
hoverfly vs butterfly Illustration
Hoverflies and butterflies both play crucial roles as pollinators, but hoverflies are often more efficient in cooler or shaded environments due to their ability to fly in lower temperatures. While butterflies rely on nectar from a variety of flowers, hoverflies contribute by feeding on pollen and pollen-rich flowers, enhancing cross-pollination. Hoverflies' rapid, agile flight allows them to visit multiple flowers quickly, making them valuable pollinators alongside butterflies in diverse ecosystems.
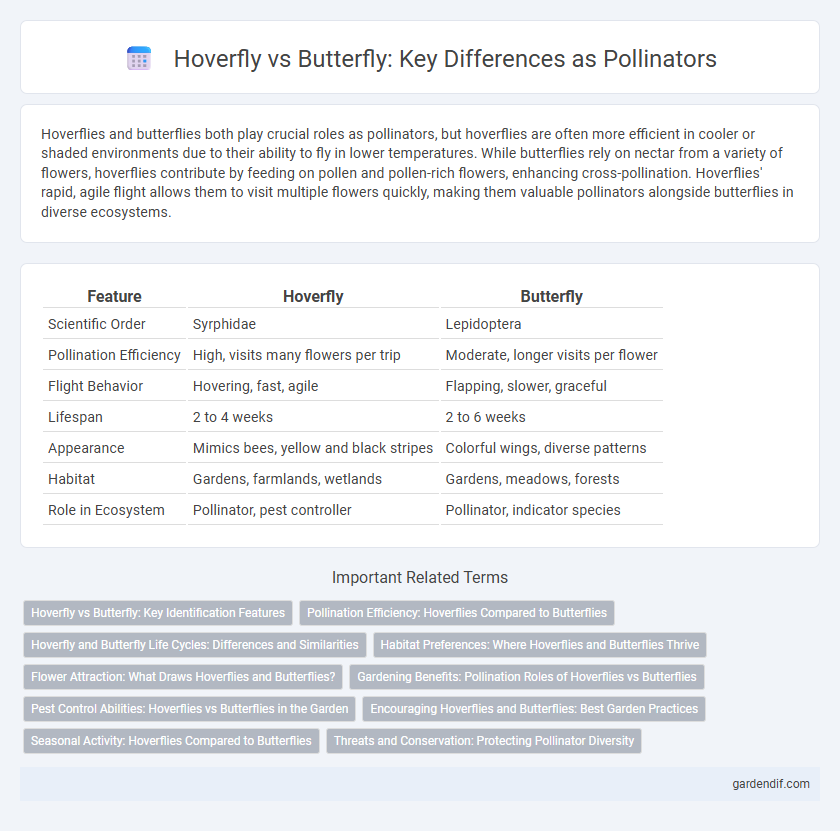
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Hoverfly | Butterfly |
|---|---|---|
| Scientific Order | Syrphidae | Lepidoptera |
| Pollination Efficiency | High, visits many flowers per trip | Moderate, longer visits per flower |
| Flight Behavior | Hovering, fast, agile | Flapping, slower, graceful |
| Lifespan | 2 to 4 weeks | 2 to 6 weeks |
| Appearance | Mimics bees, yellow and black stripes | Colorful wings, diverse patterns |
| Habitat | Gardens, farmlands, wetlands | Gardens, meadows, forests |
| Role in Ecosystem | Pollinator, pest controller | Pollinator, indicator species |
Hoverfly vs Butterfly: Key Identification Features
Hoverflies can be identified by their characteristic hovering flight, shorter antennae, and large, compound eyes with a distinct separation, unlike butterflies that have long, slender antennae with clubbed tips and more colorful, scale-covered wings. Hoverflies often mimic bees or wasps with yellow and black banding patterns but lack stingers, while butterflies exhibit diverse wing shapes and patterns with smoother flight. Recognizing these key identification features helps distinguish hoverflies from butterflies in pollination studies and ecological surveys.
Pollination Efficiency: Hoverflies Compared to Butterflies
Hoverflies exhibit higher pollination efficiency than butterflies due to their ability to visit a greater diversity of flower species and frequent flowers more rapidly. Hoverflies' body morphology enables effective pollen transfer, especially on open and composite flowers, while butterflies often transfer less pollen because of their long proboscis and selective flower preferences. Studies show hoverflies contribute significantly to the pollination of crops and wild plants, making them essential pollinators alongside butterflies.
Hoverfly and Butterfly Life Cycles: Differences and Similarities
Hoverflies undergo complete metamorphosis with egg, larva, pupa, and adult stages, while butterflies also experience complete metamorphosis but with distinct caterpillar and chrysalis phases. Both insects play crucial roles in pollination during their adult stages, although hoverflies often have shorter lifespans compared to butterflies. Their larvae differ significantly, with hoverfly larvae commonly feeding on aphids and organic matter, whereas butterfly caterpillars primarily consume plant leaves.
Habitat Preferences: Where Hoverflies and Butterflies Thrive
Hoverflies thrive in diverse habitats including gardens, woodlands, and wetlands where abundant flowers and decaying organic matter support their larvae. Butterflies prefer sunny, open areas like meadows, grasslands, and forest edges with host plants for caterpillars and nectar sources. Both pollinators play crucial roles in ecosystems but display distinct habitat preferences linked to their life cycle requirements.
Flower Attraction: What Draws Hoverflies and Butterflies?
Hoverflies are primarily attracted to flowers with open, shallow blossoms that provide easy access to nectar, such as umbels and composites, due to their short mouthparts. Butterflies favor brightly colored flowers, especially red, orange, and purple, with landing platforms that accommodate their long proboscis and allow them to extract nectar efficiently. Both pollinators rely on visual cues and scent, but their preferences in floral shape and color distinctly influence the types of plants they frequent.
Gardening Benefits: Pollination Roles of Hoverflies vs Butterflies
Hoverflies and butterflies both serve as vital pollinators in garden ecosystems, with hoverflies excelling in pollinating a wide range of plants due to their high activity and ability to visit flowers in varied weather conditions. Butterflies contribute by targeting nectar-rich flowers, promoting genetic diversity through their selective feeding patterns and vibrant movement between blossoms. The combined presence of hoverflies and butterflies enhances overall pollination efficiency, supporting healthier plant growth and increased garden biodiversity.
Pest Control Abilities: Hoverflies vs Butterflies in the Garden
Hoverflies exhibit superior pest control abilities compared to butterflies due to their larvae's voracious appetite for aphids, thrips, and other harmful garden pests. Butterflies primarily contribute to pollination with minimal direct impact on pest populations. Incorporating hoverflies into garden ecosystems enhances natural pest regulation and reduces reliance on chemical pesticides.
Encouraging Hoverflies and Butterflies: Best Garden Practices
Encouraging hoverflies and butterflies in your garden involves planting a diverse range of nectar-rich flowers such as marigolds, lavender, and dill, which attract these essential pollinators. Providing habitats like shallow water sources and avoiding pesticides supports hoverfly larvae development and butterfly caterpillar growth, enhancing pollination efficiency. Incorporating native plants and maintaining continuous blooms throughout the growing season maximizes habitat suitability for both hoverflies and butterflies, boosting biodiversity and garden health.
Seasonal Activity: Hoverflies Compared to Butterflies
Hoverflies display a broader seasonal activity than butterflies, often emerging earlier in spring and persisting later into autumn due to their ability to exploit a wide range of floral resources and cooler temperatures. Butterflies typically have more restricted flight periods aligned with specific host plant availability, limiting their presence primarily to the warmer mid-summer months. This extended activity window of hoverflies enhances their role as pollinators across multiple growing seasons, supporting ecosystem resilience and crop pollination.
Threats and Conservation: Protecting Pollinator Diversity
Hoverflies face habitat loss and pesticide exposure, mirroring the threats butterflies encounter, which critically endanger their pollination roles. Conservation efforts targeting floral diversity, reduced pesticide use, and habitat restoration bolster both hoverfly and butterfly populations. Protecting these pollinators enhances ecosystem resilience and agricultural productivity through sustained pollination services.
hoverfly vs butterfly Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com