ideal for woody plants like roses and camellias. Tip cuttings, taken from the ends of shoots, root well in softwood and herbaceous plants such as coleus and hydrangeas, ensuring quicker growth with less stem material. Selecting the right cutting type depends on plant species and growth stage, maximizing propagation success and overall plant health.
Heel Cuttings vs Tip Cuttings Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com