
Hoverfly visitation vs Bee visitation Illustration
Hoverflies play a crucial role in pollination, often visiting flowers more frequently than bees in certain ecosystems, especially in cooler or shaded environments where bees are less active. Their ability to hover and forage efficiently complements bee visitation, contributing significantly to the pollination of various crops and wild plants. While bees are renowned for their pollen-carrying capacity, hoverflies enhance biodiversity by pollinating a broader range of plant species with their diverse feeding habits.
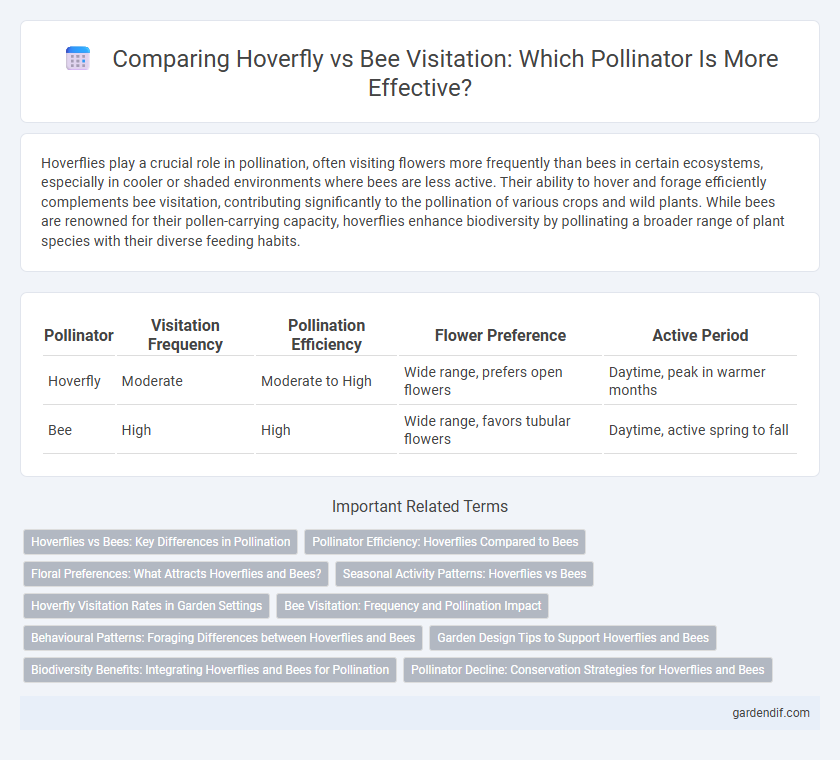
Table of Comparison
| Pollinator | Visitation Frequency | Pollination Efficiency | Flower Preference | Active Period |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hoverfly | Moderate | Moderate to High | Wide range, prefers open flowers | Daytime, peak in warmer months |
| Bee | High | High | Wide range, favors tubular flowers | Daytime, active spring to fall |
Hoverflies vs Bees: Key Differences in Pollination
Hoverflies and bees differ significantly in pollination efficiency and behavior, with bees generally exhibiting higher pollen transport due to their hairy bodies adapted for collecting pollen. Hoverflies contribute to pollination primarily through nectar feeding and exhibit less flower fidelity, which can reduce their effectiveness compared to bees. Research shows that while bees often dominate in crop pollination, hoverflies play a crucial complementary role, especially in ecosystems where bee populations are declining.
Pollinator Efficiency: Hoverflies Compared to Bees
Hoverflies exhibit notable pollinator efficiency, often matching or surpassing bees in certain crop pollination scenarios due to their rapid visitation rates and ability to pollinate under cooler, low-light conditions. Bees, particularly honeybees and bumblebees, generally demonstrate higher pollen transfer efficiency per visit, but hoverflies compensate with greater abundance and broader floral visitation. Studies indicate that integrating hoverfly populations into pollination management strategies enhances overall pollination success and crop yield resilience.
Floral Preferences: What Attracts Hoverflies and Bees?
Hoverflies are primarily attracted to flowers with open, flat structures such as umbellifers and composite flowers, which provide easy access to nectar and pollen, unlike many bees that prefer tubular or bell-shaped flowers. Bees, particularly bumblebees and honeybees, exhibit a strong preference for brightly colored flowers, especially blue and violet hues, and those with higher nectar rewards. Floral scent composition also plays a crucial role, as hoverflies are drawn to sweet, subtle fragrances, while bees respond to more complex scent profiles associated with their preferred flower species.
Seasonal Activity Patterns: Hoverflies vs Bees
Hoverflies exhibit peak visitation during early spring and late autumn, periods when bee activity significantly declines, highlighting their crucial role in pollination outside the prime bee foraging season. Bees typically dominate pollination from late spring through summer, driven by floral abundance and optimal temperature conditions. This complementary seasonal activity enhances year-round pollination stability across diverse ecosystems.
Hoverfly Visitation Rates in Garden Settings
Hoverfly visitation rates in garden settings often rival or exceed those of bees, particularly in urban and suburban environments where floral diversity supports their populations. Studies reveal that hoverflies contribute significantly to pollination, especially during cooler or overcast conditions when bee activity declines. Their ability to visit a wide range of flower species enhances pollination efficiency and biodiversity in garden ecosystems.
Bee Visitation: Frequency and Pollination Impact
Bee visitation frequency significantly surpasses that of hoverflies, with honeybees and bumblebees accounting for the majority of pollination events in various ecosystems. The efficiency of bee pollination is attributed to their specialized body structures adapted for pollen collection, resulting in enhanced fertilization rates and higher crop yields. Research indicates that increased bee activity directly correlates with improved floral reproductive success, emphasizing their critical role in sustaining biodiversity and agricultural productivity.
Behavioural Patterns: Foraging Differences between Hoverflies and Bees
Hoverflies exhibit distinct foraging behaviors compared to bees, often visiting a wider variety of flowers due to their ability to hover and access nectar from open and shallow blossoms. Unlike bees, which show flower constancy by repeatedly visiting the same species during foraging trips, hoverflies display more opportunistic and generalized visitation patterns. These behavioral differences impact pollination efficiency and floral resource competition within ecosystems.
Garden Design Tips to Support Hoverflies and Bees
Incorporate a variety of native flowering plants with staggered bloom times to sustain both hoverflies and bees throughout the growing season. Design garden beds with flat-topped flowers such as umbels to attract hoverflies while including tubular and composite flowers favored by bees. Provide undisturbed ground patches and shallow water sources to support nesting and hydration for both pollinator groups, enhancing garden biodiversity and pollination efficiency.
Biodiversity Benefits: Integrating Hoverflies and Bees for Pollination
Hoverflies and bees provide complementary pollination services, enhancing biodiversity by supporting a wider range of plant species across different habitats. Hoverflies contribute to pollination in shaded or cooler environments where bees are less active, increasing ecosystem resilience and plant reproductive success. Combining hoverfly and bee visitation promotes genetic diversity and stabilizes pollination networks crucial for agricultural productivity and natural ecosystems.
Pollinator Decline: Conservation Strategies for Hoverflies and Bees
Hoverfly visitation plays a crucial role in pollination alongside bees, often compensating for declines in bee populations. Effective conservation strategies must prioritize habitat diversity, floral resource availability, and reduced pesticide use to support both hoverflies and bees. Monitoring visitation patterns reveals that enhancing hoverfly habitats can bolster pollination services, contributing significantly to ecosystem resilience amid ongoing pollinator decline.
Hoverfly visitation vs Bee visitation Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com