
Pesticide-Free Gardening vs Conventional Gardening Illustration
Pesticide-free gardening promotes a healthy ecosystem by protecting pollinators such as bees and butterflies from harmful chemicals that conventional gardening often relies on. By avoiding synthetic pesticides, plants can thrive naturally, supporting biodiversity and enhancing soil quality. This approach ensures a safer environment for pollinators, crucial for the pollination of many fruits and vegetables.
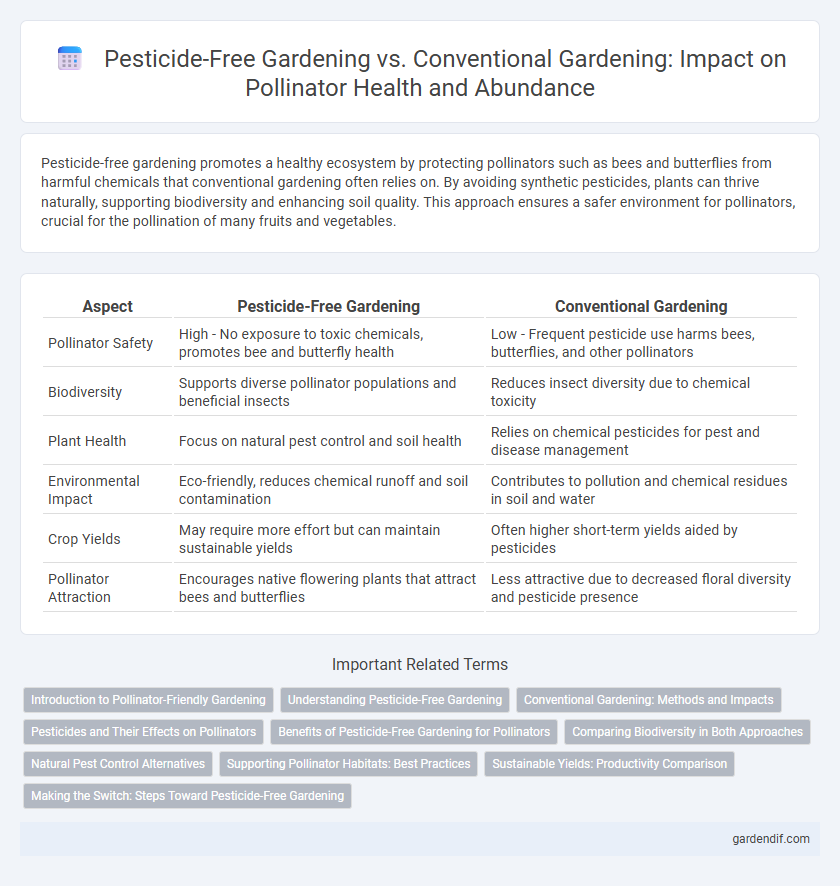
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Pesticide-Free Gardening | Conventional Gardening |
|---|---|---|
| Pollinator Safety | High - No exposure to toxic chemicals, promotes bee and butterfly health | Low - Frequent pesticide use harms bees, butterflies, and other pollinators |
| Biodiversity | Supports diverse pollinator populations and beneficial insects | Reduces insect diversity due to chemical toxicity |
| Plant Health | Focus on natural pest control and soil health | Relies on chemical pesticides for pest and disease management |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, reduces chemical runoff and soil contamination | Contributes to pollution and chemical residues in soil and water |
| Crop Yields | May require more effort but can maintain sustainable yields | Often higher short-term yields aided by pesticides |
| Pollinator Attraction | Encourages native flowering plants that attract bees and butterflies | Less attractive due to decreased floral diversity and pesticide presence |
Introduction to Pollinator-Friendly Gardening
Pesticide-free gardening prioritizes the health and survival of pollinators by eliminating harmful chemicals that disrupt their foraging and reproductive behaviors. Conventional gardening often relies on synthetic pesticides, which pose significant risks to bees, butterflies, and other essential pollinators critical for ecosystem balance and crop production. Embracing pollinator-friendly gardening techniques enhances biodiversity, supports native pollinator populations, and promotes sustainable plant growth without the ecological drawbacks of chemical use.
Understanding Pesticide-Free Gardening
Pesticide-free gardening prioritizes natural pest control methods, promoting biodiversity and providing a safer habitat for pollinators such as bees, butterflies, and hummingbirds. Avoiding synthetic chemicals protects pollinators from harmful toxins that disrupt their foraging behavior and reproductive cycles. Organic mulches, companion planting, and attracting beneficial insects create a resilient garden ecosystem supporting pollinator health and sustainability.
Conventional Gardening: Methods and Impacts
Conventional gardening relies heavily on synthetic pesticides and fertilizers to control pests and boost plant growth, often leading to reduced biodiversity and harming beneficial pollinators like bees and butterflies. These chemical inputs can contaminate soil and water, disrupting ecosystems and decreasing the resilience of garden habitats. Persistent pesticide exposure compromises pollinator health by impairing navigation, reproduction, and immune functions, ultimately threatening pollination services essential for crop yields and plant diversity.
Pesticides and Their Effects on Pollinators
Pesticide-free gardening eliminates the use of harmful chemicals that disrupt pollinator health by preventing exposure to neurotoxic substances like neonicotinoids, which cause disorientation and reduced foraging ability in bees. Conventional gardening often relies on synthetic pesticides that contaminate nectar and pollen, leading to pollinator population declines and impaired reproduction. Promoting pesticide-free practices supports biodiversity and enhances ecosystem resilience by safeguarding essential pollinator species such as honeybees, bumblebees, and butterflies.
Benefits of Pesticide-Free Gardening for Pollinators
Pesticide-free gardening significantly enhances pollinator health by eliminating exposure to harmful chemicals that disrupt their navigation and reproduction. Native bees, butterflies, and other vital pollinators thrive in environments free from synthetic pesticides, resulting in increased pollination efficiency and biodiversity. Creating pesticide-free habitats promotes sustainable ecosystems and supports long-term agricultural productivity through improved pollinator populations.
Comparing Biodiversity in Both Approaches
Pesticide-free gardening significantly enhances biodiversity by creating a safer habitat for pollinators such as bees, butterflies, and native insects, promoting ecological balance. Conventional gardening often relies on chemical pesticides that reduce pollinator populations and disrupt natural predator-prey relationships, leading to diminished biodiversity. Studies show that pesticide-free gardens support a wider variety of pollinator species and contribute to healthier, more resilient ecosystems.
Natural Pest Control Alternatives
Pesticide-free gardening promotes natural pest control alternatives such as companion planting, introducing beneficial insects like ladybugs and predatory wasps, and using organic mulches that enhance soil health and reduce pest populations. Conventional gardening often relies on synthetic chemicals that can harm pollinators like bees and butterflies, disrupting ecosystem balance and reducing biodiversity. Emphasizing ecological pest management supports pollinator health and encourages sustainable garden ecosystems.
Supporting Pollinator Habitats: Best Practices
Pesticide-free gardening significantly enhances pollinator habitats by eliminating harmful chemicals that disrupt bee and butterfly populations, fostering a diverse range of native flowering plants that provide essential nectar and pollen sources. Conventional gardening often relies on synthetic pesticides and herbicides that diminish pollinator food availability and degrade habitat quality, reducing biodiversity and ecosystem resilience. Emphasizing organic composting, mulching, and planting pollinator-friendly perennials creates sustainable environments where vital pollination services thrive, supporting food security and ecological balance.
Sustainable Yields: Productivity Comparison
Pesticide-free gardening supports sustainable yields by encouraging a balanced ecosystem where pollinators thrive, enhancing fruit and seed production through natural pest control. Conventional gardening often relies on chemical pesticides that can disrupt pollinator populations, leading to potential declines in crop productivity over time. Studies show that integrating pollinator-friendly practices in pesticide-free systems maintains or improves productivity while preserving biodiversity and long-term soil health.
Making the Switch: Steps Toward Pesticide-Free Gardening
Transitioning to pesticide-free gardening involves selecting native plants that support local pollinators and improving soil health through organic composting techniques. Implementing integrated pest management practices, such as introducing beneficial insects and using natural repellents, reduces pest populations without harmful chemicals. Regular monitoring and maintaining plant diversity create a resilient garden ecosystem that fosters pollinator attraction and sustainability.
Pesticide-Free Gardening vs Conventional Gardening Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com