
Hoverflies vs Wasps Illustration
Hoverflies and wasps both play important roles in pollination, but hoverflies are generally more efficient due to their frequent visits to flowers and their brush-like bodies that gather pollen easily. Unlike wasps, which can be aggressive and primarily consume other insects, hoverflies are harmless and primarily feed on nectar and pollen, making them vital for plant reproduction. Their mimicry of wasps provides protection from predators without compromising their valuable pollination activities.
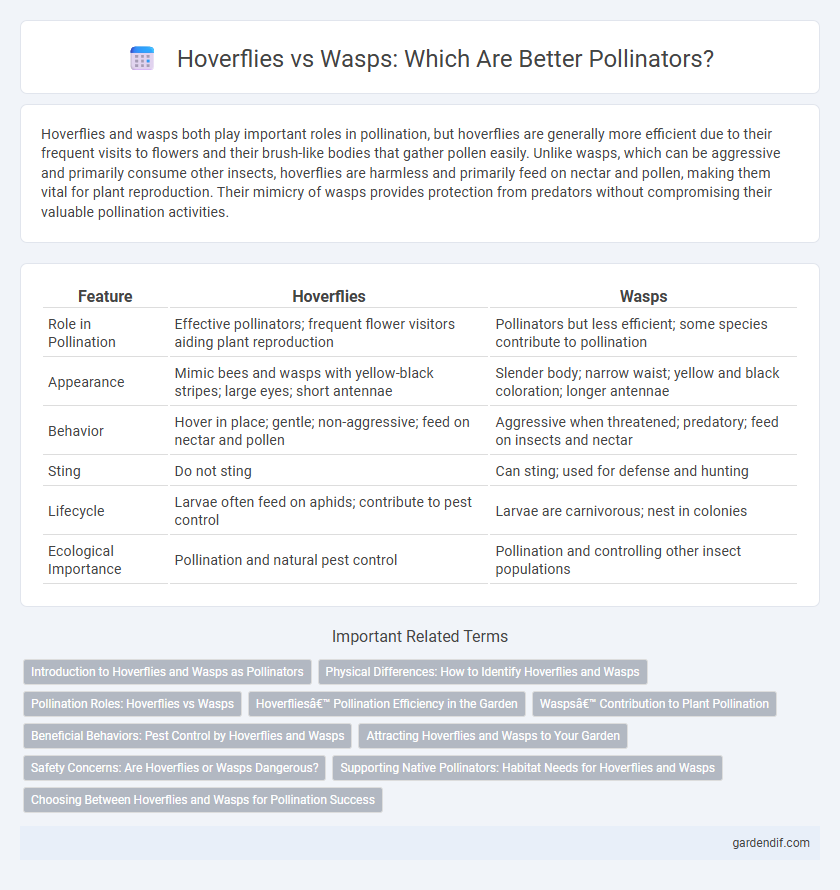
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Hoverflies | Wasps |
|---|---|---|
| Role in Pollination | Effective pollinators; frequent flower visitors aiding plant reproduction | Pollinators but less efficient; some species contribute to pollination |
| Appearance | Mimic bees and wasps with yellow-black stripes; large eyes; short antennae | Slender body; narrow waist; yellow and black coloration; longer antennae |
| Behavior | Hover in place; gentle; non-aggressive; feed on nectar and pollen | Aggressive when threatened; predatory; feed on insects and nectar |
| Sting | Do not sting | Can sting; used for defense and hunting |
| Lifecycle | Larvae often feed on aphids; contribute to pest control | Larvae are carnivorous; nest in colonies |
| Ecological Importance | Pollination and natural pest control | Pollination and controlling other insect populations |
Introduction to Hoverflies and Wasps as Pollinators
Hoverflies, belonging to the family Syrphidae, are effective pollinators known for their mimicry of wasps and bees, contributing significantly to the pollination of various flowering plants. Wasps, despite often being overlooked, play a vital role in pollination by transferring pollen as they visit flowers for nectar, especially in ecosystems where typical pollinators like bees are less abundant. Both hoverflies and wasps enhance biodiversity and support agricultural productivity by facilitating the reproduction of many crops and wild plants.
Physical Differences: How to Identify Hoverflies and Wasps
Hoverflies can be identified by their large, compound eyes and short antennae, while wasps have longer, segmented antennae and narrower waists. Hoverflies often display bright yellow and black bands mimicking wasps but lack the stinger and have a more robust, rounded body shape. Wasps possess a slimmer, elongated body with a distinct constriction between the thorax and abdomen, aiding in differentiating these important pollinators from potentially harmful insects.
Pollination Roles: Hoverflies vs Wasps
Hoverflies contribute significantly to pollination by visiting a wide variety of flowers, transferring pollen efficiently while feeding on nectar, making them vital for ecosystem health and crop production. Wasps, although less efficient pollinators than hoverflies, still play a role by accidentally transferring pollen during their visits to flowers for nectar or prey. The distinct pollination behaviors and flower preferences of hoverflies and wasps influence plant reproduction and biodiversity in different habitats.
Hoverflies’ Pollination Efficiency in the Garden
Hoverflies exhibit remarkable pollination efficiency in the garden due to their frequent visits and preference for a wide variety of flowering plants, transferring pollen effectively between blooms. Their ability to hover and access nectar from shallow and tubular flowers enhances pollen distribution compared to many wasp species that are less consistent pollinators. Research indicates hoverflies contribute significantly to the pollination of fruits, vegetables, and ornamental plants, supporting biodiversity and crop yield.
Wasps’ Contribution to Plant Pollination
Wasps contribute significantly to plant pollination by transferring pollen while foraging for nectar, especially in early spring when bees are less active. Certain wasp species, such as fig wasps and paper wasps, play specialized roles in pollinating specific plants, enhancing biodiversity. Their pollination efficiency supports ecosystem health and agricultural productivity by complementing other pollinators like hoverflies and bees.
Beneficial Behaviors: Pest Control by Hoverflies and Wasps
Hoverflies and wasps both contribute significantly to natural pest control by preying on harmful insects like aphids, caterpillars, and other crop-damaging pests. Hoverfly larvae are especially effective in agricultural settings, consuming large quantities of aphids during their development, while adult hoverflies pollinate flowers. Wasps, particularly parasitic and predatory species, help regulate pest populations by targeting various insect larvae and eggs, reducing the need for chemical pesticides.
Attracting Hoverflies and Wasps to Your Garden
Planting a diverse mix of nectar-rich flowers such as umbellifers, marigolds, and alyssum effectively attracts hoverflies, which are vital pollinators and natural pest controllers. To draw wasps, incorporate flowering plants like fennel, goldenrod, and ivy, which provide essential nectar sources and support their role in controlling garden pests. Creating habitats with varied plant heights and shelter options enhances both hoverfly and wasp populations, promoting a balanced and healthy garden ecosystem.
Safety Concerns: Are Hoverflies or Wasps Dangerous?
Hoverflies are generally harmless to humans, lacking stingers and posing minimal safety concerns, whereas wasps can sting repeatedly and may cause allergic reactions in sensitive individuals. Although wasps can be aggressive in defending their nests, hoverflies mimic wasps' appearance as a natural defense mechanism without the associated threat. Prioritizing identification of these insects helps reduce unnecessary fear and promotes safe coexistence in pollination environments.
Supporting Native Pollinators: Habitat Needs for Hoverflies and Wasps
Hoverflies require diverse flowering plants and sheltered areas with decaying organic matter for larval development, supporting pollination and natural pest control. Wasps thrive in habitats with abundant nectar sources, prey availability, and nesting sites such as underground burrows or tree cavities. Providing a variety of native plants and undisturbed habitats fosters the coexistence and effectiveness of both native pollinators in ecosystems.
Choosing Between Hoverflies and Wasps for Pollination Success
Hoverflies are highly effective pollinators, known for their ability to visit a wide variety of flowers and their larval stages that control aphid populations, improving overall plant health. Wasps also contribute to pollination but are less efficient due to their more carnivorous diet and less frequent flower visits. Choosing hoverflies over wasps for pollination ensures better crop yields and balanced ecosystem benefits by enhancing pollination while controlling pests naturally.
Hoverflies vs Wasps Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com